Everybody has somehow heard about left-sided chest pain and how it’s related to cardiac reasons, mostly heart attacks. But how many times have you thought about what could cause pain in the right side of the chest? The first thing you need to know is that you can’t rule out cardiac reasons even if it’s on the right side. However, several other reasons that may trigger this pain.
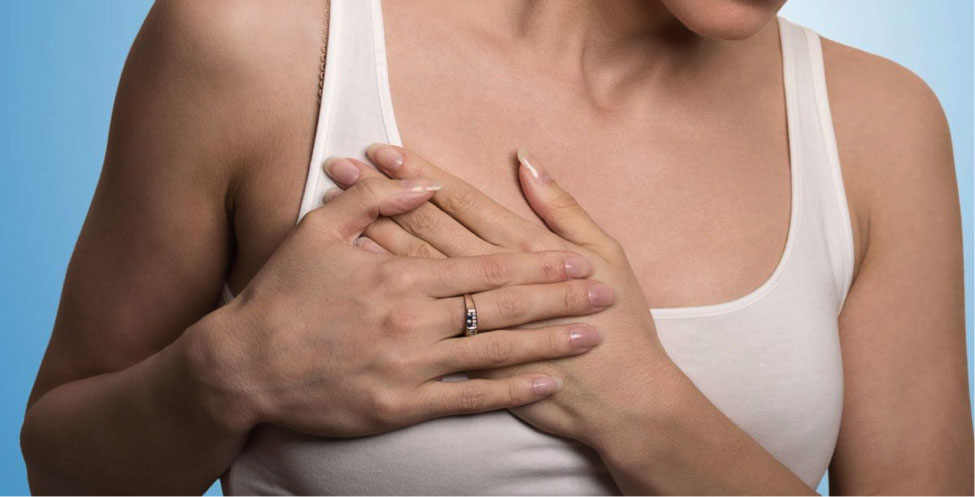

Chest pain affects frequently between 20 and 40% of the general population during their lifetime. Approximately 1.5% of the general population consult a healthcare professional every year, because of chest pain.
In the UK, chest pain constitute 1% of all primary care consultations, more than 5% of visits to emergency departments, and up to 40% of emergency admissions.
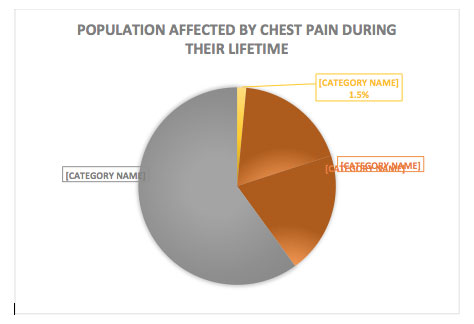 IN THE UK:
IN THE UK:
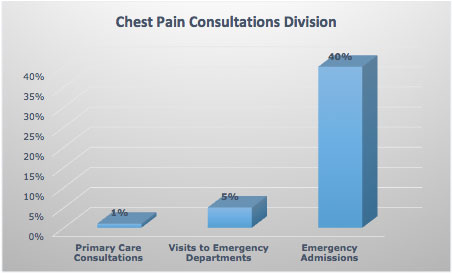
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF CHEST PAIN ON THE RIGHT SIDE?
Pain in the right side of your chest can be related to problems with the skeletal, muscular, respiratory, cardiovascular, and digestive systems.
These are some reasons that might be causing this discomfort in the right side:
-
Panic, anxiety, and stress
Anxiety and panic attacks can be due to stressful events or can happen randomly without any trigger. Their symptoms can be the same as those of a heart attack. When a panic attack or a severe stress situation happens, a person may experience the following:
- Dyspnea.
- Chest pain.
- Palpitations.
- Hyperventilating.
- Sweating.
- Tingling in the arms and face.
• Muscle Strain
There are several muscles located in the chest wall. Overuse or extra efforts such as exercises, heavy lifting, or vigorous activities can cause muscle strains and thereby chest pain on either side.
• Chest trauma
Direct trauma to the chest caused by a fall or a hit can cause intense pain in the chest due to the injury of muscles, nerves, blood vessels, or bones. Damage to the bones can include a tear, fracture, or misalignment of the ribs which can even make breathing painful. Chest trauma can also be accompanied by:
- Shortness of breath.
- Bruising.
- Swelling.
- Tenderness.
If an accident ever happens to you, get checked by your doctor, even if you don’t feel anything. Sometimes the injuries are internal and could be very serious.
• Indigestion or heartburn
Indigestion happens after you eat a meal and your body is unable to digest it as it should. This condition could happen with anyone and is not considered dangerous most of the time. Even though it’s rare but this condition could lead to pain in the right side of the chest.
Other symptoms of indigestion include:
- Discomfort in the upper abdomen.
- A burning sensation in the upper abdomen.
- Bloating.
- Nausea.
