WHAT IS A VAGINAL YEAST INFECTION?
A vaginal yeast infection is a fungal infection that causes irritation, discharge, and severe itchiness of the vagina and the vulva — the tissues at the vaginal opening.
Otherwise known as vaginal candidiasis, vaginal yeast infection affects as many as three out of four women at some point in their lifetimes. Many women go through at least 2 episodes.
A vaginal yeast infection is not considered a sexually transmitted disease (infection). However, there is a greater risk of vaginal yeast infection at the time of the first regular sexual activity. There is also some evidence that infections might be associated with the mouth through genital contact (oral-genital sex).
Medications could effectively treat vaginal yeast infections. If you have recurring yeast infections — four or more during the year — you might require a longer course of treatment and a maintenance plan.
SYMPTOMS
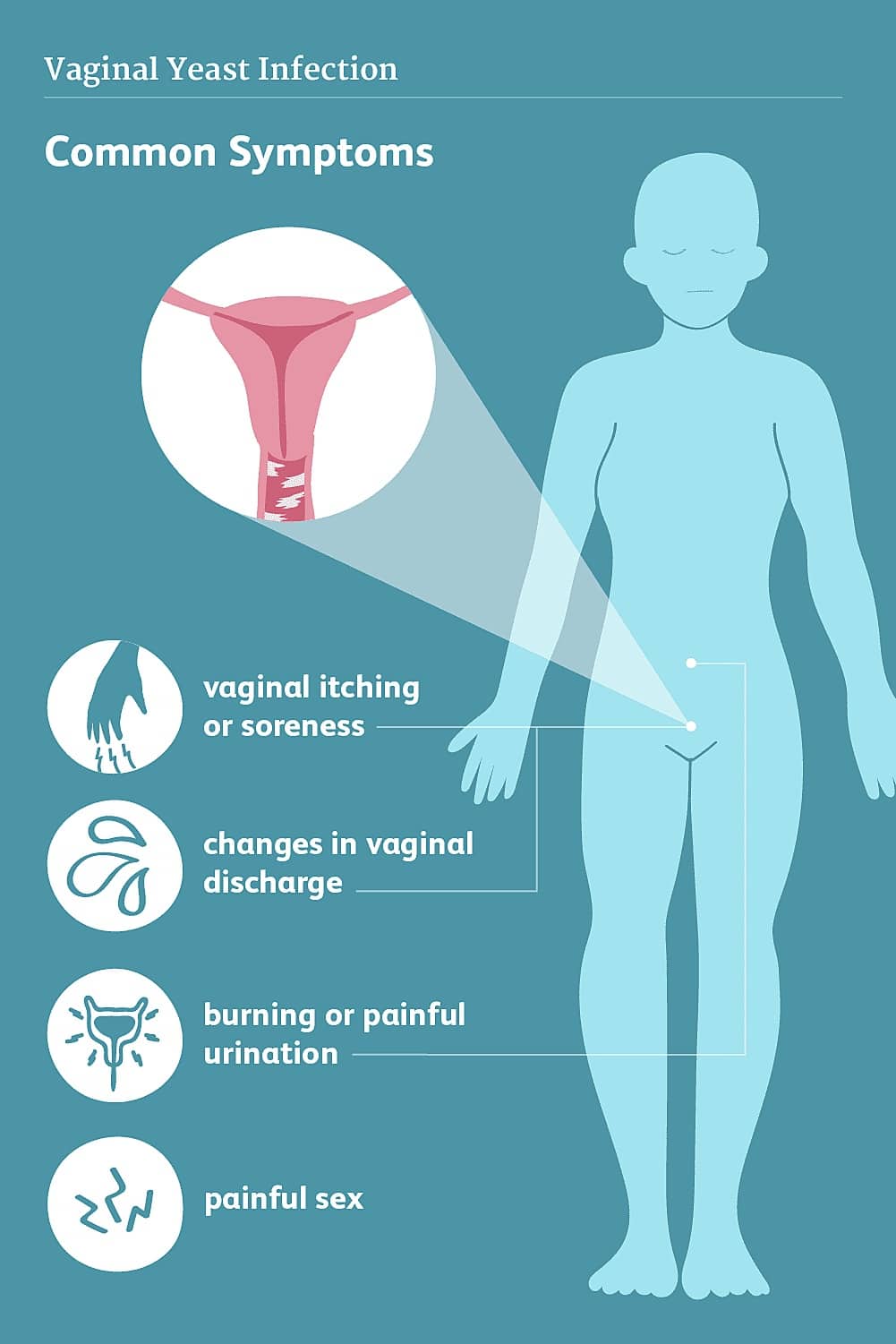
Yeast infection symptoms could range from mild to moderate and involve:
- Itchiness and discomfort of the vagina and the vulva
- A burning feeling, particularly during intercourse or while urinating
- Redness and inflammation of the vulva
- Vaginal pain and soreness
- Vaginal rash
- Thick, white, smell-less vaginal discharge with a cottage cheese appearance
- Watery vaginal discharge
COMPLICATED YEAST INFECTION
You could get a complicated yeast infection if:
- You have severe signs and symptoms, like extensive redness, inflammation, and itching that leads to tears, cracks, or sores
- You have four or more yeast infections in one year
- Your infection is the result of a less typical kind of fungus
- You are pregnant
- You have uncontrolled diabetes
- Your immune system is weakened due to specific medications or conditions like HIV infection
WHEN SHOULD YOU SEE A DOCTOR?
