Narcolepsy is a sleep disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness. People with narcolepsy are unable to stay awake for long duration which affects their daily social and work life. This disorder is relatively rare because of which it is not diagnosed until initial symptoms appear. Narcolepsy affects both children and adults and can occur at any age.
Normal sleep happens in stages: initial stage, followed by deep sleep and finally the Rapid Eye Movement (REM) stage which occurs after more than an hour. But in narcolepsy REM sleep occurs earlier, within minutes after falling asleep.
TYPES OF NARCOLEPSY
Narcolepsy is of two types:
- Type 1 narcolepsy– It is narcolepsy accompanied with ‘Cataplexy’ which is sudden loss of muscle tone. This causes inability to control one’s muscles and weakness.
- Type 2 narcolepsy – It is narcolepsy without cataplexy.
Narcolepsy Symptoms
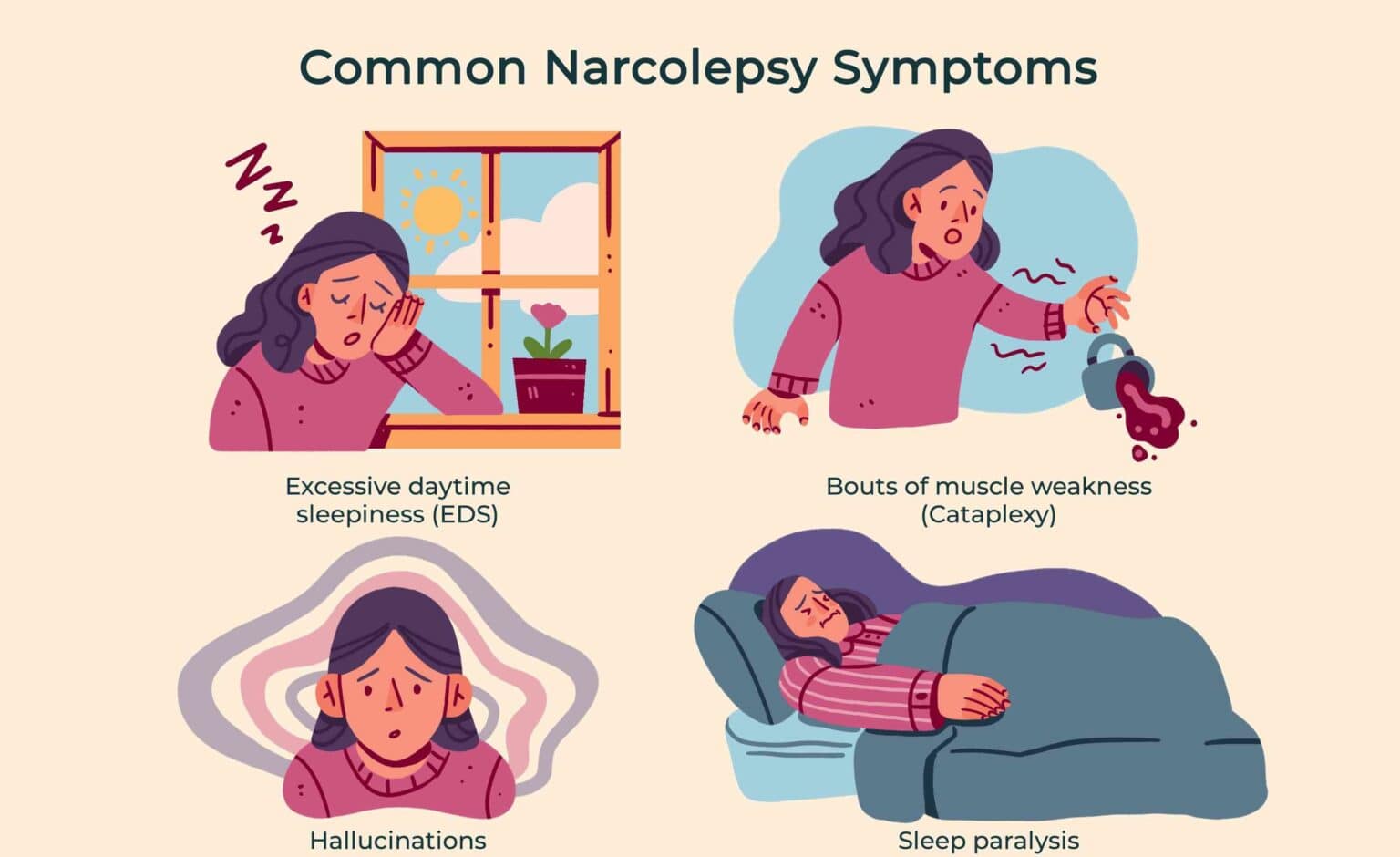
SYMPTOMS OF NARCOLEPSY
Narcolepsy affects a person’s day schedule and even sleep at night. The main symptoms are:
- Excessive daytime sleepiness: Making it difficult for the person to perform day activities. A person can fall asleep without warning and wake up after a short nap feeling temporarily refreshed.
