WHAT IS MARCH FRACTURE?
March fractures are sub-typed under fatigue or stress fractures. It is caused from repeated trauma to the metatarsal of the foot, mainly second and third. But, it can also occur in other weight-bearing bones of the lower limb and pelvis.
The second metatarsal is the longest and is subjected to the most force. Also, the micro-fractures consolidate together to cause stress fractures. It commonly causes foot pain mainly when you suddenly increase their activities.
Stress could cause a small crack in a bone, or severe bruising within a bone. These could be caused by overuse and repetitive activity. These could be common in runners and athletes or running sports, like soccer and basketball.
It can also occur in people trying a new exercise, suddenly increasing the intensity of their workouts, or changing the workout surface or medical conditions like osteoporosis or other diseases that have weakened the bones.
The bones bearing weight of the foot and lower leg are vulnerable to stress fractures. The bones have to absorb the repetitive forces during activities such as walking, running, and jumping.

WHAT IS THE CAUSE OF MARCH FRACTURE?
Stress fractures are most commonly caused due to a sudden increase in physical activity. This increase might be in the frequency of activity like exercising more days per week, duration or intensity of activity like running longer distances. When the non-athlete experiences a sudden increase in activity it could cause a stress fracture.
Bone adapts to the increased loads through remodeling. This is a normal process which speeds up the process to bear increased load on the bone. During the remodeling process the bone tissue is destroyed (resorption) and then rebuilt.
Bones when subjected to unusual force without enough time for recovery would resorb cells faster than your body could replace them. This would make you more susceptible to stress fractures.
Some of the common causes of stress fracture are:
