WHAT IS JAUNDICE?
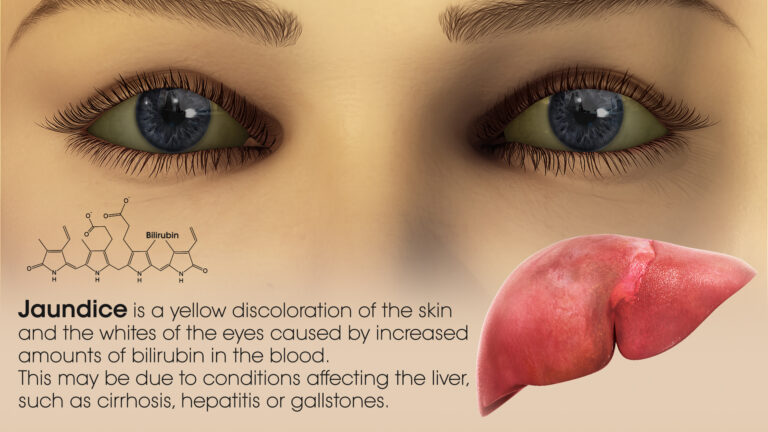
Jaundice is a condition in which a yellowish tinge develops on the skin, mucous membranes, and the whites of the eye. Body fluids might also change color. Jaundice commonly indicates a problem with the liver or bile ducts. When the liver is not working properly, it can cause a waste material known as bilirubin to build up in the blood.
With moderate bilirubin levels, a person’s skin, eyes, and mucous membranes could turn yellow. As it progresses, the color could also change from yellow to green. The green color occurs because of biliverdin, the green pigment present in bile. Jaundice could develop in people of all ages and is normally the result of an underlying condition. Newborns as well as older adults have the highest likelihood of developing jaundice.
This article discusses what causes jaundice, how healthcare professionals diagnose and treat the condition, and how a person could help to prevent it from occurring. It also explores the symptoms a person could expect.
JAUNDICE CAUSES AND JAUNDICE RISK FACTORS
According to the American Family Physician (AAFP), jaundice is the yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes, and the whites of the eyes that happens when the body does not process bilirubin as it should.
Bilirubin levels rise as the red blood cells naturally break down. Typically, the liver filters this waste material out of the bloodstream and turns it into a new form known as conjugated bilirubin. The new form then leaves the body in a person’s stool.
If there is too much bilirubin for the liver to process, it could build up in the body. This is called hyperbilirubinemia, and it causes a yellow color in the skin and eyes. Jaundice typically occurs because of an underlying disorder that either causes the production of too much bilirubin or prevents the liver from eliminating it.
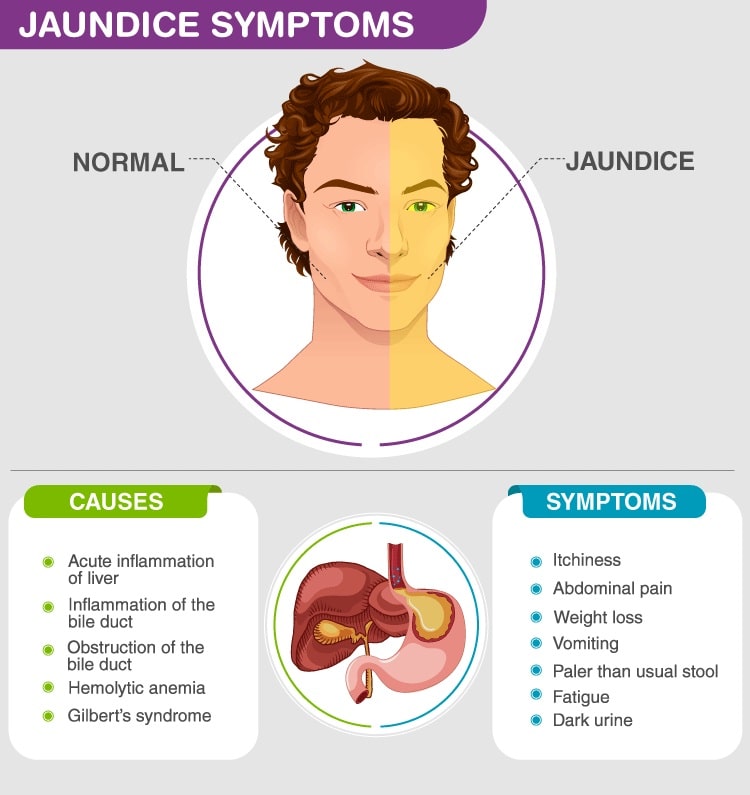
Some possible underlying conditions and causes of jaundice are:
- Side effects of specific medications
- Gallstone disease
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Gallbladder or pancreatic cancer
- Cirrhosis is a condition that causes scar tissue to replace healthy tissue in the liver
- Hepatitis or other liver infections
- Hemolytic anemia
JAUNDICE TREATMENT
Treatment will depend upon the underlying cause of jaundice. Jaundice could lead to itching or pruritis. A 2021 article notes that a person could have warm baths containing oatmeal and take antihistamines for mild pruritis. A healthcare professional might prescribe medications for those experiencing moderate to severe pruritis, such as cholestyramine or colestipol. As jaundice might sometimes indicate damage to the liver, a liver transplant may be necessary in some cases, depending on the severity of the injury.