Decreased attention and feeling of exhaustion. - Cataplexy: The sudden loss of muscle tone can cause problem in speech (example slurring) to even full body collapse, depending on the muscles involved. Both sides of the body are generally affected, and it lasts for a few seconds to a few minutes. It can be caused by strong emotions like excessive joy, laughter, or anger.
- Hallucinations: Vivid and scary visions occur in patients suffering from narcolepsy. They can occur while falling asleep or while waking up.
- Sleep paralysis: This scary symptom causes an inability to move or speak while falling asleep or waking up. It usually accompanies hallucinations.
- Disturbed night sleep: Due to vivid dreams and waking up multiple times at night a person has disrupted sleep at night.
EFFECTS OF NARCOLEPSY
The symptoms of narcolepsy majorly affect a patient’s health and social life. There is a greater likelihood of car accidents in such patients due to daytime sleepiness and decreased muscle tone. Children suffering from narcolepsy suffer from restlessness and irritability which can be interpreted as behavioral problems and affect their school performance.

CAUSES OF NARCOLEPSY
The exact cause of narcolepsy is yet to be completely understood. In Narcolepsy type 1, clinicians have reported loss of those brain nerve cells that are responsible for production of a chemical called hypocretin. Hypocretin regulates awake and sleep cycles of a person. Family history and genetic variations can also be responsible for this loss.
Narcolepsy type 2 has a less marked loss of hypocretin-producing nerve cells, and some clinicians consider it to be a precursor to type 1 narcolepsy.
Changes in parts of the brain responsible for REM sleep have also been found in narcoleptic patients.
NARCOLEPSY DIAGNOSIS
As the disorder is rare, symptoms can be associated with other causes and narcolepsy can go undiagnosed for many years. Careful assessment by a doctor familiar with narcolepsy is required. The diagnosis involves:
- Proper Physical examination and medical history
- Evaluation of Sleep records: This involves keeping a record of symptoms while the patient is asleep for a period of few weeks.
- Polysomnogram: This is an overnight sleep test conducted in a specialized clinic to evaluate a patient’s sleep cycle.
- Multiple sleep latency test (MSLT): In this test a patient is directed to try to fall asleep at five different intervals while they are connected to the sensors used in the polysomnography. Narcoleptic patients fall asleep fast and enter REM sleep.
- Assessment of level of hypocretin in cerebrospinal fluid.

TREATMENT OF NARCOLEPSY
There is no cure for narcolepsy. But lifestyle modification and medication can help reduce symptoms, improve quality of life and aid in keeping the disease stable over time.
Lifestyle modification:
- Incorporation of short naps to one’s schedule to reduce excessive daytime sleepiness
- Following a proper sleep schedule at night, in a calm environment and with limited use of electronic devices.
- Avoid alcohol and other sedatives
- Drive with caution and avoid long journeys.
- Balanced diet and exercise help to improve sleep cycle
- Support groups to prevent social withdrawal and chances of depression.
Medications which have proven to be effective are:
- Modafinil, Armodafinil, Solriamfetol- for management of excessive daytime sleepiness
- Stimulants to treat sleepiness. Ex: Methylphenidate
- Sodium oxybate: to reduce cataplexy
- Pitolisant: a wakefulness promoting medication
Treatments for narcolepsy type 1 and 2 are similar except that type 2 doesn’t include medication for cataplexy.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from narcolepsy, consult our specialists. Call us today at (469) 545-9983 to book an appointment.
