IS CARDIAC ARREST THE SAME AS HEART ATTACK?
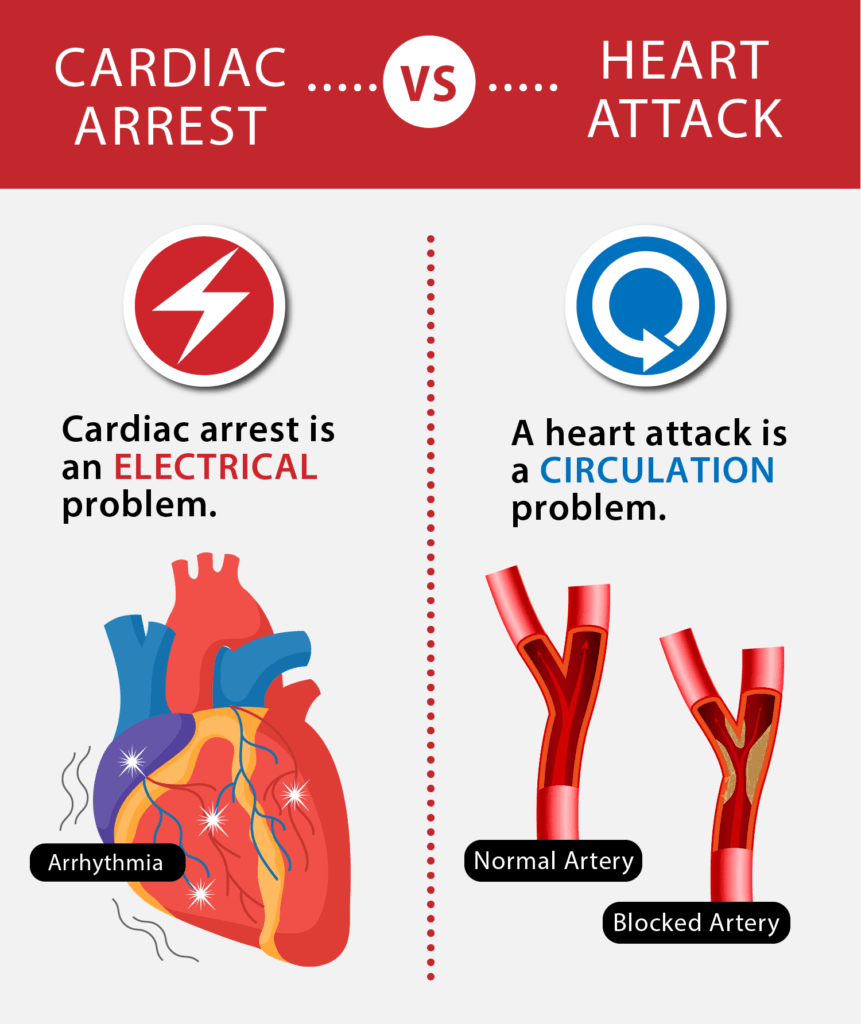
Our body is like a house that has various problems some are plumbing problems and others are electrical. Similar is the difference between heart attack and cardiac arrest. So to understand better, heart attacks are plumbing or blood flow problem; whereas, sudden cardiac arrest is an electrical or heart rhythm problem.
Sudden cardiac arrest is different from a heart attack, although people often interchange these terms. Both these conditions are life-threatening heart conditions. Understanding the differences between both could be lifesaving for many people.
HEART ATTACK
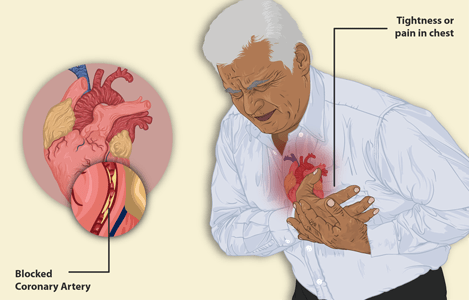
The coronary arteries are like pipes supplying blood to the heart. The arteries of the heart get clogged by fatty deposits called plaques. This condition is known as atherosclerosis causing it harder for the blood to flow around the plaque.