Schedule an appointment with your doctor if:
- This is your first-time experiencing symptoms of yeast infection
- You are not sure whether you have a yeast infection
- Your symptoms are not eased after treating with over-the-counter antifungal vaginal creams or suppositories
- You develop other symptoms
CAUSES
The fungus candida Albicans is accountable for the majority of vaginal yeast infections.
Your vagina naturally comprises a balanced mix of yeast, including candida, and bacteria. Specific bacteria (lactobacillus) act to stop the overgrowth of yeast.
But that balance could be disturbed. An overgrowth of candida or penetration of the fungus inside deeper vaginal cell layers causes the signs and symptoms of a yeast infection.
Overgrowth of yeast could result from:
- Antibiotic use, which leads to an imbalance in the natural vaginal flora
- Pregnancy
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- An impaired immune system
- Taking oral contraceptives or hormone therapy to increase estrogen levels
Candida albicans is the most common kind of fungus that causes yeast infections. Yeast infections caused by other kinds of candida fungus could be harder to treat and usually require more aggressive treatments.
RISK FACTORS
Factors that raise your risk of developing a yeast infection include:
- Antibiotic use – Yeast infections are frequent in women who take antibiotics. Broad-spectrum antibiotics, which kill an array of bacteria, also kill healthy bacteria in your vagina, resulting in the overgrowth of yeast.
- Increased estrogen levels – Yeast infections are more common in women with higher estrogen levels — like pregnant women or women taking high-dose estrogen birth control pills or estrogen hormone therapy.
- Uncontrolled diabetes – Women with poorly controlled blood sugar are at higher risk of yeast infections compared to women with well-controlled blood sugar.
- Impaired immune system – Women with lowered immunity — like from corticosteroid therapy or HIV infection — are more likely to develop yeast infections.
PREVENTION
To lower your risk of vaginal yeast infections, wear an undergarment that has a cotton crotch and does not fit too tightly.
It may also help to avoid:
- Tight-fitting pantyhose
- Douching, which removes some of the natural bacteria in the vagina that protect you from the infection
- Fragrant feminine products, including bubble baths, pads, and tampons
- Hot tubs and very hot baths
- Unnecessary antibiotic use, like for colds or other viral infections
- Staying in wet clothes, like swimsuits and workout attire, for long periods of time

DIAGNOSIS
To diagnose a yeast infection, your doctor might do the following:
- Ask questions about your medical history – This may include gathering information about past vaginal infections or sexually transmitted diseases (infections).
- Perform a pelvic examination – Your doctor checks your external genitals for signs of infection. Next, your doctor places an instrument (speculum) inside your vagina to hold the vaginal walls open to check the vagina and cervix — the lower, narrower part of your uterus.
- Test vaginal secretions – Your doctor might send a sample of vaginal fluid for testing to determine the kind of fungus causing the yeast infection. The identification of the fungus could help your doctor prescribe a more effective treatment against recurring yeast infections.
TREATMENT
Treatment for yeast infections depends upon the severity and frequency of your infections.
For mild to moderate symptoms and uncommon episodes, your doctor may suggest:
- Short-course vaginal therapy – Taking an antifungal medication for 3 to 7 days will generally clear a yeast infection. Antifungal medicines — which are accessible as creams, ointments, tablets, and suppositories — include miconazole (Monistat 3) and terconazole. Some of these medications are available over-the-counter (OTC) and others by prescription only.
- Single-dose oral medicine – Your doctor may prescribe a one-time, single oral dose of fluconazole (Diflucan). Oral medication is not suggested if you are pregnant. To manage more-severe symptoms, you may take two single doses three days apart.
Consult your doctor again if treatment does not resolve your symptoms or if your symptoms return within two months.
If your symptoms are serious, or you have frequent yeast infections, your doctor may suggest:
- Long-course vaginal therapy – Your doctor may prescribe an antifungal medicine to be taken daily for up to 2 weeks and then once a week for 6 months.
- Multidose oral medication – Your doctor may prescribe 2 or 3 doses of antifungal medicine to be taken orally (by mouth) rather than vaginal treatment. Although, this therapy is not suggested for pregnant women.
- Azole resistant therapy – Your doctor may suggest boric acid, a capsule inserted into your vagina. This medicine might be deadly if taken by mouth and is used only to treat candida fungus that is resistant to the usual antifungal agents.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from vaginal yeast infection, our expert providers at Specialty Care Clinics will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call us on (469) 545-9983 to book an appointment with our specialists.
