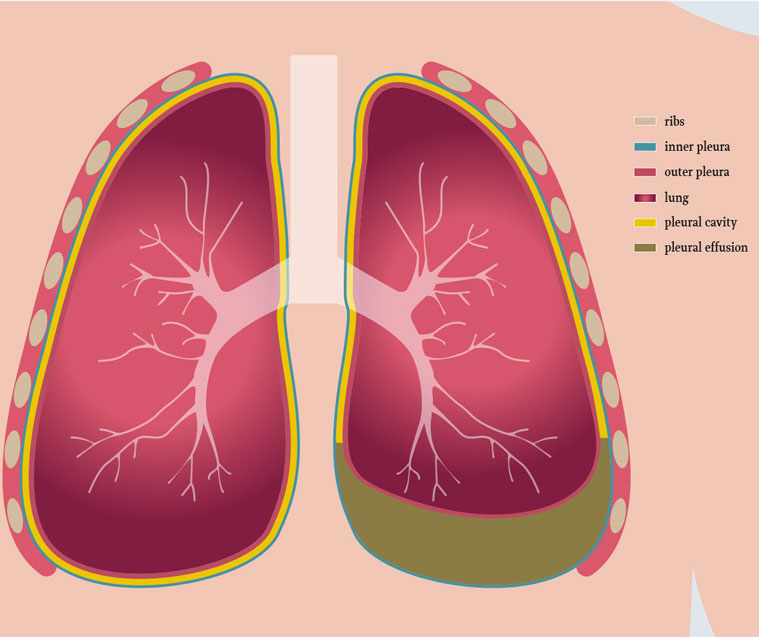
In healthy lungs, the pleural cavity consists of the space filled with fluid. The Pleura is a thin membrane like structure that lines the surface of lungs and inside part of the chest wall. This prevents the friction as lungs expand and contract while breathing. The fluid is usually about 2 teaspoons in the pleural space that acts like a lubricant.
In Pleural Effusion also known as water on the lungs, the excess fluid gets accumulated in the pleural cavity. Excessive fluid in the pleural cavity decreases the lymphatic absorption. The fluid build-up restricts the lungs movement while breathing and creates pressure on the lungs as well as other organs.
The condition might become severe depending on the primary cause of pleural effusion. Infection due to a virus, pneumonia or heart failure can be treated or controlled effectively.
CAUSE OF PLEURAL EFFUSION
Pleural effusion occurs when fluid seeps into the pleural cavity, which is a tiny space between the visceral and pleural membrane present in the chest cavity. Malignant cells, infectious agents and fluid under pressure make it difficult for the lungs to expand due to abnormal amounts of fluid in the pleural cavity.
In case of infection, irritation or inflammation in the pleura causes excessive fluid build-up. The fluid build-up could be transudative (protein-poor) or exudative (protein-rich).
- Transudative Pleural Effusion – This is caused by leaking of the fluid in the pleural cavity which is the result of increased pressure in the blood vessels as well as low count of protein in blood.Common cause for transudative also referred to as watery fluid is due to Heart failure, pulmonary embolism, cirrhosis and post open heart surgery.
- Exudative Pleural Effusion – This is caused due to leakage of tissue due to local cellular damage or inflammation. On the other hand, exudative, also referred to as protein-rich fluid, is commonly caused by pneumonia, cancer, pulmonary embolism, kidney disease and inflammatory disease.
Smoking and alcohol consumption may increase the risk of pleural effusion as they can cause heart, lung or liver disease. Pollutants like asbestos can also lead to pleural effusion.
SYMPTOMS OF PLEURAL EFFUSION
Usually, people do not feel any symptom and disorder is diagnosed on a chest X-ray which might be performed for another reason. The fluid build-up may cause other reasons or conditions related to various organs. Common symptoms that patients might experience are :
- Sharp chest pain which might worsen with cough or deep breaths
- Cough which is dry and non-productive
- Fever along with chills
- Rapid Breathing
- Hiccups which is persistent
- Shortness of Breath or dyspnea
- Orthopnea which is inability to breathe properly until the person is sitting in a straight position or standing erect.