• Acid reflux
When the acid used by your body to digest food, comes back into the esophagus, it causes “acid reflux”. Along with chest pain, acid reflux causes epigastric and throat pain.
If this happens in a repetitive way you may suffer from a condition called “GERD” or “Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease”. This condition should be treated and followed up by a medical professional to prevent further and more serious complications.
• Costochondritis
The ribs are connected to the sternum by cartilage. When the cartilage becomes inflamed, it’s called costochondritis. The pain caused by this condition may be similar to a heart attack. It also comes along with:
- Pain when you cough or sneeze.
- Tenderness of the rib joints.
- Fever.
- Trouble breathing.
• Shingles
Shingles are caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. It’s a rash that develops on one side of the body. Sometimes, nerve damage happens as a result of shingles complications, and results in chest pain, a tingling or burning sensation, itching, and sensitivity to touch the affected area.
• Pleurisy
The pleura is formed by two layers: one layer covers the lung and the other layer lines the inner chest wall. Pleurisy happens when the pleura gets swollen resulting in the layers rubbing against each other.
Pleurisyaortic causes a painful sensation each time the person inhales and exhales. It can become worse with coughing, sneezing, or laughing.
• Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a lung infection due to bacterial, viral, or fungal organisms. It can happen in one or both lungs.
Some pneumonia symptoms are:
- Chest pain.
- Coughing.
- Dyspnea.
- Fever.
- Sweating.
- Shaking.
• Pneumothorax
There is a small space between the two layers of the pleura called the “pleural space” filled with a small amount of fluid. When air enters the pleural space, it causes the lung to collapse (a pneumothorax). It can happen after an injury to the chest or without an obvious reason.
Pneumothorax symptoms include:
- Chest pain.
- Shortness of breath.
- Tachycardia.
- Cough.
- Fatigue.
• Cardiac inflammation:
There are two types of cardiac inflammation, “Pericarditis” which is the inflammation of the sac around the heart, and “Myocarditis” which is the inflammation of the heart muscle.
These are very serious conditions that could lead to dangerous consequences. They are due to an infection and can cause intense chest pain along with:
- Trouble breathing.
- Fever.
- Irregular heartbeats.
- Coughing.
- Pneumothorax
• Pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension is caused by high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries. This condition makes your heart work harder to pump blood leading to chest pain. Pulmonary hypertension also causes fatigue, shortness of breath, swelling in the ankles or legs, and lips turning into blue color.
• Pulmonary embolism
A pulmonary embolism is a blockage, mostly a blood clot, in the pulmonary arteries. If the clot is situated in the right artery it will cause right-sided chest pain. Pulmonary embolism is a life-threatening condition that needs immediate medical attention. Go directly to the emergency if you experience these symptoms:
- Chest pain.
- Palpitations.
- Shortness of breath.
- Rapid breathing.
- Coughing up blood.
• Pleural effusion
Normally, in the pleural space separating the two layers of the pleura, there is a small amount of fluids. When this fluid builds up and turns into an excessive amount, it is called pleural effusion. This condition causes chest pain and difficulty of breathing.
• Chest tumors and lung cancer
Chest tumors can develop in all the chest cavity and put pressure on the nerves, triggering chest pain, shortness of breath, and coughing (sometimes blood). Lung cancer is one of the most common chest tumors and causes a lot of damage to the tissues.
• Aortic aneurysm
An aortic dissection is a tear in the aorta. Often described as a sharp, stabbing sensation in the chest, it’s a life-threatening condition. You should never wait to seek medical attention if you ever experience this type of pain.
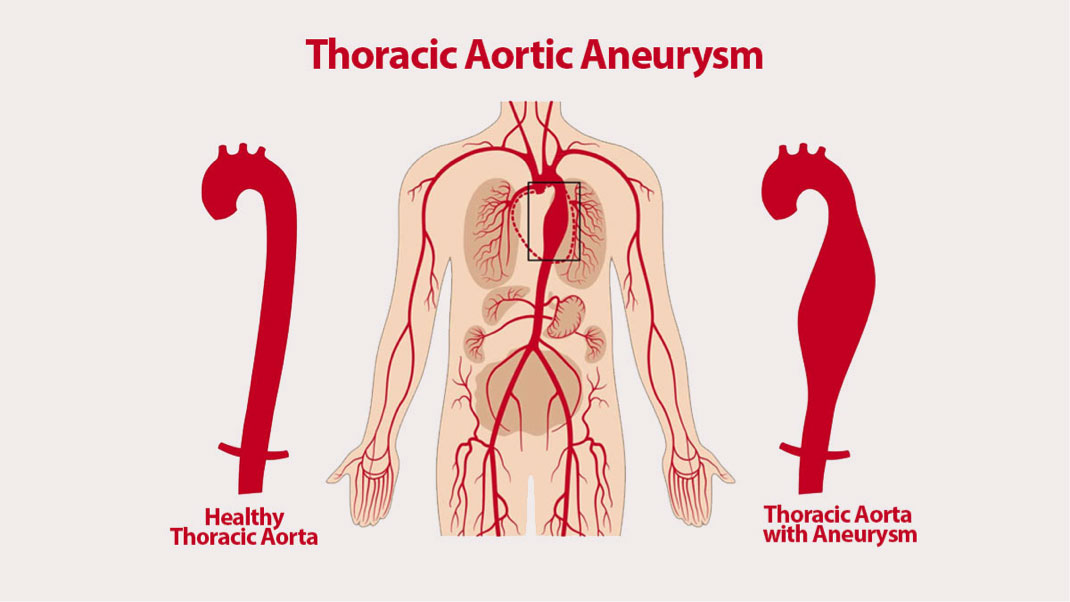
• Gallbladder disease
Even though the gallbladder has nothing to do with the chest, gallstones, and cholecystitis (an infection of the gallbladder) can lead to severe pain radiating to the right side of the chest, but also to the back and the right shoulder.
• Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis pain can also be very serious and reach the chest causing discomfort.
• Liver Disease
Different liver diseases such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, or tumors cause pain that can spread to the right side of the chest. You may also notice a discoloration of the skin turning into a yellow color.
WHEN TO SEE A DOCTOR:
Chest pain should never be taken lightly. Whenever you experience discomfort in your chest whether it is right-sided or left-sided, you should always call your doctor. Some reasons are harmless, can be treated with home remedies, and may even disappear after a few days, however, some symptoms cannot be ignored and should immediately be checked by a professional. These symptoms include:
- Stabbing pain in the chest.
- Continuous cough.
- Coughing blood.
- Desaturation (low oxygen level).
- Numbness or tingling in the arms, back, or face.
- Loss of consciousness.
HOW TO TREAT PAIN IN THE RIGHT SIDE OF THE CHEST?
The treatment will typically depend on the diagnosis. Once the diagnosis is determined, accurate treatment will be given. Common treatments include:
- Over-the-counter medications to ease the pain if it’s a simple matter.
- Chemotherapy and radiotherapy for cancer.
- Rest and close monitoring for some cases such as a pneumothorax.
- Surgery is required for serious conditions like a dissecting aortic aneurysm.
- Antibiotics for some conditions such as pancreatitis.
- Thoracic drainage for pleural effusion.
- Anticoagulants: drugs used to prevent blood clots from happening.
HOW TO DIAGNOSE PAIN IN THE RIGHT SIDE OF THE CHEST?
In order to determine the reason behind the patient’s discomfort the doctor will need to follow several steps.
First, examining the patient: Checking the ABCs, which stands for airway, breathing, and circulation. It may include listening to the lungs and heart using a stethoscope, measuring the level of oxygen, checking the throat, etc.
The doctor will also ask about a detailed description of the pain, the time it started and how long has it been. In addition to that, he needs to be fully aware of any allergies, procedures done before, any known health conditions, and any constant or new medications taken by the patient.
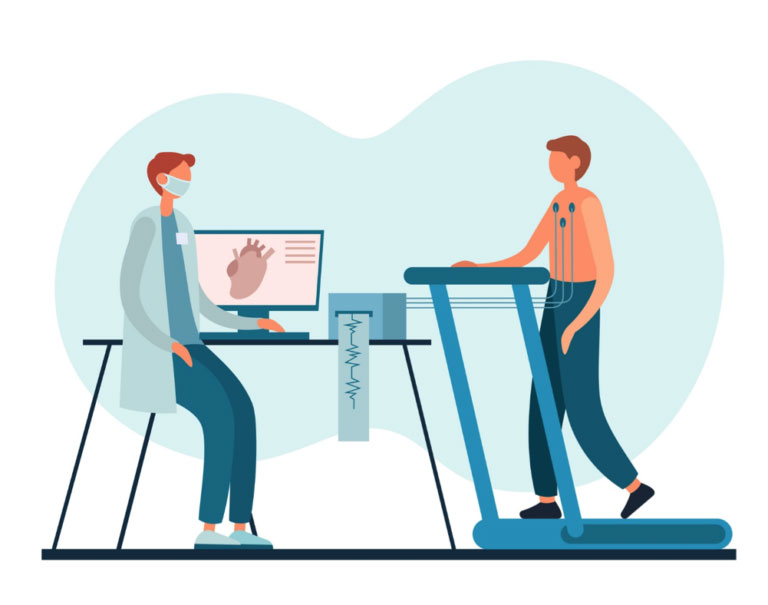

If it’s not enough the doctor will also order:
- Blood tests.
- Chest x-ray or chest CT scan to get a better look at the lungs.
- EKG to check the cardiac rhythm.
- Pet scan to confirm a cancer diagnosis.
- Bronchoscopy to take an internal look at the lungs.
- Cardiac stress test to search for any cardiac abnormalities.
