WHAT IS GUT MICROBIOME?
People nowadays are paying hundreds of dollars in the U.S. to have their gut microbes analyzed. They hope to get insights that will allow them to adjust their diet and improve their health. The microbiome is a genetic snapshot of our body’s microscopic organisms, mainly gut micro-organisms.
The body’s “microbiota” is the collection of microbes, including bacteria, viruses, yeast, and other microscopic organisms. Researchers have mostly studied these microbes that exist throughout our bodies, generally the gut microbiome.
Some of these microbes can harm us, like potential pathogens—salmonella and E. coli are two well-known gut pathogens. Other microbes actively help us by producing vitamins or inhibiting the replication of pathogens. Some of the microbes are seemingly neutral, neither actively helping nor harming, but thriving as a part of our internal microbial ecosystem.
It has been proved in various studies that abnormal or dysbiotic microbiomes are associated with several diseases, such as Crohn’s disease, cardiovascular disease, and even some cancers. The dysbiotic microbiome may illustrate significantly less diversity of bacteria than the typical microbiome or may show overgrowth of certain bacteria that have been linked to health conditions.

WHO SHOULD TAKE A MICROBIOME TEST?
As per the doctors, everyone who can afford the microbiome test should get it done. Microbiome tests have been advanced as well as scientific understanding of our gut microbiome has developed making it easier for everyone to take the test. It is even beneficial in discussing the results and ensuing actions with your healthcare professionals.
The goal of microbiome tests is to detect the presence of different species of microorganisms in a fecal sample. The test results provide a lot of information such as:
- The diversity and richness of the gut microbiome.
- Comparison of your gut microbiome to that of others.
- Details about your overall health and aging process.
- Impact of the gut microorganisms.
- Improving your health through specific dietary modifications.

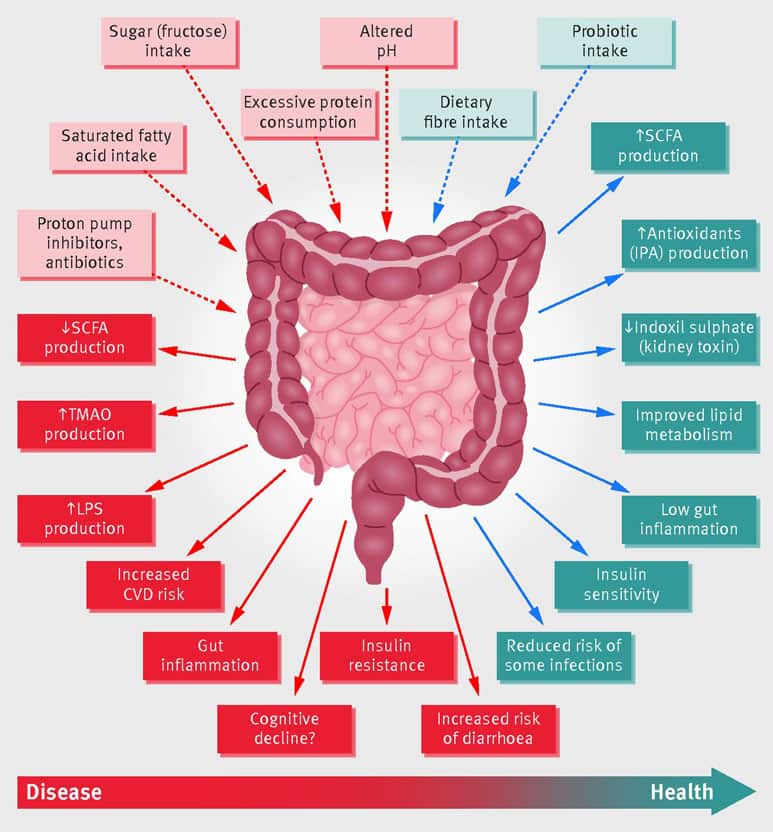
The imbalance of gut microbes can result in various health effects. Some of the common symptoms of gut disruptions include bloating, stool changes, and heartburn.
