GOUT: URIC ACID PAIN
A deposit of uric acid crystals accumulates in the joints due to high blood levels of uric acid causing hyperuricemia leading to pain. The accumulation of these crystals leads to flare-ups of painful inflammation in and around joints.
The high amount of uric acid intermittently causes severe joint or tissue pain and inflammation. Increases in uric acid levels lead to several diseases, like a painful type of arthritis called gout. Gout is categorized by sudden swelling, severe attacks of pain, redness and tenderness in one or more joints, usually in the big toe.
Elevated blood uric acid level is caused by factors like genetics, obesity, some medications like diuretics (water pills), and chronic decreased kidney function (kidney disease).
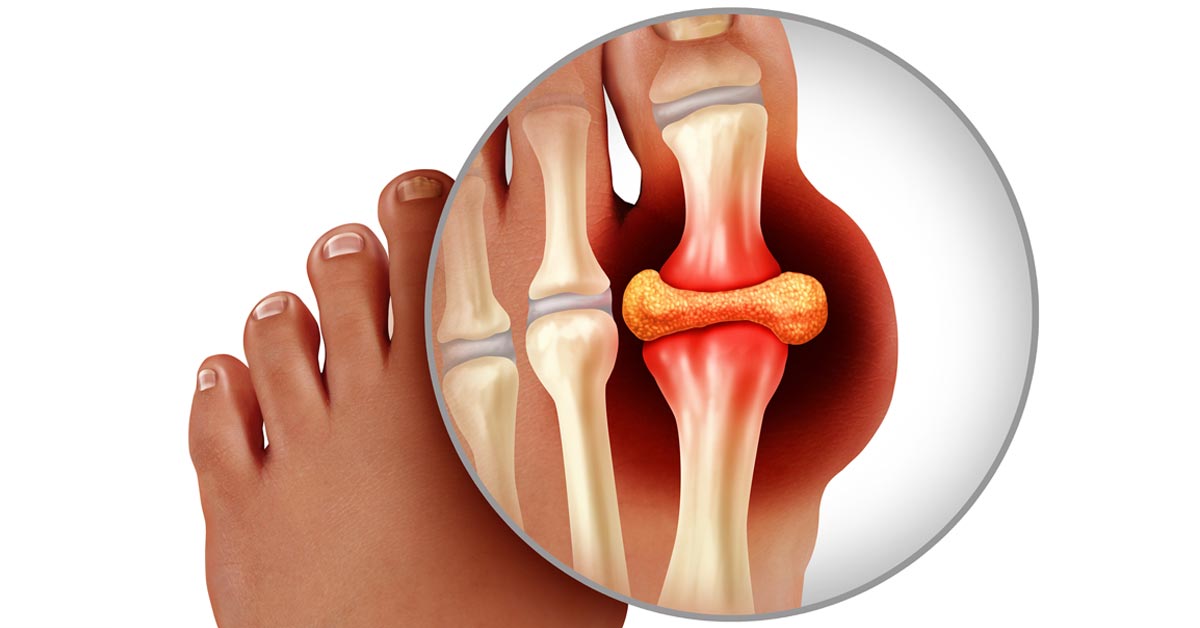
WHAT CAUSES GOUT?
Gout is caused by uric acid crystals accumulating in the joint, causing the inflammation and intense pain of a gout attack. Urate crystals are formed due to high levels of uric acid in blood. The crystals formed as sharp, needle-like causing pain.
Your body produces uric acid when it breaks down purines, a substance found naturally in your body. Alcoholic beverages, like beer, and drinks containing fruit sugar (fructose) also promote higher levels of uric acid.
Some underlying medical conditions like blood and metabolism disorders or dehydration tend to increase the uric acid production. Medical conditions like kidney or thyroid disorder or an inherited disorder makes it difficult to remove excess uric acid from the body.
Some conditions or people prone to gout are:
- Middle-aged man or postmenopausal woman
- Family members, parents or siblings suffering from gout
- Drinking alcohol
- Medications like diuretics and cyclosporine
- Medical conditions such as high blood pressure, kidney disease, thyroid disease, diabetes, or sleep apnea
WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF URICEMIA?
