IS SLEEP APNEA IMPACTING YOUR HEART CONDITION?
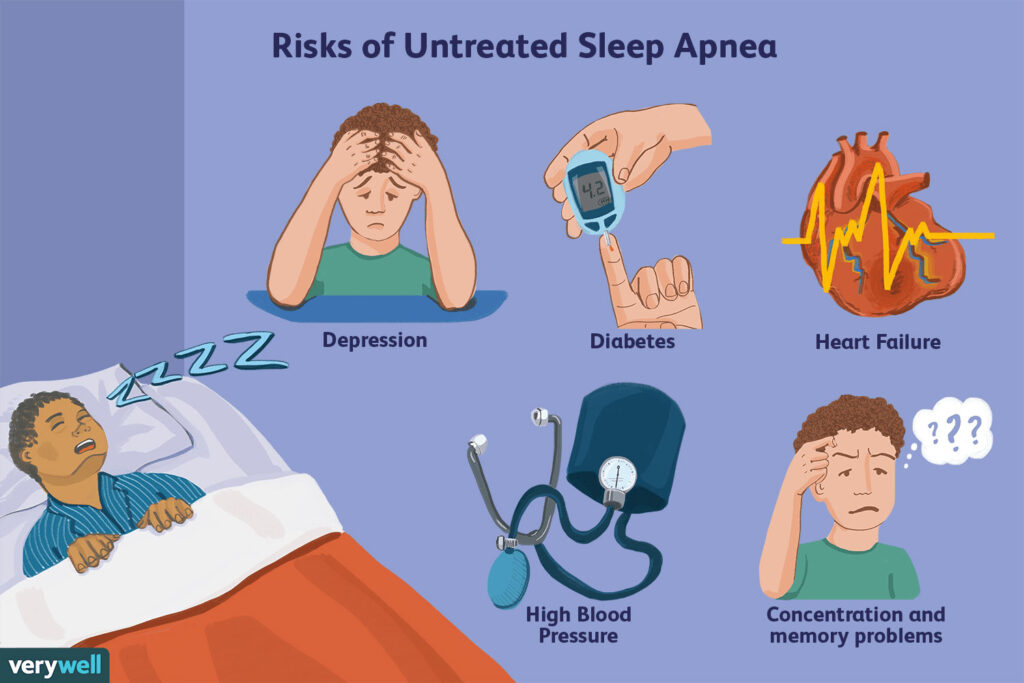
Sleep plays a vital role in almost all aspects of physical health as it provides time for the body to restore and recharge. Insufficient or fragmented sleep caused by sleep apnea can contribute to problems with the cardiovascular system including blood pressure along with a high risk of heart disease, heart attacks, diabetes, and stroke.
Quality of sleep decreases the effort of your heart, as blood pressure and heart rate go down at night. If you are sleep-deprived your heart rate is usually elevated instead of fluctuating normally. Lack of sleep may also increase insulin resistance, which is a risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Recurrent interruptions in-breath deprive the lungs of oxygen and cause significant stress on the body. Sleep apnea leads to a range of serious health complications, including coronary heart disease, heart failure, stroke, and an irregular heartbeat. If left untreated sleep apnea may result in breathing stopping repeatedly during sleep, causing loud snoring and daytime tiredness, even with a full night’s sleep. Sleep apnea most often affects older men who are overweight.
DOES SLEEP APNEA LEAD TO HEART PROBLEMS?
Sleeping problems like sleep apnea leads to sleep deprivation and fragmented sleep causing negative effects on heart health. Sleep is an essential time for the body to build up its strength. The heart rate slows, blood pressure drops, and breathing stabilizes during the non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep stages. During the changes in the NREM stage, the stress on the heart is reduced, allowing it to recover from the strain that occurs during waking hours.
During insufficient night sleep, your body doesn’t spend enough time in the deep stages of NREM sleep that benefit the heart. This is similar to the problems affecting people whose sleep is frequently interrupted. Chronic sleep deprivation is linked to numerous heart problems including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, heart attack, obesity, diabetes, and stroke.
Biofeedback is beneficial to conditions initiated or worsened by stress that makes internal processes overactive. Biofeedback therapy is the use of instrumentation to mirror psycho-physiologic processes, which an individual is not normally aware of but may be able to bring under voluntary control.
In sleep apnea, your airway gets blocked repeatedly during sleep causing you to stop breathing for short amounts of time. This is associated with atrial fibrillation, which is a dangerous heart rhythm that, if untreated, can lead to a stroke. Sleep apnea is commonly caused in people with excessive weight, large neck, and structural abnormalities reducing the diameter of the upper airway, such as nasal obstruction, a low-hanging soft palate, enlarged tonsils, or a small jaw with an overbite.
Sleep apnea is categorized as obstructive and central:
- Obstructive sleep apnea – This is the more common includes a airflow occurrence as repetitive episodes of complete or partial upper airway blockage during sleep. The diaphragm and chest muscles work harder due to the increase in pressure to open the airway during an apneic episode and the breathing resumes with a loud gasp or body jerk. This would interfere with sound sleep, reduce the flow of oxygen to vital organs, and cause heart rhythm irregularities.
