COMMON CAUSE FOR BACK PAIN: HERNIATED DISK
A herniated disk is a typical reason for back pain. People usually suffer from herniated disks when the delicate focal point of a spinal circle gets out of its packaging. This can influence close nerves, prompting pain, numbness, or weakness in the limbs.
Certain individuals experience no pain from a herniated disk, especially on the off chance that the disk pushes on no nerves. Individuals additionally allude to the condition as a slipped disk or disk prolapse. Even though it can once in a while be very painful, a herniated disk has many promising treatment choices. Symptoms regularly decrease or resolve following various weeks, however, an individual might require a medical procedure if these endure or deteriorate.
Many people might not have any symptoms from a herniated disk. For individuals who truly do have symptoms, the symptoms will more often than not work after some time. Surgery is typically not important to treat the issue.
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF HERNIATED DISK?
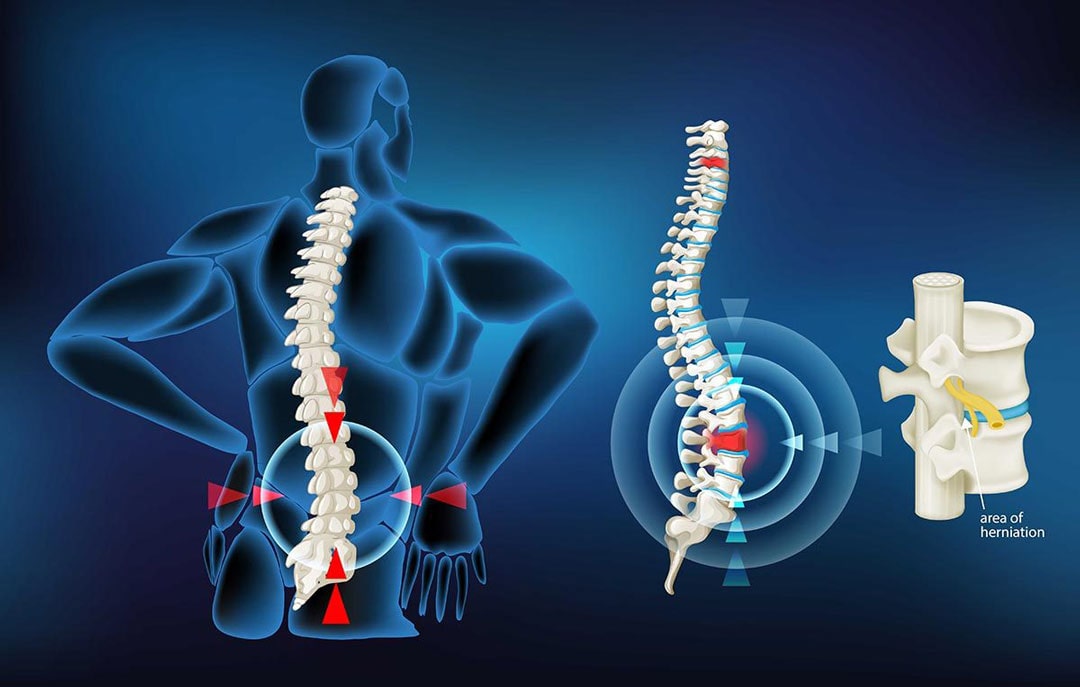
A herniated disk is a physical issue of the spine (spine). You have a progression of bones (vertebrae) in your spine, extending from the foundation of your skull to your tailbone. Between your vertebrae are round pads referred to as disks. The disks go about as supports between your bones, permitting you to curve and move effortlessly. At the point when one of these disks tears or releases, it’s known as a herniated disk.
Disks contain delicate, gel-like focuses and a firmer external layer. With time, the external layer debilitates and can break. A herniated disk happens when the internal “jelly” substance pushes through the break. The released material might push on adjacent spinal nerves.
A few factors might lead to the disk rupture, including:
- Aging.
- Being over-weight.
- Tiresome movements.
- Sudden strain from improper lifting or twisting.
If you are between the ages of 30 to 50 you are probably going to get a herniated disk. The issue influences men two times as frequently as ladies. Some of the other risk factors may include:
- Sitting for long periods in the same position.
- Being overweight.
- Lifting heavy things.
- Repetitive twisting or bending motions.
- Smoking.
Consistently, up to 2% of individuals get a herniated disk. Herniated disks are the main source of neck and arm, as well as back and leg pain (sciatica). They can happen anyplace along the spine, however herniated disks most frequently happen in the lower back or the neck. It’s intriguing for a herniated disk to be in the mid-back.
HOW CAN YOU IDENTIFY HERNIATED DISK?