Primary hyperuricemia involves increased production of uric acid from purine and a kidney is unable to get rid of the uric acid in blood.
Secondary hyperuricemia includes:
- Some cancers or chemotherapy agents might cause an increased rate of cell death and high uric acid levels.
- As a result of chemotherapy, the amount of cellular destruction, and tumor lysis syndrome might be caused.
- Kidney disease might be caused making it unable to clear the uric acid from your system, causing hyperuricemia.
- Medications might result in increased levels of uric acid in the blood
- Endocrine or metabolic conditions like diabetes or acidosis might cause hyperuricemia
- Elevated uric acid levels may cause kidney problems.
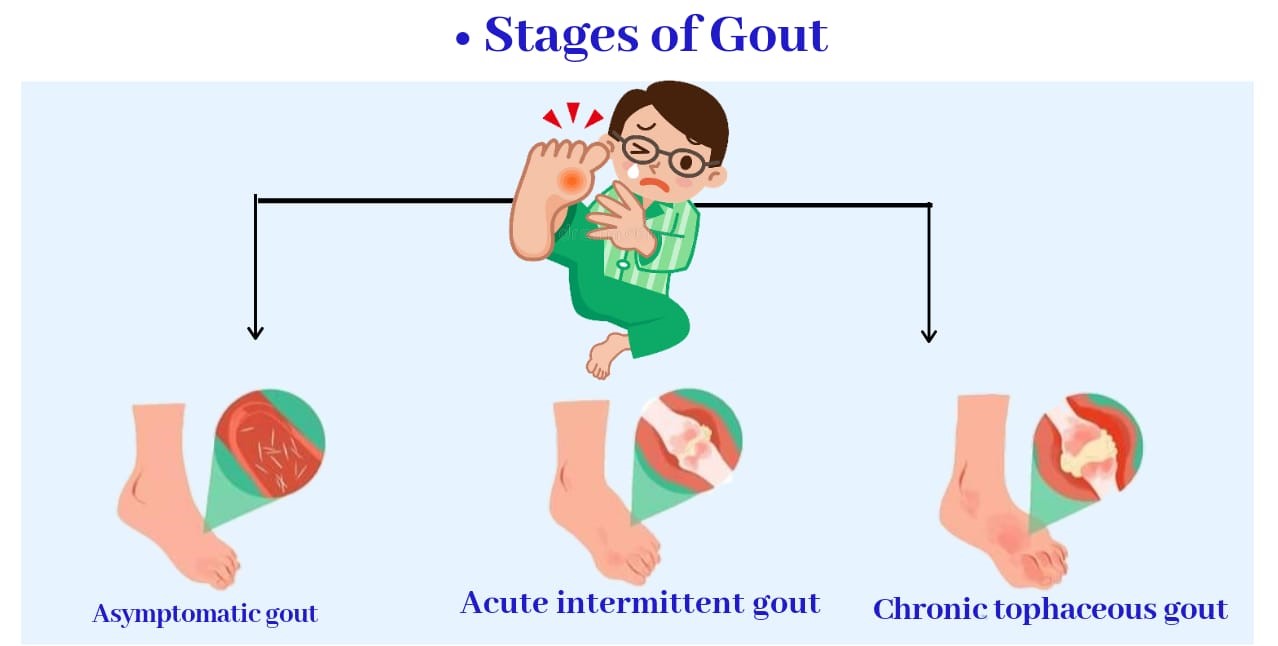
In case the gout is not treated, it might become chronic. Hard lumps known as tophi could develop eventually in the joints along with the skin and soft tissue surrounding the hard lumps which are usually painless but might become inflamed and painful. These are deposited in the synovial lining or cartilage and might also lead to kidney stones.
These deposits might permanently damage the joints. Tophi usually develop in the fingers, hands, feet or tough band. These might extend from the calf muscles to the heel (known as Achilles tendon), or around the elbows.