JAUNDICE PREVENTION
Jaundice is associated with liver function.
People could help take care of their liver with several lifestyle changes, such as:
- Eating a balanced diet
- Exercising regularly
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Avoiding toxins from chemicals and other sources, both inhaled as well as touched
- Managing medications carefully
A 2021 article also suggests:
- Avoiding herbal medications without first consulting a healthcare professional
- Avoiding smoking, alcohol, and intravenous drugs
- Avoiding taking more than the recommended dosage of prescribed medications
- Getting the recommended vaccinations prior to traveling
- Practicing safe sex, like using barrier methods of contraception
JAUNDICE SYMPTOMS
Common symptoms of jaundice include:
- A yellow tinge on the skin, mucous membranes, and the whites of the eyes
- Pale stools
- Dark urine
- Itchiness
In infants, the yellowish tinge could start at the head and spread down the body to the toes.
The United Kingdom’s National Health Service (NHS) notes that jaundice might be less apparent on Black and Brown skin. It is more obvious in the whites of your eyes.
Accompanying symptoms of jaundice might include:
- Fatigue
- Abdominal pain
- Weight loss
- Vomiting
- Fever
JAUNDICE COMPLICATIONS
High levels of bilirubin could be toxic and lead to a rare type of brain damage known as kernicterus in infants. The underlying conditions causing jaundice could also lead to their own complications.
TYPES OF JAUNDICE
Three main types of jaundice are:
- Prehepatic Jaundice – This happens before the liver processes the waste and results in higher unconjugated bilirubin levels.
- Hepatic Jaundice – This happens in the liver and results in both higher conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin levels.
- Posthepatic Jaundice – This happens after the liver has processed the waste and results in higher conjugated bilirubin levels.
JAUNDICE IN NEWBORNS
Jaundice is a common health problem in newborn children. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) note that approximately 60 percent of newborns develop jaundice, and signs appear within 48 hours of birth. A doctor or nurse should examine the baby when they are between 3 to 5 days old. This is because the bilirubin levels are generally at their highest during this time.
Red blood cells in the body of an infant are often broken down and replaced. This result in the production of more bilirubin. In addition to this, the livers of infants are less developed and are therefore less effective at filtering bilirubin from the body.
Symptoms will generally resolve without treatment in mild cases. However, infants with extremely high bilirubin levels will need treatment with either a blood transfusion or phototherapy. In these cases, jaundice treatment in newborns is important to help prevent kernicterus.
Causes of Jaundice in Newborns
Although jaundice in babies is common and often resolves without treatment, some underlying medical conditions could cause jaundice. These include:
- Underactive thyroid gland
- Blood group incompatibility is when the blood of both the pregnant person and infant gets mixed in the womb or during birth
- Rhesus disease is a condition in which the pregnant person’s antibodies destroy the infant’s blood cells
- Urinary tract infection
- A blockage in the bile ducts or gallbladder
- Crigler-Najjar syndrome is a condition that affects the enzymes that process bilirubin
Breastfeeding or chest feeding could also increase the chance of jaundice in newborns. Nevertheless, there is no need for a person to stop feeding the baby this way. In these cases, the symptoms of jaundice resolve within a couple of weeks.
BILIRUBIN LEVELS
According to a 2021 article, normal bilirubin levels are less than one milligram per deciliter (mg/dl). A person has jaundice if these levels reach about 3 mg/dl. A 2021 article notes that doctors might diagnose jaundice in infants if the bilirubin levels increase to 5 mg/dl per day or more than 0.2 mg/dl per hour. These ranges might differ between laboratories. How far above the normal range of a person’s levels will help a doctor determine the best course of treatment.
JAUNDICE DIAGNOSIS
Doctors will most likely start with the person’s history and a physical examination to diagnose jaundice. They may later also order laboratory tests. During an examination, they will pay special attention to the abdomen, liver, and skin.
The doctor may often include laboratory tests to help determine the underlying cause of jaundice. These include:
- Bilirubin tests – A high level of unconjugated bilirubin compared to levels of conjugated bilirubin indicate hemolytic jaundice.
- Full blood count (FBC) and complete blood count (CBC) – This measures levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Hepatitis A, B, and C tests – These tests detect a range of liver infections.
The doctor will also examine the structure of the liver if they suspect a blockage. In these cases, they will use imaging tests, such as MRI, CT, and ultrasound scans. In addition, they might carry out an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). It is a procedure that combines endoscopy with X-ray imaging.
The AAFP states that a healthcare professional might perform a liver biopsy. A liver biopsy could check for inflammation, cirrhosis, cancer, and fatty liver. This test includes inserting a needle into the liver to obtain a tissue sample. The healthcare professional will then examine the sample under a microscope.
SUMMARY
Jaundice refers to the yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes, and whites of the eyes. It is a symptom of an underlying condition or health concern that includes the liver. It happens when the liver cannot keep up with the demand to process waste in the blood or when the liver becomes damaged. Several conditions could cause liver issues and result in jaundice. Treatment for jaundice generally involves treating the underlying condition.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from jaundice, our expert providers at Specialty Care Clinics will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call 469-545-9983 to book a telehealth appointment for an at-home check-up.