Due to clogging of the arteries, the blood is not able to flow freely making this problem life-threatening. If not enough oxygenated blood reaches the heart muscle, the muscle tissue begins to die causing a heart attack.
CAUSE OF HEART ATTACK
The main cause of heart attack is coronary heart disease (CHD), in which the major blood vessels supply the heart get clogged with deposits of cholesterol, known as plaques.
The plaques bursts or rupture, causing a blood clot to develop at the site of the rupture. This may block the supply of blood to the heart, triggering a heart attack.
Some of the health conditions, your lifestyle, age, and family history can increase your risk for heart disease and heart attack. Almost half of Americans are at risk for heart disease: high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, and smoking.
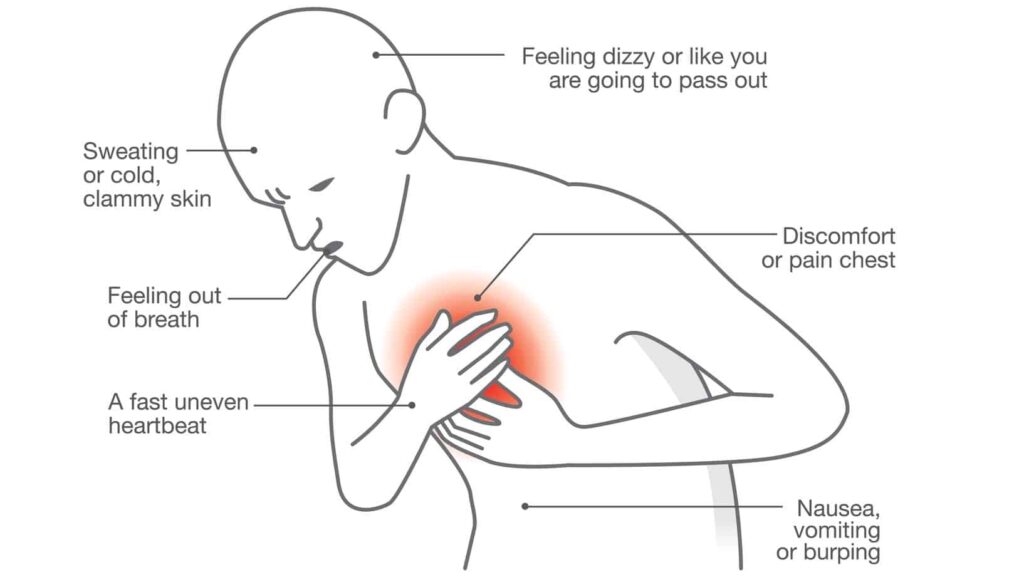
SYMPTOMS OF HEART ATTACK
People experiencing a heart attack often stay conscious and awake. During an acute heart attack, there’s usually one major blockage and some blood can flow around. Blood circulation is weak, but it still reaches vital organs and the brain keeping the person awake. People having a heart attack might experience below symptoms over hours, days or weeks:
- Chest pain or discomfort.
- Discomfort or pain in the jaw, neck, or back.
- Discomfort or pain in one or both arms or shoulders.
- Nausea or flu-like symptoms.
- Shortness of breath.
- Stomach pain.
- Sweating.
- Weakness.
Sometimes, people might not feel any of these symptoms due to medical conditions like diabetes. This is referred to as a silent heart attack.
Heart attack can become serious and life-threatening due to certain complications, including:
- Arrhythmias – These are abnormal heartbeats, leading to the heart beating faster, then stopping beating causing cardiac arrest.
- Cardiogenic shock – The heart muscles are severely damaged and can no longer contract properly. This would disrupt the supply of blood to maintain many body functions.
- Heart rupture – The heart’s muscles, walls, or valves rupture or split apart.