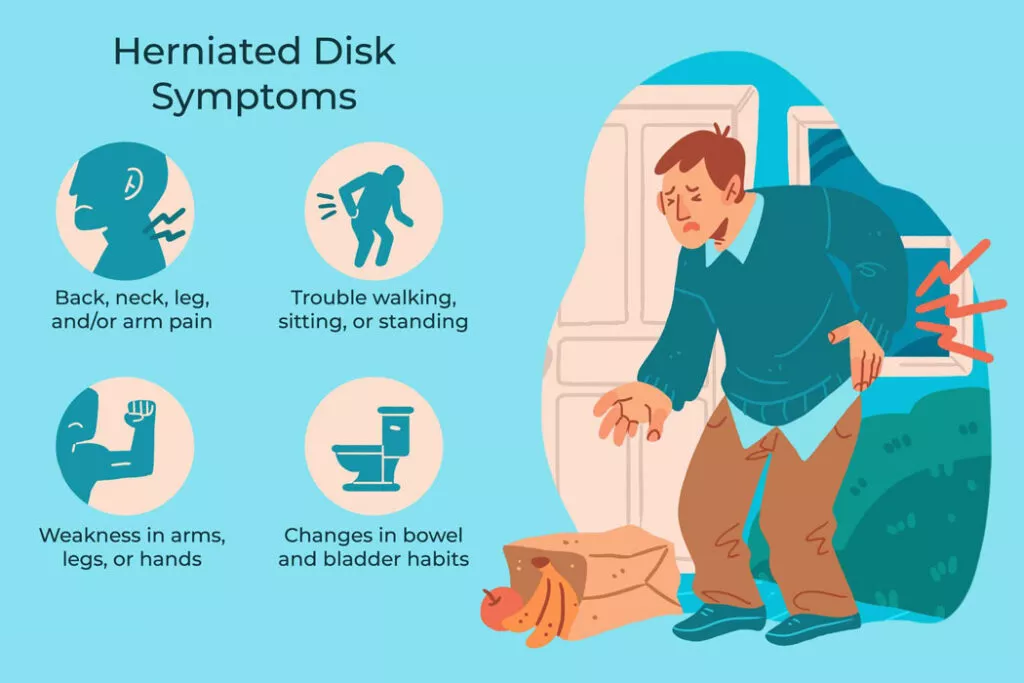
Most herniated disks happen in the lower back, yet they can likewise happen in the neck. Signs and symptoms rely upon where the disk is arranged and whether the disk is pushing on a nerve. Herniated disks normally influence one side of the body.
For a herniated disk in your neck, you’ll feel the most pain in your shoulder and arm. This pain could shoot into your arm or leg when you hack, sniffle or move into specific positions. Pain is much of the time portrayed as sharp or copying.
- Arm or leg pain: If your herniated disk is in your lower back, other than a pain in your lower back, you’ll regularly feel pain in your hindquarters, thigh, and calf. You could have pain in the piece of the foot also.
- Numbness or tingling: People who have a herniated disk frequently have radiating numbness or tingling in the body part served by the impacted nerves.
- Weakness: Muscles served by the impacted nerves will quite often debilitate. This can make you stagger, or influence your capacity to lift or hold things.
You can have a herniated disk without symptoms. You might not know you have it unless it shows up on a spinal image. A seriously herniated disk in any locale of the back might create issues with bowel or bladder control. Assuming an individual has back pain and abrupt changes to their bladder or bowel control, this is normally a sign that crisis clinical assistance is required.
HOW TO TREAT HERNIATED DISK?
Moderate treatment — predominantly altering exercises to stay away from development that causes pain and taking pain prescription — alleviates symptoms in the vast majority inside a couple of days or weeks.
Medications
- Nonprescription pain medications: Your doctor may prescribe pain medication without prescription if your pain is mild to moderate.
- Neuropathic drugs: These drugs affect nerve impulses to decrease pain.
- Muscle relaxers: You might be prescribed these if you have muscle spasms. Sedation and dizziness are common side effects.
- Opioids: Because of the symptoms of narcotics and the potential for dependence, many specialists wonder whether or not to endorse them for disk herniation. If different prescriptions don’t assuage your pain, your primary care physician should seriously mull over the transient utilization of narcotics.
- Cortisone injections: If your pain doesn’t improve with oral meds, your primary care physician could suggest a corticosteroid that can be infused into the region around the spinal nerves. Spinal imaging can assist with directing the needle.
- Therapy: Your doctor recommends physical treatment to assist with your pain. Actual advisors can show you positions and activities intended to limit the pain of a herniated disk.
- Surgery: People with herniated disks require a medical procedure. Your primary care physician could recommend a medical procedure on the off chance that moderate therapies neglect to work on your symptoms following a month and a half, particularly assuming you keep on having:
- Poorly controlled pain
- Numbness or weakness
- Difficulty standing or walking
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
HOW CAN HERNIATED DISK BE PREVENTED?
Some of the following things that help prevent a herniated disk include:
- Exercise: Strengthening the chest muscles soothes and supports the spine.
- Maintain good posture: This reduces tension on your spine and disks. Keep your back straight and adjusted, especially while sitting for significant stretches. Lift weighty articles appropriately, making your legs — not your back — do the majority of the work.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight comes down on the spine and discs, making them more powerless to herniation.
- Quit smoking
OUTLOOK
Herniated disks get better all alone over the long haul or with nonsurgical treatment for 9 out of 10 people. If different medicines don’t ease your symptoms, your medical services provider might suggest some medical procedure. Remaining active along with follow-up with your healthcare provider is the best way to treat herniated disks. Gentle movement combined with an over-the-counter pain reliever assists a great many people with feeling improved in half a month.
PEOPLE ALSO READ:
- Working and Treatment of Opioid Dependent Patients
- Treatment of Chronic Pain
If you or anyone you know is suffering from back pain, our expert providers at Specialty Care Clinics will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call us on 469-545-9983 to book an appointment with our specialists.