- Central sleep apnea – The airway is not blocked but the brain fails to signal the muscles to breathe due to instability in the respiratory control center. This causes adverse effects on the function of the central nervous system.
Effects of Sleep Apnea include:
- Activating the Sympathetic Nervous System: The level of oxygen in the blood decreases when a person with sleep apnea stops breathing. When the body becomes deprived of oxygen the chemoreceptors detect these changes and activate the sympathetic nervous system to activate. The sympathetic nervous system triggers the body to gasp for air, which sometimes wakes a person out of sleep.
- Changes in Pressure within the Chest: When a person with sleep apnea attempts to breathe, they inhale against a narrowed or closed upper airway. This would result in forced inhalations causing substantial changes in pressure within the chest cavity. These repetitive changes, over time, puts intrathoracic pressure leading to heart damage including problems with blood flow to the heart, and even heart failure.
- Oxidative Stress: a person with sleep apnea once again inhales successfully after each pause in breath providing much-needed oxygen back into the lungs, blood, and body tissues. The frequent changes in oxygen levels can cause significant stress on the body, called oxidative stress. This can promote systemic inflammation, as well as neurochemical and physiological reactions that increase the risk of heart disease
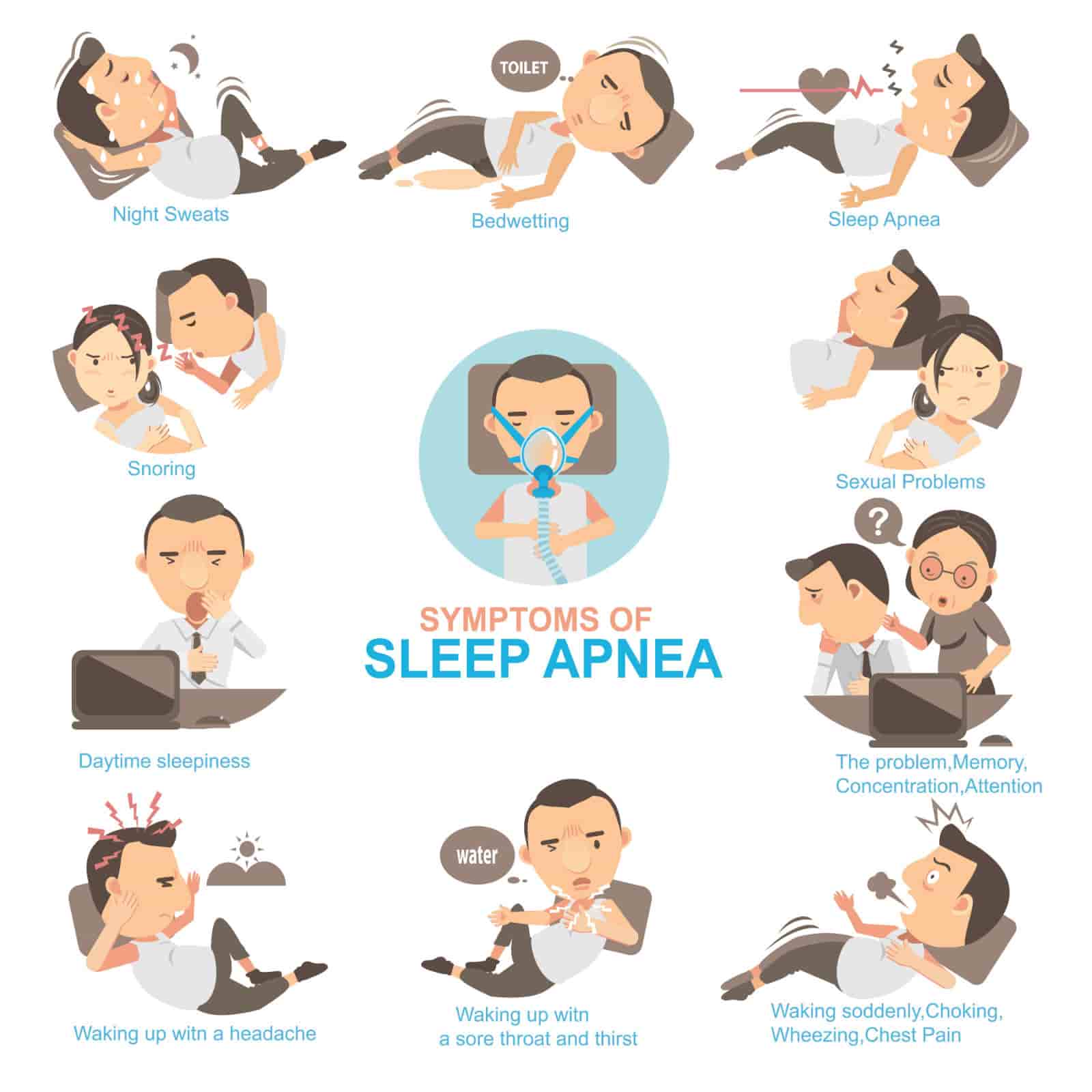
HOW TO IDENTIFY SLEEP APNEA?
