The urinary tract is the body’s drainage system for the removal of urine, which contains waste products and excess water. For normal urination to take place, all parts of the urinary tract must work together in the correct order. The urinary tract has two kidneys, two ureters, a bladder, and a urethra.
Kidney: Your kidneys filter about 150 quarts of blood each day. Most of the water and other substances filtered by the glomeruli are returned to the blood through the renal tubules. Only 1 to 2 quarts are turned into urine.
Ureters: A thin muscular tube that connects the kidneys to the bladder and carries urine to the bladder.
Bladder: The hollow, muscular, balloon-shaped organ that enlarges when urine is filled. The bladder is located in the pelvis between the hip bones. A normal bladder works like a reservoir. It can hold 1.5-2 cups of urine. You can’t control how your kidneys work, but you can control when your bladder empties. Emptying the bladder is called urination.
Urethra: A tube at the bottom of the bladder that allows urine to drain out of the body when you urinate.
WHAT IS URINARY TRACT INFECTION?
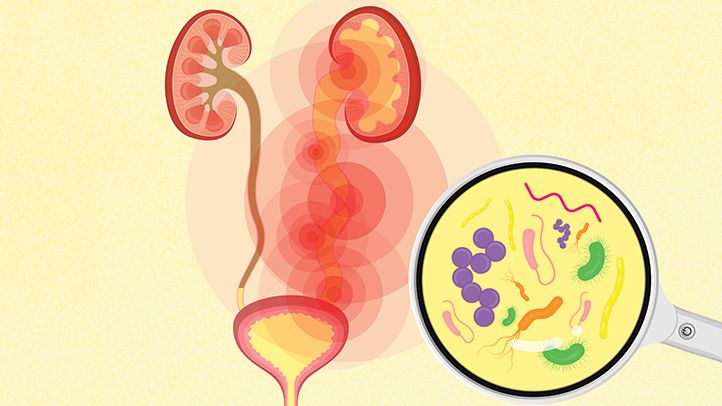
Any infection in the urinary system is called a urinary tract infection (UTI). Kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra are organs of the urinary tract. Most infections affect the bladder and urethra. This sort of infection can affect the urethra, causing urethritis, the kidneys (causing pyelonephritis), or the bladder (a condition called cystitis).
Urine does not normally contain bacteria (germs). Urine is filtered by our kidneys. Urine is produced when waste and excess water are removed from the blood by the kidneys. Urine normally passes through the urinary system uncontaminated. However, bacteria enter the urinary tract from the outside and cause problems such as infection and inflammation.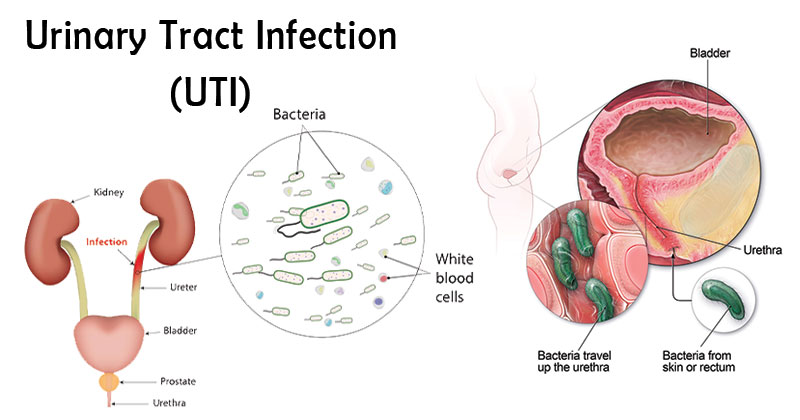
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF URINARY TRACT INFECTION?
