FOOT AND LEG ULCERS
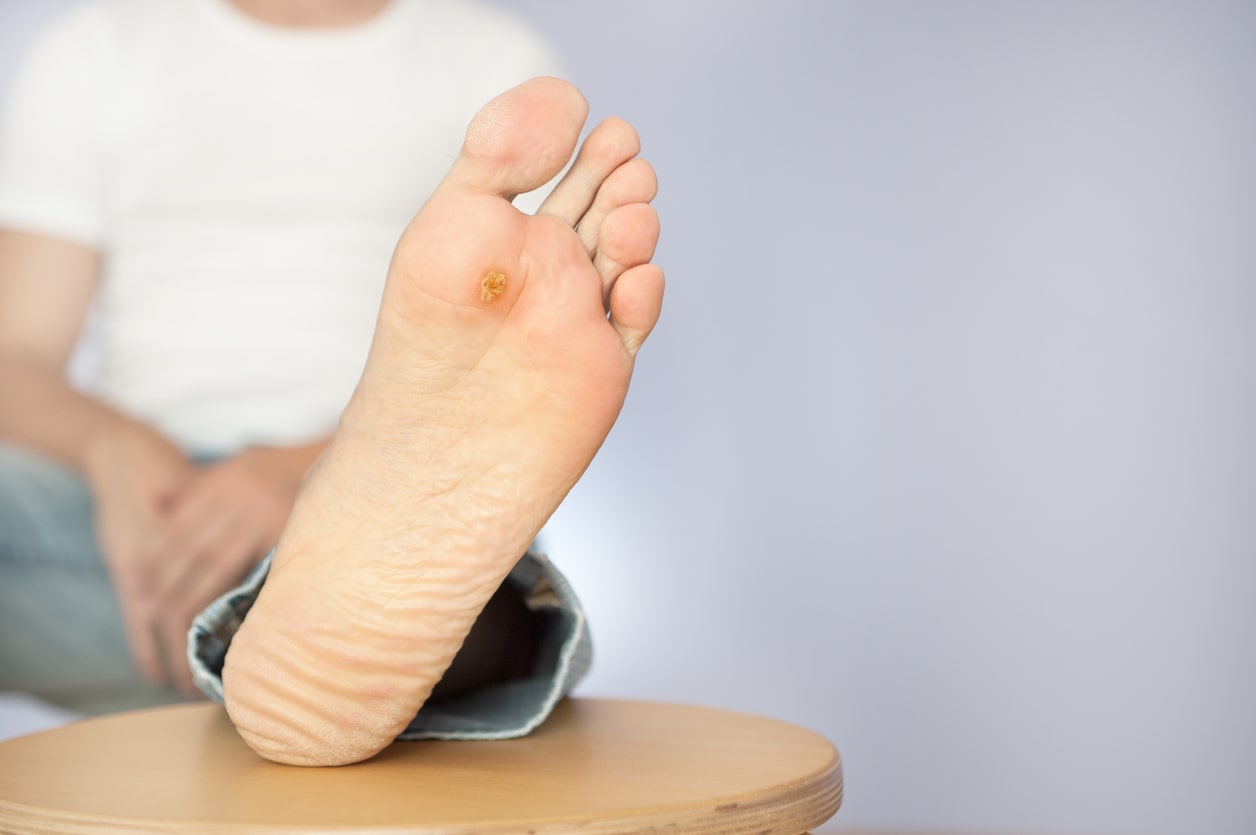
A foot ulcer is a damaged area on the foot. Ulcers of the foot do not heal and keep returning. The open sores due to the breakdown of the skin or tissues become infected. This would lead to pain, swelling, and a burning sensation.
Foot and Leg ulcers mostly cause pain. Foot and leg ulcers due to nerve problems such as diabetes, you may not feel any pain. This might lead to leg infection as you tend to ignore the ulcer.
There may be other symptoms in your legs and feet including:
- Heaviness
- Large varicose veins
- Pus, bleeding, and discharge
- Swelling
- Change of color
Foot ulcers typically appear due to suffering poor blood flow in the legs. People with diabetes are at high risk of developing foot ulcers, due to poor blood flow or less sensation in the feet.
RISK FACTORS
Other causes of foot ulcers such as:
- Traumatic injury
- Tumors
- Infections
- Vascular disease including stroke, heart attack, angina
The types of leg and foot ulcers are:
- Arterial ulcers
- Neurotrophic ulcers (diabetic ulcers)
- Venous stasis ulcers
- Arterial Ulcers: It is also known as ischemic ulcers. Arteries carry pure blood from the heart to all organs of the body. The arteries may become narrowed by plaque called peripheral arterial disease (PAD). In severe cases, the skin and tissues do not heal completely due to a lack of blood supply. Arterial ulcers appear mainly on the heels, tips of the toes, between the toes, or protruding bones. It might also occur when the socks rub against skin, shoes, or bed sheets. The ulcers appear yellow, brown, black, or gray, and surrounding skin look punched out. Arterial ulcers normally do not weep or bleed. Minor skin damage such as accidental cuts or callus can also result in an arterial ulcer.
- Neurotrophic Ulcers: Also known as diabetic ulcers. These are common among people suffering from diabetes. These can also occur in anyone who has lost sensation in the feet. These ulcers are caused by either trauma or increased pressure points at the bottom of the feet. The ulcers can appear pinkish-red or brownish-black depending on the blood circulation. The surrounding skin is usually calloused and the borders of the ulcer are punched out. Nerve damage in the feet is the main cause of loss of foot sensation. The changes in the sweat-producing glands increase the risk of foot calluses or cracks, injury, or infection. Symptoms of neuropathy are tingling, numbness, burning, or pain.