LIFESTYLE CHANGES FOR HEART ATTACK
The vast majority of heart attacks are caused by known risk factors, many of which can be reduced or controlled. Adopting lifestyle changes can lower your risk factors and lessen the chance of having another heart attack, as long as you are setting SMART goals:
- Specific
- Measurable
- Attainable
- Realistic
- Time-oriented
Lifestyle changes include diet, exercise, and quitting smoking. The diet should be low in cholesterol, saturated fat, and salt, and is full of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Cardiovascular exercise strengthens your heart, helps maintain healthy body weight, lowers your blood pressure and cholesterol levels, relieves stress, and enhances your mood.
CARDIAC ARREST
The heart has a built-in electrical conduction system keeping it beating at a steady pace. Some of the underlying medical conditions, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or previous heart attacks, result in problems with our electrical system. The malfunction leads to a dangerously fast and erratic heart rhythm or arrhythmia. The heart might stop beating and it can no longer pump blood to the brain and other organs.
Cardiac arrest usually affects aged people. But, it can also affect young people with genetic heart problems. This is a serious condition causing the heart to cease beating.
 CAUSES OF CARDIAC ARREST
CAUSES OF CARDIAC ARREST
Cardiac arrest is a life-threatening condition causing abnormal heart rhythm leading to ventricular fibrillation (VF). This is caused when the electrical activity of the heart becomes so chaotic causing the heart to stop, stop pumping. Other causes of cardiac arrest include:
Heart attack caused by coronary heart disease.
- Cardiomyopathy.
- Congenital heart disease.
- Heart valve disease.
- Acute myocarditis due to inflammation of the heart muscle.
The survival rate is bleak (almost 10%) if sudden cardiac arrest occurs outside the hospital. But, that rate increases to 90% when the person receives below treatment within minutes of collapsing:
- CPR, to circulate blood and oxygen.
- Shock therapy to reset the heart’s electrical system.
SYMPTOMS OF CARDIAC ARREST
People suffering from sudden cardiac arrest lose consciousness within minutes due to a lack of blood flow to the brain. Usually, there is a little-to-no warning. More than half of people suffering from sudden cardiac arrest usually have no symptoms. Others may have:
- Blue discoloration of the face.
- Breathing difficulty.
- Chest pains.
- Dizziness as the heart quivers.
- Overall malaise or unwell feelings.
LIFESTYLE CHANGES AFTER CARDIAC ARREST
A sudden cardiac arrest can be reversed if treated within the first few minutes. Lifestyle changes help in avoiding any further occurrence, that include:
- Diet – Following a healthier diet and certain dietary restrictions, such as sodium and fatty foods, is necessary.
- Medical devices – Ensuring you and your family are aware of functions of implanted defibrillator (ICD) after the event.
- Medications – Chest pains.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN CARDIAC ARREST AND HEART ATTACK
People usually use cardiac arrest and heart attack interchangeably, but both are different from each other. It is important to know the difference between the both as these can be life-threatening. A heart attack is caused due to interrupted blood flow to the heart, usually by a blood clot, while a sudden cardiac arrest is an electrical malfunction in the heart that causes it to stop beating entirely.
Similar to the saying “time is tissue”, the longer you wait to get help, the more damage can occur to the heart tissue. If you or your loved any of the above symptoms, knowing the difference can help you make lifesaving decisions.
In severe cases like below:
- Sudden loss of consciousness: Call 911, begin CRP immediately if possible and look for an automated external defibrillator (AED).
- Conscious with symptoms: Call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room. Also, if you have previously had a heart attack or have any heart disease, you’re at higher risk for sudden cardiac arrest. The risk of SCA after a heart attack is greatest in the first three months that gradually decreases. Follow the preventive steps suggested by your doctor strictly.
OUTLOOK
Heart attack is different from cardiac arrest, as one is an electric problem and other is a blockage problem. Finally, there are many different causes of a cardiac arrest; whereas the main cause of a heart attack is coronary heart disease. Heart attack can lead to cardiac arrest. It is important to know the difference between both.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from heart problems, our expert providers at Specialty Care Clinics will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call us on (469) 545-9983 to book an appointment with our specialists.