The first signs of sleep apnea are recognized not by the patient, but by the bed partner. Sometimes, those who are affected have no sleep complaints. The most common signs and symptoms include:
- Snoring.
- Daytime sleepiness or fatigue.
- Restlessness during sleep repeated nighttime awakenings.
- Sudden awakenings with a sensation of gasping or choking.
- Dry mouth or sore throat upon awakening.
- Cognitive impairment, like trouble concentrating, forgetfulness, or irritability.
- Mood disturbances (depression or anxiety).
- Night sweats.
- Frequent nighttime urination.
- Sexual dysfunction.
- Headaches.
HOW TO DIAGNOSE SLEEP APNEA?
The doctor would focus on sleep evaluation or may order an overnight sleep study to objectively evaluate for sleep apnea. This include various tests, such as:
- Polysomnogram (PSG) – This is performed in a sleep laboratory under the direct supervision of a trained technologist. The test monitors variety of body functions, such as the electrical activity of the brain, eye movements, muscle activity, heart rate, breathing patterns, air flow, and blood oxygen levels are recorded at night during sleep. The study provides details like the number of times breathing is impaired during sleep and the severity of the sleep apnea.
- Home Sleep Test (HST) – This is a modified type of sleep study that can be done in the comfort of home. The test monitors fewer body functions than PSG, including airflow, breathing effort, blood oxygen levels, and snoring to confirm a diagnosis of moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea.
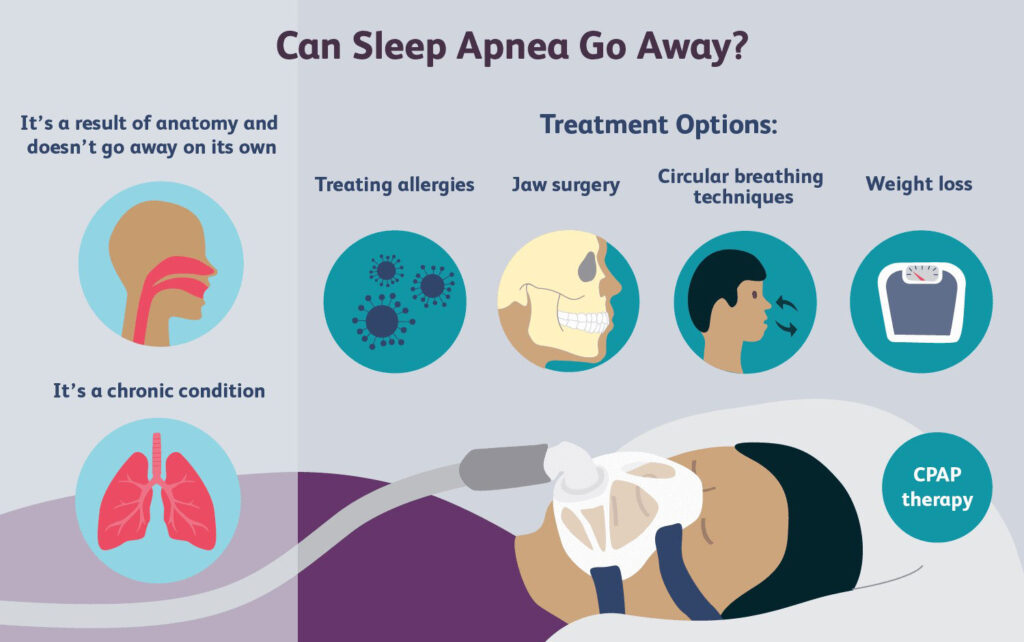
HOW TO TREAT SLEEP APNEA?
- Conservative treatments – This is beneficial in mild cases of obstructive sleep apnea. The treatment options include:
Losing Weight
Avoiding the use of alcohol and certain sleeping pills.
Using a wedge pillow or other devices that help you sleep.
Using nasal sprays or breathing strips. - Mechanical Therapy – Positive Airway Pressure (PAP) therapy is beneficial for most people diagnosed with obstructive sleep apnea. These include:
CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) – The machine is set at one single pressure.
Bi-Level PAP – This uses one pressure during inhalation (breathing in), and a lower pressure during exhalation (breathing out).
Auto CPAP or Auto Bi-Level PAP – This uses a range of pressures that self-regulates during use depending on pressure requirements detected by the machine.
Adaptive Servo-Ventilation (ASV) – It is non-invasive ventilation used for patients with central sleep apnea. - Mandibular advancement devices – This is beneficial for mild to moderate obstructive sleep apnea.
- Hypoglossal nerve stimulator – This involves a stimulator to activate the hypoglossal nerve resulting in opening the airway during sleep.
- Surgery – Surgical procedure such as Somnoplasty, Tonsillectomy, Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP), Mandibular/maxillary advancement surgery, and Nasal surgery
OUTLOOK
Insufficient sleep due to sleep apnea affects your heart health along with your mental health. If you struggle with sleep apnea, insomnia, or any other sleep issues, you should contact a doctor to explore your treatment options.
People Also Read:
If you or anyone you know is suffering from heart disease and sleep disorders, our expert providers at Specialty Care Clinics will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call us on (469) 545-9983 to book an appointment with our specialists.
