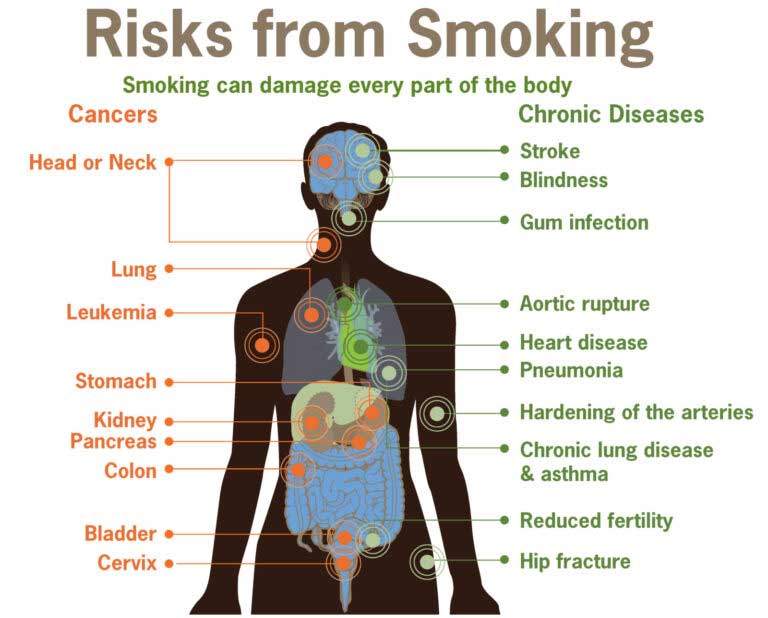
You might be aware of the relationship between smoking and lung cancer. But did you know smoking is also linked to heart disease, stroke, and other chronic diseases?
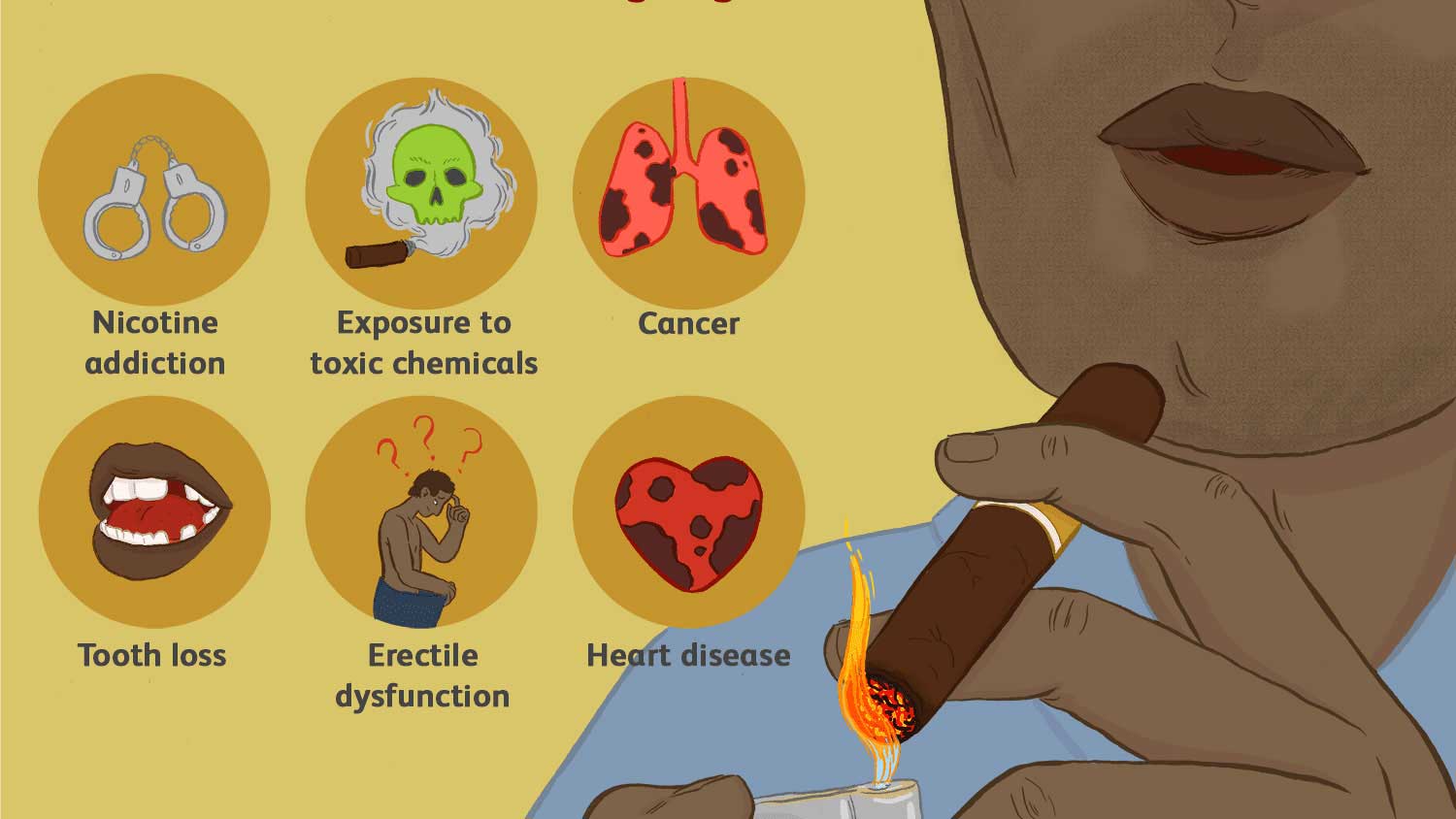
If you are at risk of heart disease, stroke, and even diabetes you should stop smoking as soon as possible. Nicotine is a highly addictive chemical found in cigarettes and other tobacco products. Effects of nicotine on your heart and vascular system. Smoking has been reported as one of the most preventable causes of death in the United States.
This might be because of the chemicals found in cigarettes. The average cigarette contains over 5,000 chemicals, including arsenic, formaldehyde, and tar. Your lungs take in oxygen and deliver it to your heart as you breathe. The heart will pump this oxygen-rich blood to the rest of your body through the blood vessels.
When you breathe the cigarette smoke also gets mixed with the oxygen. The blood that is distributed to the rest of the body becomes contaminated with the smoke’s chemicals that can damage your heart and blood vessels. This can lead to cardiovascular disease (CVD), which is the leading cause of all deaths in the United States.
WHAT CARDIOVASCULAR CONDITIONS CAN BE CAUSED BY SMOKING?
Cigarettes contain a high amount of nicotine. Smoking cigarettes causes permanent damage to your heart and blood vessels. This can result in serious cardiovascular disease.