- Bone Insufficiency: Various medical conditions, like osteoporosis, and some long-term medications decrease bone strength and density. This could lead to stress fracture-even when you are performing normal everyday activities. Stress fracture is common in winters due to lower amounts of vitamin D.
- Poor Conditioning: Doing strenuous activities fast is a common cause of stress fracture. This often affects the individuals beginning an exercise program-but also occurs in experienced athletes. The athletes not only increase their activity levels, but push through any discomfort. Athletes mainly do not give their bodies the opportunity to recover, leading to stress fractures.
- Improper Technique: Using improper technique in sports and daily activities would affect the mechanics of how your foot absorbs impact as it strikes the ground leading to increase your risk for a stress fracture.
- Age: Older people might suffer from underlying bone density issues like osteoporosis. This causes weakened bone and develops a stress reaction causing fracture quicker than healthy bone.
- Weight: Underweight and overweight people are at high risk for stress injuries. People with a low BMI or underweight individual with weakened bones and people with a high BMI doing repetitive loading with their body weight are also at high risk for injuries.
- Anatomy: Foot problems sometimes affect the way foot strikes the ground. The foot problems such as bunions, blisters, tendonitis, and low or high arches. March fractures could also be caused by muscle weakness, imbalances or lack of flexibility.
- Sex: Females are prone to march fractures if they have irregular menstrual periods or no periods.
- Medical conditions: Osteoporosis or other medical conditions weaken bone strength and density. The weak and the soft bones are not able to handle the changes in activity.
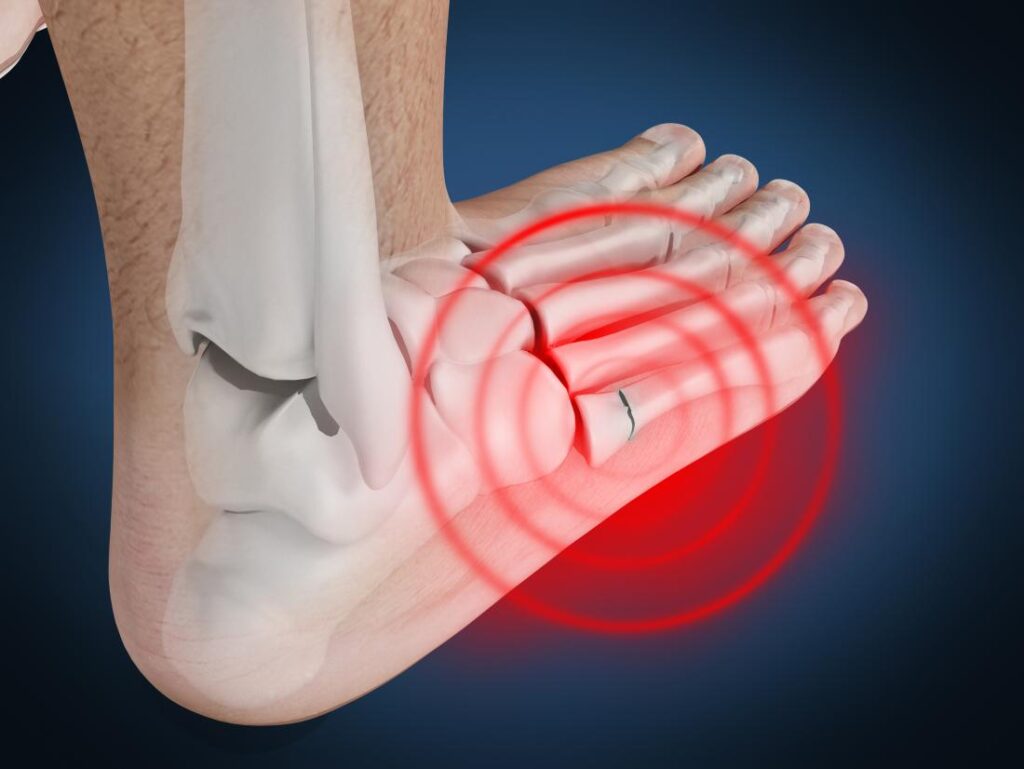
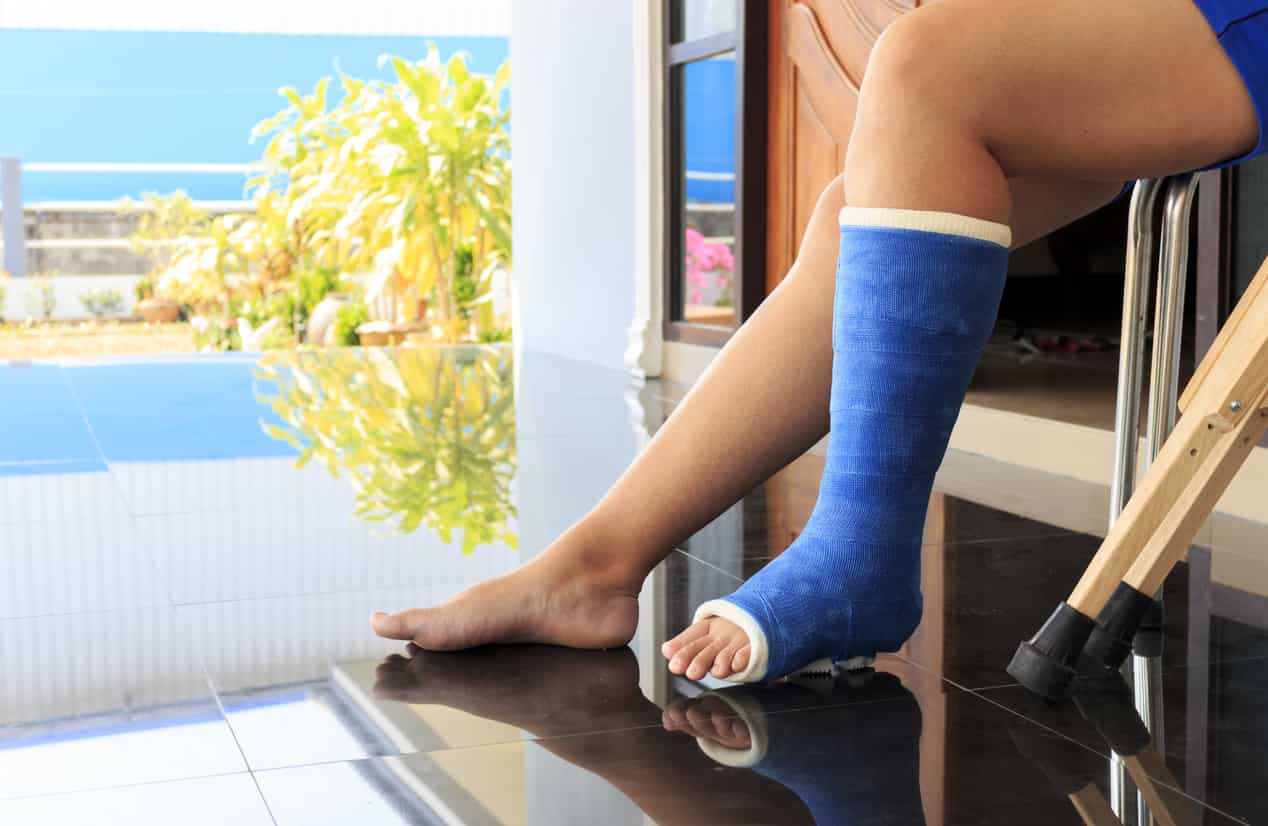
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF MARCH FRACTURE?