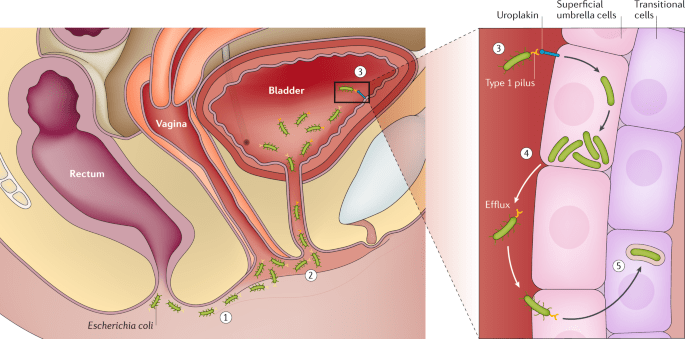
Bacteria enter the urinary tract via the urethra and start spreading in the bladder. The urinary system is developed to keep the bacteria away, but it sometimes fails. When this happens the growing bacteria results in a full-grown infection.
WOMEN COMMONLY SUFFER FROM THE FOLLOWING URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS:
Bladder Infection: Bladder infection is UTI that is usually caused by Escherichia coli (E. coli). E. coli is a bacteria often found in the gastrointestinal tract. But sometimes other bacteria cause the infection.
Urethra Infection: Anus to urethra transmission of GI bacteria can result in this kind of UTI. Sexually transmitted infections can also result in an infection of the urethra. They include mycoplasma, chlamydia, gonorrhoea, and herpes. Women’s urethras are located close to the vagina, which makes this possible.
WHAT SYMPTOMS DOES URINARY TRACT INFECTION SHOW?
- Urge to urinate that does not go away.
- Burning sensation when urinating.
- Frequently urinating small amount of urine.
- Cloudy urine.
- Red, pale pink, or cola-like urine.
- A strong smell of urine.
- Pelvic pain in the case of women – in the middle of the pelvis and around the pubic bone.
UTI TREATMENT AT SPECIALTY CARE CLINIC:
- Specialists in urology, renal disease, obstetrics and gynaecology, and infectious diseases are present at Specialty Care Clinic and may collaborate closely to diagnose and treat your condition.
- Having all of these experts in one location allows the team to discuss your care. Additionally, test results are readily available, appointments are coordinated, and the world’s most highly qualified professionals are all collaborating for your health.
- If you come across any symptoms of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) visit Specialty Care Clinics, our team of professionals will diagnose and treat the infections by taking urgent care.
HOW IS URINARY TRACT INFECTION DIAGNOSED?
- Analysis of urine samples.
- Culture of urinary tract bacteria in the laboratory.
- Create an image of the urinary tract.
- Use the scope to see inside the bladder.
HOW TO TREAT URINARY TRACT INFECTION?
There are two types of UTIs
Simple UTI: Simple urinary tract infections are treated by antibiotics and it happens to people with a normal urinary tract.
Complicated UTI: Complicated urinary tract infections are not cured even after taking many antibiotics. Broad-spectrum antibiotics may be necessary to treat complicated UTIs in order to more effectively eradicate germs within the urinary tract. To assist the healing process go faster, you’ll also need to consume a lot of water.
WHAT ARE THE COMPLICATIONS CAUSED BY URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS?
- Repeated infections are experienced when two or more UTIs occur in a period of six months or three or more in a 12-month period. Repeated infections are more common in women.
- Damage to the kidneys that cannot be repaired because of an untreated UTI.
- Delivering a child that is underweight or early when UTI happens during pregnancy.
- Males have a narrower urethra as a result recurrent urethral infections may occur.
- Sepsis is a hazardous complication of an infection. Particularly if the infection progresses up the urinary tract to the kidneys, this is a concern.
WHAT CAN PREVENT URINARY TRACT INFECTION?
The following is a list of preventive measures which should be performed:
- Drink a lot of liquids, mainly water.
- Drink Cranberry Juice.
- Urinate after having sex.
- Avoid feminine products that may irritate you.
- Change to safe methods of birth control.
- Wipe organs after urination.
- Do not wear tight synthetic underwear like nylon.
- Do not drink a lot of alcoholic beverages as they can irritate the bladder.
- Avoid sugary foods and drinks as they can encourage bacterial growth.
If you are seeking urgent care for Urinary Tract Infection(UTI) visit Specialty Care Clinics, dial 469-545-9983 to book a telehealth appointment for an at-home check-up.