Cardiovascular disease is an umbrella term for conditions affecting the heart and/or blood vessels, which include:
- Coronary heart disease.
- The narrowing of blood vessels carrying blood to the heart.
- Hypertension or high blood pressure.
- Heart attack.
- Stroke.
- Aneurysms or a bulge as well as weakness in an artery.
- Peripheral artery disease.
Smoking cigarettes can also cause cardiovascular disease by changing your blood chemistry leading to the formation of plaque. The plaque is a waxy substance comprised of cholesterol, scar tissue, calcium, fat, and other material. The plaque gets built up in your arteries, the major blood vessels that carry blood from your heart to your body, resulting in atherosclerosis.
The chemicals in cigarette smoke also cause atherosclerosis along with thickened blood in the arteries. This makes it more difficult for blood cells to move through arteries and other blood vessels to get to vital organs like the heart and brain. This can create blood clots and ultimately lead to a heart attack or stroke and even death.
Other cardiovascular effects that might not be seriously caused by smoking include aggravation of stable angina pectoris, intermittent claudication, vasospastic angina, and restenosis after thrombolysis or angioplasty of coronary or peripheral arteries. Nicotine consumption also promotes progression or aggravation of heart failure, chronic kidney disease, and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in people with chronic kidney disease. This may also increase the risk of developing atrial fibrillation.