Other less evident impacts of a gut microbiome imbalance may include:
- Mood swings,
- Various mental health conditions like depression or anxiety,
- Obesity,
- Skin disorders, like eczema,
- Cardiovascular diseases,
- Inflammation,
- Diabetes
- Cancers,
- Liver diseases, and
- Oral health problems, like tooth decay.
WHAT CAN DOCTORS LEARN FROM MICROBIOME TEST?
The gut microbiome testing tells a lot about your gut health. The most complex part of our body is the digestive system. Microbiome tests are fecal tests that require fresh stool samples. The primary aim is to analyze microbes and potential imbalances in your GI system. These tests help the healthcare provider to collect a lot of information, such as:
- Parasites: The sample will indicate the signs of a parasite and labs can diagnose them by the presence of their DNA. The parasites are more common than you think and cause common infections including Blastocystis hominis and Dientamoeba fragilis. These cause common symptoms like nausea and stomach pain.
- Yeast Overgrowth: The microbiome tests can determine a high amount of yeast, like the common yeast called Candida albicans. This helps the doctors to determine a wide range of GI symptoms as well as other symptoms such as acne, weight gain, and brain fog.
- Bacterial Overgrowth: Bacteria in the gut include both “potentially pathogenic” and pathogenic bacteria. A “potentially pathogenic” bacteria may become pathogenic if present in large amounts. A small number of these bacteria will not cause symptoms but a large number might. Unlike, pathogenic bacteria such as salmonella are harmful even in small numbers. The severity of the infection may vary.
- Calprotectin: Calprotectin is an inflammatory marker associated with irritable bowel disease and tumors. If your levels are significantly elevated, you’d need to consult a GI specialist about the next steps.
- Immune Markers: Diagnosing the immune markers helps reveal the status of the immune system if it is over-or under-active. Specific inflammatory markers, such as IgA, indicate a food sensitivity or presence of a microbe in the GI tract such as fungus or bacteria. These may trigger an immune response. High levels of eosinophils indicate an allergy or a parasite.
- Pancreatic elastase: This enzyme should be present in appropriate amounts; if not, your pancreas might not be functioning well. This might indicate that your food is not breaking down effectively.
- Fat and Protein: The presence of protein and fat in the stool, will tell your doctor how well you’re digesting and absorbing your food. This indicates the health of your overall digestive system.
- Beneficial Bacteria: These tests look for short-chain fatty acids (like butyrate) that should be in your colon and stool in high quantities. The high amount of these short-chain fatty acids indicates that you have a vast, robust microbiome. In case you’re not eating enough fiber, these bacteria might be missing.
Apart from the above benefits from microbiome testing, there are some limitations too. These include:
- No standard reference Range: There is no single reference range for what constitutes a healthy, normal gut microbiota. no such standard of ‘normal and healthy’ exists for the gut microbiota.
- Not Specific to Microbe: Clinical microbiome test data often aren’t specific enough to be meaningful such as the presence of E.coli and its variants.
- Influence of Diet: It’s not even clear to what extent your gut microbiota can be micromanaged through any means. A significant number of people appear resistant to colonization by supplemental probiotics – and even those who can be colonized, the effect is short-lived.
WHEN SHOULD YOU SEE YOUR DOCTOR?
In case of chronic digestive problems or other underlying health concerns, you should make an appointment with a doctor. You should not wait if you have the symptoms that aren’t improving despite making lifestyle changes.
You should skip any at-home testing and contact a doctor or clinic immediately if you’re experiencing any of the following symptoms:
- Fever
- Bloody or black stools
- Yellowing of your skin or eyes (jaundice)
- Unintentional weight loss
- Chronic vomiting
- Severe abdominal or stomach pain
- Trouble swallowing food
OUTLOOK
People are nowadays more concerned about gut health, and this makes more private companies introduce at-home microbiome tests. Microbiome tests are fecal tests that rely on stool samples to determine the types and numbers of microbes in your GI tract.
Microbiome testing is the first step toward understanding your gut health and preventing any health condition associated with it.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from digestive problems, our expert providers at Specialty Care Clinics will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call us on (469) 545-9983 to book an appointment with our specialists.