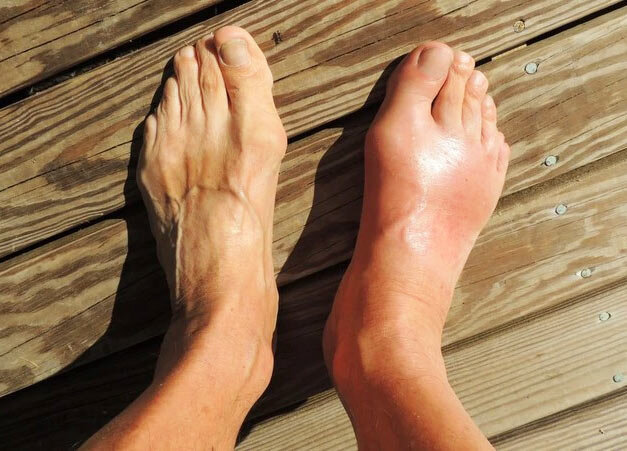
The pain might become severe if a stress fracture is not treated at an early stage (stress reaction). The fracture might become displaced (the fractured bone moves out of normal alignment). Some of the stress fractures like hip are considered high risk stress fractures because they might have an unfortunate outcome such as needing surgery.
- Pain, swelling or aching at the location of fracture
- Tenderness or pinpoint pain when touched on the affected area
- Pain beginning after an activity and then resolves with rest
- Pain present throughout the activity which does not go away after the activity
- Pain occuring while at rest, during normal activity or with everyday walking
- Pain worsening with hopping on one leg
- Pain due to inability to shift weight or hop on affected leg or foot
Initially you might hardly notice the pain associated with a stress fracture. However, it tends to worsen with time. The tenderness initiates at a specific spot and decreases during rest. You might experience swelling around the painful area.
People engaged in high-impact sports such as track and field, basketball, tennis, dance or gymnastics are prone to stress fractures. Some stress fractures might not heal completely. This would cause chronic problems. If underlying medical condition causes are not taken care of, you may be at higher risk of additional stress fractures.
HOW TO DIAGNOSE MARCH FRACTURES?
The tests recommended by the podiatrist would include:
- Physical Examination: A podiatrist would examine you physically as well as check for medical history, work or activities you are involved in and any medications that you are taking.
- Imaging tests such as X-ray, bone scan and MRI.
HOW TO TREAT MARCH FRACTURES?
There are several ways to treat stress fractures. The podiatrist would discuss the treatment options based on the location and severity of your fracture. Also, they would aim to treat any risk factors you have for future injuries.
The treatment regime would include:
- Stopping the activity causing pain – Stress fractures are caused due to repetitive stress and overuse. It’s important to avoid the activity causing the fracture.
- RICE method – Applying an ice pack or ice massage to the injured area reduces the inflammation and the pain. Resting for roughly two to eight weeks helps in the healing process. Elevating your foot above the level of your heart reduces the swelling in your leg, ankle or foot.
- Cross-Training – Cross training by doing non-impact exercise such as using a pool or bike. The exercise should be started after discussion with your podiatrist. You should start with low-impact activities for extended periods without pain and then start doing high-impact exercises. Usually, physical therapy is helpful in returning to activities and making adjustments to avoid re-injury.
- Medication – Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines help relieve pain and swelling.
- Protective Footwear – Using protective footwear helps to reduce stress on your foot or leg. This might include a stiff-soled shoe, a wooden-soled sandal, or a post-op shoe that has a rigid sole. Crutches help to keep weight off your foot or leg for the bone to heal fast.
OUTLOOK
It is important to prevent the fracture from happening again. Some of the tips that help in prevention are:
Accommodate changes slowly: Start any new exercise slowly and progress further gradually.
Use proper footwear: The shoes should fit well and are appropriate for your activity.
Cross-train: Incorporate low-impact activities to avoid repetitively stressing a particular part of your body.
Get proper nutrition: It is necessary to keep bones strong, by including enough calcium, vitamin D and other nutrients in your diet.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from foot problems, our expert providers at Specialty Care Clinics will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call us on (469) 545-9983 to book an appointment with our specialists.