- Venous stasis ulcers: These are common if you are suffering from varicose veins, leg swelling, or blood clots in the superficial or deep veins of the legs. Unlike arteries, veins return blood to the heart from the legs and the rest of the body. The blood would flow backward if the veins are damaged or blocked. Insufficiency in blood circulation will cause blood to pool resulting in open sores that are slow to heal. These ulcers occur on the inner part of the leg just above the ankle as red and covered in yellow fibrous tissue. In case of an infection, there will be significant green or yellow discharge with irregularly shaped borders and discolored and swollen surrounding skin.
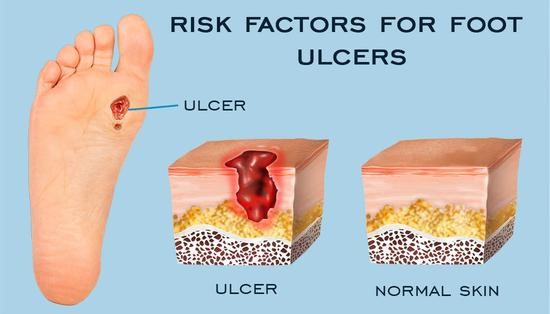
SYMPTOMS OF FOOT AND LEG ULCERS
Foot and leg ulcers sometimes might not be painful. You might have a swollen leg and may feel burning or itching. You might also have a rash, redness, brown discoloration, or dry, scaly skin.
Depending on the type of foot and leg ulcers may have other symptoms such as:
- Appear red, yellow, brown, or gray
- Drain fluid
- Look swollen or bleed when irritated
- Leg swelling or cramping
- Hardened skin that is purple, dark red, or brown
- Itching and tingling
- Dry, scaly skin
- Fluid-filled blisters
- Rash or redness
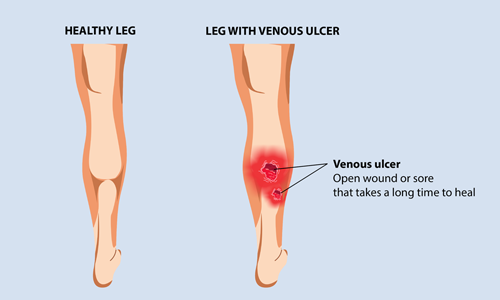
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF FOOT AND LEG ULCERS
Diagnosis is the key to quick treatment. The podiatrist would use various imaging tests to collect information:
Ankle-brachial index test– This test measures blood pressure in the arm and leg using high-frequency sound, and comparing the two together.
Arterial Doppler: This is a type of ultrasound that helps podiatrists check any decrease in blood flow in the arteries and veins.
Venous Doppler: It is also an ultrasound that determines any leakage in your veins or varicose veins.
Computed tomography scans (CT scan): This help podiatrist see the blood vessels in the legs and ulcer. It is determined using detailed cross-sectional images of the vessels.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): This uses radio waves to create a detailed picture of the affected area. It also helps check for infection in the bone and deeper tissue.
Treatment aims to relieve pain, prevent infection and spread of the wound. Few changes to your lifestyle will help foot and leg wounds and ulcers to heal quickly:
- Avoid standing for long periods
- Increase water intake
- Regular feet checks
- Podiatry care especially if you have diabetes or smoke
- Perform the regular or moderate-intensity exercise
- Raise your legs at night
- Wear good walking shoes
The treatment regime would depend on the type of ulcer including:
Venous Ulcer Treatment –Compression of the leg to minimize edema or swelling. Wearing compression stockings, multi-layer compression wraps, wrapping an ACE bandage, dressing from the toes or foot to the area below the knee are compression ways.
The dressing is determined by the type of ulcer and the appearance at the base of the ulcer including:
- Moist to moist dressings
- Hydrogels/hydrocolloids
- Alginate dressings
- Collagen wound dressings
- Debriding agents
- Antimicrobial dressings
- Composite dressings
- Synthetic skin substitutes
Arterial Ulcer Treatment: The treatment would vary, depending on the severity of the arterial disease. Depending on the condition of the ulcer, the podiatrist may recommend invasive testing, endovascular therapy, or bypass surgery to restore circulation to the affected leg.
The aim for arterial ulcer treatment include:
- Providing adequate protection on the skin surface
- Preventing new ulcers
- Removing contact irritation with the existing ulcer
- Monitoring signs and symptoms of infection involving the soft tissues or bone
Neurotrophic ulcers Treatment: This includes avoiding pressure and weight-bearing on the affected leg. The removal of infected tissue is necessary for a neurotrophic ulcer can heal faster. A podiatrist would recommend special shoes or orthotic devices.
PREVENTION OF FOOT AND LEG ULCERS
It is important to prevent ulcers is to manage chronic health conditions, quit smoking, and keep a healthy lifestyle.
Other ways to prevent foot and leg ulcers include:
- Avoid sitting and standing for a long duration
- Regular exercise
- Maintaining healthy weight
- Control blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes.
- Eat healthy diet
- A regular check of leg and foot tissues
- Avoiding trauma to the feet and legs
- Stop Smoking
TAKEAWAY
Diabetic people are prone to leg and foot ulcers with underlying causes such as venous insufficiency, peripheral neuropathy, or peripheral arterial occlusive disease.
The locations of the ulcers and underlying medical conditions like edema, callus, or decreased pulses, help diagnose the cause of an ulcer. Treatment strategies include compression therapy, unloading treatments, and arterial revascularization.
Infection in an ulcer increases the risk for adverse outcomes. It can be managed with local and systemic therapy.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from foot problems, our expert providers at Specialty Care Clinics will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call us on (469) 545-9983 to book an appointment with our specialists.