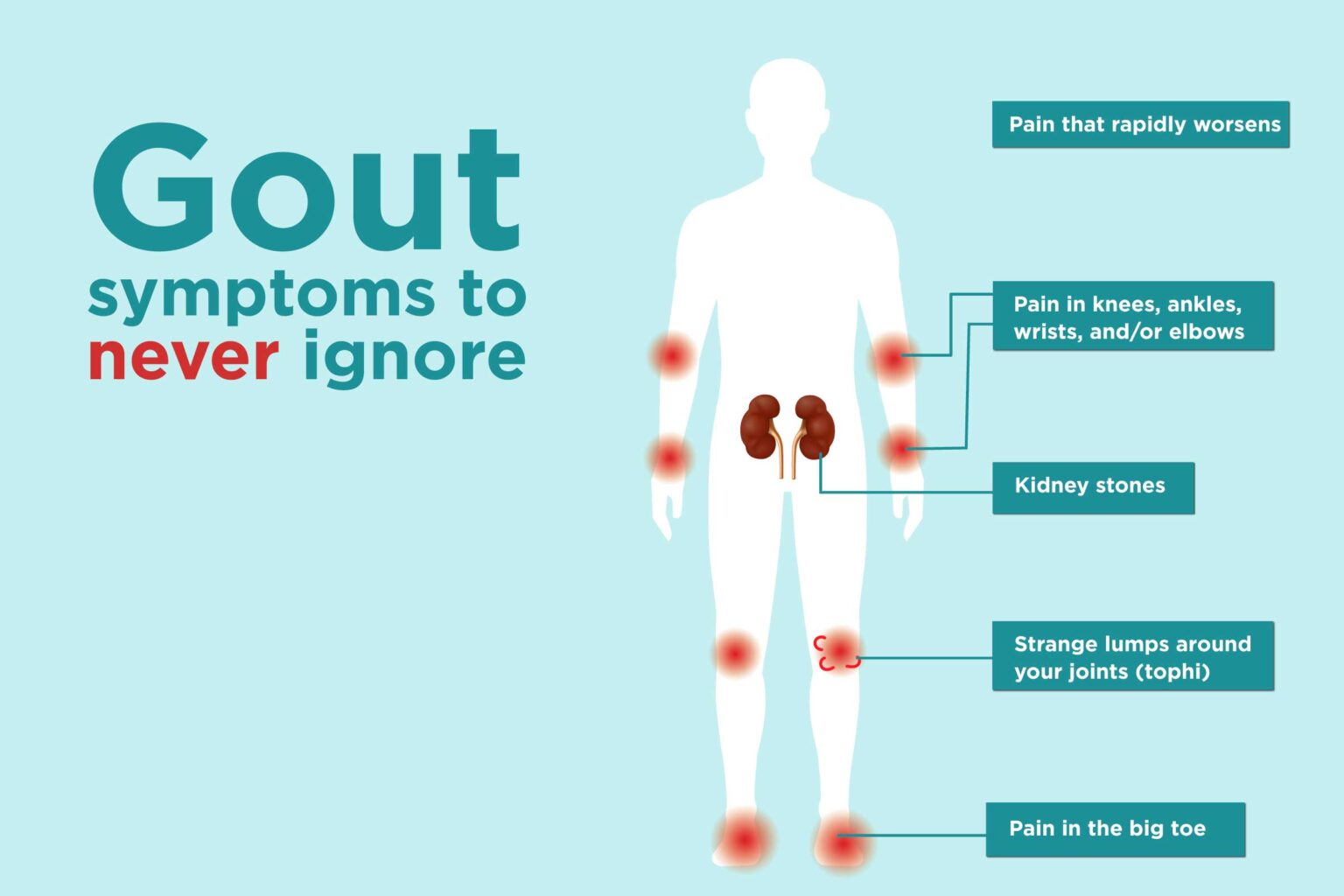
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF GOUT?
The signs and symptoms of gout usually occur suddenly, often at night. The symptoms would gradually disappear with normal joint movement until the next flare-up. These would include:
- Intense Joint Pain: It can affect any joint including the ankles, knees, elbows, wrists and fingers but usually affects the big toe. The pain is severe in the initial first 4 to 12 hours after it starts.