These symptoms are common and they resemble other lung conditions also. It is important that the treatment is started early to recover fast.
As the effusion grows with more fluid in the pleural cavity it becomes harder for the lungs to expand properly making it difficult for the patient to breath. This causes shortness of breath which is the most common symptom.
Pleural lining is irritated due to excess fluid in the pleural cavity which causes chest pain. The chest pain is described as sharp pain which usually worsen with deep breathing. Usually the pain is localized to the chest but if the inflammation of the diaphragm is caused due to effusion, the patient might experience pain in the shoulder or upper abdomen as well. More is the fluid build-up, higher would be the degree of pain.
The fluid may develop cancer which is malignant in nature. It might spread to different organs and cause cancers like lung cancer, breast cancer, lymphoma and leukemia depending on the organ it affects. Adults are more at risk than children to get infected by pleural effusion.
DIAGNOSING PLEURAL EFFUSION
Diagnosis of pleural effusion is difficult as many people do not have any symptoms. Healthcare practitioners would start with the complete history of the patient. The prognosis would include auscultation (listening to the sound of heart and lungs) and percussion (tapping of the lungs). If a patient is suffering from pleural effusion the tapping would be dull on one side of the chest as compared to the other side due to decrease in air entering the lungs. In case of inflammation of the pleura (pleurisy) there would be friction and a squeak would be heard. Some tests that would be required to diagnose pleural effusion are:
- Chest X-Ray – This helps in confirming the fluid presence in the pleural cavity by whitish appearance at the lung base. The appearance could be unilateral (one sided) or the bilateral patient is positioned downward making the fluid move due to the effect of gravity.
- Chest Ultrasound – This is the quickest method to determine the presence of fluid and its location. It also determines if the fluid is loculated (stationed at one place) or free flowing within the pleural space. With the help of ultrasound the doctor can also carry out thoracentesis. In this procedure they extract a small amount of fluid by inserting a needle and catheter between the ribs (into the pleural space). Analysis of the fluid is done by various methods like : 1. Chemical analysis – This helps in differentiating transudate and exudates by measuring the protein concentration.
2. Lactate dehydrogenase – This also helps in differentiating the type of effusion.
3. Complete Blood Analysis – This helps in determining infection and tumor cells by cell analysis. The analysis contains cell count, cytology, and cultures. - CT (Computed tomography) scan – This helps in determining the effusion, its extent and other potential cause of effusion by constructing the entire (inside and outside) images of the chest.
TREATMENT OF PLEURAL EFFUSION
Treatment of pleural effusion depends on its cause. It is important to remove the excess fluid from the chest for any further infection.
- Chest draining – This procedure involves insertion of a small tube that helps in removing the excess fluid from the pleural cavity. This procedure is also referred to as thoracostomy. With removal of excess fluid lungs can expand more thus providing relief from shortness of breath. The fluid is then tested for further infection or possibility of cancer.
- Pleurodesis – After removing the excess fluid from the pleural cavity, the drug is injected in the cavity. This drug is a mixture of talc which prevents the two layers of the pleura to stick together and prevents the build-up of fluid again.
- Surgery or Pleurectomy – In cases that do not respond to any other treatment. This helps in redirecting the fluid from the chest to the abdomen region, and then removed easily from the abdomen. In pleurectomy, doctors remove a part of the pleural lining that is infected.
- Antibiotics – In case of pleural effusion being caused by bacteria or virus infection can be treated by antibiotics (especially pneumonia). Diuretics like furosemide (Lasix) are also prescribed to reduce the size of the pleural effusion.
- Chemotherapy – In case the excessive fluid is cancerous chemotherapy and radiation therapy is required along with chest draining.
OUTLOOK
Pleural Effusion can be prevented if treated at an early stage. Sometimes, the symptoms do not appear causing it difficult to detect and treat pleural effusion.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from Pleural Effusion, our expert providers at Specialty Care Clinics will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call us on 469-545-9983 to book an appointment with Dr. Badar Kanwar.
