WHAT IS NEUROENDOSCOPY?
Neuroendoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure allowing the neurosurgeon to remove the brain tumors. This could be removed by making a small hole in the skull or through the nose or mouth. This advancement unlike the traditional surgery allows doctors to reach deep parts of the brain with minimum to no damage to other parts of the brain.
Ever since the beginning of modern medicine, neurosurgeons are trying to devise a more efficacious and efficient way to surgically remove intracranial tumors, hydrocephalus, seizures, and various neurological disorders. Neuroendoscopy is useful as neurosurgeons are able to access critical areas of the brain and remove tumors without damaging other parts of the skull.
The most important role for neuroendoscopy is for management of intraventricular tumors and colloid cysts. This shows significant results in biopsy tumors, treating hydrocephalus, and absolutely removing tumors.
HOW DOES IT WORK?
The neuroendoscopy is carried out using an endoscope that is a small telescope-like device. This contains a high-resolution video camera and eye piece attached on the end, which allow the neurosurgeon to locate and access the tumor.
Neurosurgeons take a sample or biopsy of a tumor before removing it by attaching a special instrument to the endoscope such as forceps and scissors on the end. Once the sample collected is confirmed to be a tumor, the procedure is carried out for removal of the tumor completely. Tumor is also tested further to find out if it is cancerous in nature.
Equipment used for neuroendoscopy is continuously evolving. Mainly, there are two types of endoscopes.
The rigid endoscope – This is a fixed-length and fixed-geometry instrument which has several viewing angles available (0, 30, and 70 degrees to the long axis of the endoscope). The source of the light, camera, as well as shaft are all in-line allowing for easier positioning while working in the ventricular system.
The flexible fiberscope – This is maneuverable in three directions with simple controls. Its geometry is not fixed and it might be moved and positioned as per requirement.
The neurologists, oncologists or other relevant specialist asses the case and confirm the diagnosis of the ailment is confirmed on basis of various tests such as:
Imaging tests – MRI, CT, PET and PET-CT scans
- A cerebral angiogram or arteriogram
- Tissue sampling (biopsy) and/or molecular testing of the tumour
- Lumbar puncture or spinal tap
- Myelogram or myelography
- Tests to assess vision, hearing and other senses
- Neuro-cognitive assessment for brain function
- Electroencephalography (EEG)
Before the neuroendoscopy, the neurosurgeon would prepare the patient about the risks involved in the surgery and also get a signature on the consent form.
Various medications and therapies are involved prior to the surgery as well as post-surgery care for speedy recovery.
Medicines – Doctor would check for your regular medicines to know if they would interfere with the procedure. It is important to take the medicines on time unless the doctor advises otherwise. Doctor might advise to stop the medicines which might interfere with the procedure.
Tests – Before proceeding for the procedure the doctor would run various tests to know the condition. These involve blood tests and a heart trace test (ECG) apart from above mentioned tests.
Preventing Blood Clots – You would be advised to wear stockings as you would not be allowed to move around as usual after the procedure. These stockings are tight thereby squeezing your feet and legs, helping the blood circulation better. Doctors would also stop any blood thinning medicines prior to the procedure.
Eating and drinking – General anesthesia is given prior to the procedure, so you are not allowed to eat and drink for a few hours before the procedure to avoid any complications.
Washing – To avoid any chance of infection it is important to take a shower or a bath the night before your operation with a special antiseptic cleaning soap.
Recovery from Neuroendoscopy is relatively quick in comparison to traditional surgeries. Before being discharged from the hospital the neurosurgeon would provide detailed discharge instructions such as:
- Pain relief medications and therapy options
- Taking care for your wound site
- Gradual return to activity level
- Follow-up appointment schedule
WHAT IS TREATED WITH NEUROENDOSCOPY?
Neuroendoscopy is useful in treatment for tumors and cancers, cysts, neurological disorders, neurovascular conditions and damage caused by trauma. These would include conditions such as:
- Pineal region tumors
- Pituitary tumors
- Skull base tumors
- Ventricular tumors
- Acoustic neuromas
- Ventricular tumors
- Benign brain tumors
- Meningiomas
- Malignant brain tumors or brain cancer
- Glomus tumors
- Sinus cancer
- Pseudo tumors or false tumors
- Hydrocephalus
- Bell’s palsy
- Spasmodic torticollis
- Trigeminal neuralgia
- Cushing’s disease
- Hemifacial Spasm
- Optic nerve compression
- Glossopharyngeal neuralgia
- Facial bone and skull fractures
- Osteosarcoma of the skull base
- Rathke’s cleft cysts
- Brain aneurysms
- Arteriovenous malformations
- Hemorrhagic stroke
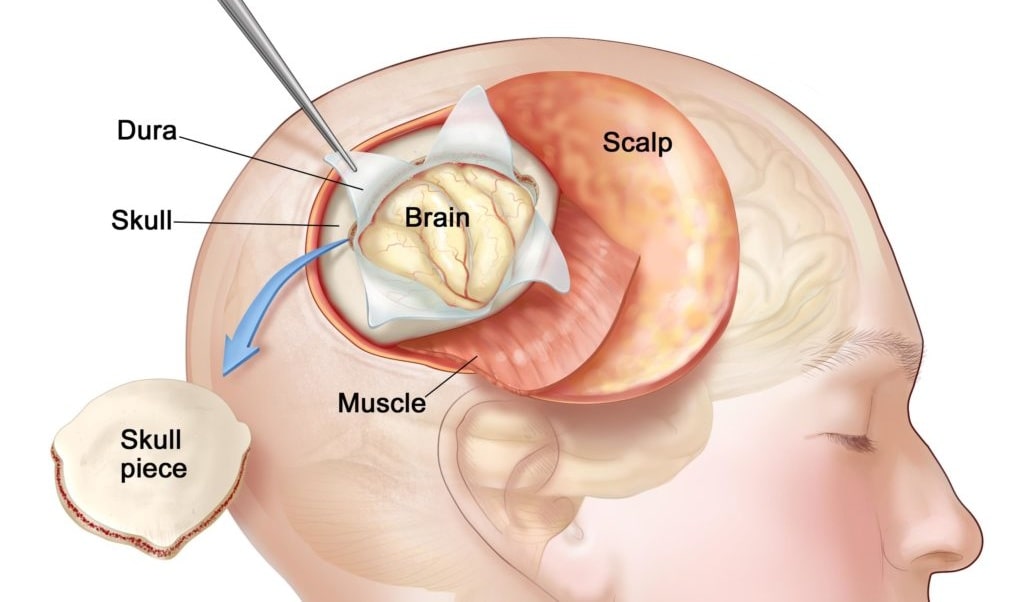
WHAT ARE THE RISKS INVOLVED?
Neuroendoscopy is a safe procedure. The doctor would always provide detail about the potential risks, however these risks outweigh the benefits to the patient. Some risks involved are:
- Brain hemorrhage or bleeding in brain tissue
- Increased intracranial pressure due to the procedure or due to hemorrhage caused by the procedure
- Infection at the site of the cut or incision
- Temporary and/or permanent impairment of functions including memory, speech, vision, coordination or balance
- Blood clot, swelling or nerve damage
- Seizure, stroke or coma
- Complications from anesthesia
OUTLOOK
Neuroendoscopy is a relatively safe procedure helpful in treating various tumors and neurological disorders. Unlike the traditional surgery it involves small incision to remove the tumor leading to less damage to the surrounding tissues and nerves in the brain.
Call us at (469) 545-9983 to book an appointment with our expert brain surgeon Dr. David Masel.