Apart from a heart attack or stroke, smoking can cause rare but serious cardiovascular conditions, which include:
- Peripheral artery disease (and peripheral vascular disease): This is caused by the narrowing of blood vessels, thereby resulting in insufficient blood flow to arms, legs, hands, and feet. Smoking is the leading preventable cause of this condition, which can result in amputation.
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm: A bulge that is formed in an area of the aorta—the main artery that distributes blood through the body—that sits in the abdomen. When an abdominal aortic aneurysm bursts, it can result in sudden death. More women than men die from aortic aneurysms, and nearly all deaths from this condition are caused by smoking.
HOW NICOTINE AFFECTS THE HEART?
The main source of nicotine entering your body is tobacco, and mostly it is through smoking. As per the study, tobacco is one of the most addictive substances responsible for taking the life of every 1 out of 5 people in the United States.
There are various ways in which nicotine affects your body. The side effect of nicotine is on the cardiovascular system. Smoking causes your heart rate to increase, major arteries have faster cholesterol deposition, and also cause an irregular heart rhythm, making your heart work harder than usual. Smoking also increases blood pressure and thus, increases the risk of stroke.
The nicotine in cigarettes is highly addictive and can have withdrawal symptoms when you try quitting. Nicotine also contributes to the hardening and thickening of your artery walls, leading to atherosclerosis. This restricts the flow of oxygen-rich blood to different parts and organs of your body.
Also, Ischemic heart disease is caused when plaques build up in the arteries which supply blood to the heart, known as coronary arteries. This would lead to many heart diseases causing chest pain, heart failure, heart attack, arrhythmia, or worse, even death.
Peripheral artery disease (P.A.D) is another condition in which plaque builds up in the arteries that carry blood to the major organs of the body such as the head and limbs. Smoking is a major cause of P.A.D.
Nicotine directly and adversely impacts your cardiovascular system and may eventually become the cause of a heart attack. Quitting nicotine will save you from various health problems. But, there are some withdrawal symptoms you might experience, such as –
- Initially, you may have trouble thinking.
- You might start getting hungrier than normal.
- You will feel irritated, anxious, or angry.
- Certainly, your body will crave tobacco.
WHAT ARE THE NEGATIVE EFFECTS OF QUITTING NICOTINE?
The effects of nicotine on the heart and blood vessels can be reduced by quitting smoking. Some of the effects begin soon after you stop smoking.

The nicotine health effects include:
- Reduced Heart Rate
- Improved blood flow to your heart
- Lower risk of heart attack
- Lower risk of coronary heart disease
- Lower risk of stroke
HOW TO QUIT NICOTINE?
Quitting smoking can be challenging and may have long-term effects on nicotine. It requires hard work and effort.
You may find it difficult to start, but your doctor can help create a plan that works for you.
Common strategies include:
-
- Nicotine Replacement Therapy: This is used to reduce cravings and manage withdrawal symptoms. It involves a product that provides nicotine in specific amounts.
NRT is available as a:- Patch
- Gum
- Lozenges
- Inhaler
- Nasal spray
- Nicotine Replacement Therapy: This is used to reduce cravings and manage withdrawal symptoms. It involves a product that provides nicotine in specific amounts.
- Smoking cessation medications: Certain medications such as varenicline or bupropion help control cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
- Counseling: The counselor can help you:
- Create a smoking cessation plan.
- Cope with cravings.
- Manage stress caused by withdrawal.
- Stay motivated.
- How to Quit Nicotine
OUTLOOK
The effects of nicotine on the body lead to various heart-related health risks such as hypertension, arrhythmia, and atherosclerosis. Over time, these conditions can lead to more serious diseases like coronary artery disease, heart attack, stroke, heart failure, peripheral artery disease, and abdominal aortic aneurysm.
The best way to prevent these conditions is to avoid nicotine or quit smoking. If you need help quitting smoking, speak with a doctor. They can help you create a nicotine cessation and improve your heart health.
People also read:
If you or anyone you know is suffering from heart-related issues, our expert providers at Specialty Care Clinics will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call 469-545-9983 to book a telehealth appointment for an at-home check-up.