- Lingering discomfort: After the severe pain subsides, joint discomfort might last from a few days to a few weeks. The attacks usually last longer and affect more joints.
- Inflammation and redness: The affected joint would become swollen, tender, warm and red. The tenderness occurs even to light touch, like from a bedsheet. Warmth and redness or a feeling like the joint is on fire.
- Limited range of motion: with the progress of gout, the joint might not be able to move normally.
- The heart rate becomes fast leading to tachycardia
- Fever with chills (rarely)
In some severe gout can progress to a severe condition like:
- Kidney stones: Uric acid crystals might get accumulated in the urinary tract forming kidney stones.
- Recurrent gout: Usually people have one flare up; however, others might have regular occurrences, leading to gradual damage to the joints and surrounding tissue.
HOW TO DIAGNOSE GOUT?
Doctors would diagnose gout on the basis of its distinctive symptoms and physical examination of the affected joints to look for swelling, redness and warmth. The following suggest the diagnosis of gout:
- Podagra that is sudden swelling, pain, and redness of the big toe
- Recurring inflammation of one or more joints
- A history of previous flare-ups that occurred suddenly and resolved unexpectedly
People suffering with gout would have a high level of uric acid in the blood. Sometimes, the uric acid level may be normal, mainly during an acute flare-up. A blood test alone is not sufficient for diagnosis. Thus doctor would suggest other tests like:
- Microscopic examination of joint fluid
- X-rays and/or ultrasonography or special CT scans
- Aspiration by pulling out the fluid from affected joint to check for uric acid crystals (confirming gout)
HOW CAN GOUT BE TREATED?
Healthcare providers would prescribe medicine to reduce the symptoms of gout and prevent it from recurring. The medicines would help reduce the inflammation and pain due to gout attacks as well as help in lowering the amount of uric acid in your blood to prevent gout complications.
MEDICATIONS
These would include medication to treat gout flares and prevent future attacks.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) include over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve). For severe pain powerful medications like indomethacin (Indocin, Tivorbex) or celecoxib (Celebrex) are prescribed.
- Colchicine such as colchicine (Colcrys, Gloperba, Mitigare) help in reducing inflammation and ease off the pain.
- Corticosteroid such as prednisone helps in controlling gout inflammation and pain.
PREVENT GOUT COMPLICATIONS
Doctors would prescribe certain medications or recommend lifestyle changes to control uric acid in the body.
- Block uric acid production – Medicines such as allopurinol (Aloprim, Lopurin, Zyloprim) and febuxostat (Uloric) limit the amount of uric acid produced by the body.
- Improve uric acid removal – Medicines such as probenecid (Probalan) improves the kidneys’ capacity to remove uric acid from the body.
LIFESTYLE CHANGES
Limiting or cutting down on alcoholic beverages or sweetened drinks (containing fructose) and avoid foods high in purines like red meat, organ meats (like liver), anchovies, sardines, mussels, scallops, trout and tuna prevents recurrence of flare-ups. Healthy body weight with regular exercise helps in reducing the risk of gout.
COLD THERAPY
Application of ice pack and elevation of the affected joint help in reducing the inflammation and dulling the pain.
SURGERY
In case of kidney stones smaller than 5 mm, the doctor would advise to drink a lot of water and prescribe over-the-counter pain medications until the stones pass. If the stone is bigger than 5mm a non-invasive procedure known as lithotripsy is recommended that breaks the stone in smaller pieces with help of ultrasonic energy or shock wave. However for stones larger than 10mm surgery is required for removal.
OUTLOOK
Asymptomatic hyperuricemia can be controlled with diet and lifestyle changes that help lower uric acid levels in your blood. For severe cases of gout which don’t respond to the treatments above, corticosteroid injections into the affected joint are recommended.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from joint or kidney pain, our expert providers at Specialty Care Clinics will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call us on (469) 545-9983 to book an appointment with our specialists.
