UNDER-DIAGNOSED CAUSE OF JOINT PAIN: ANEMIA
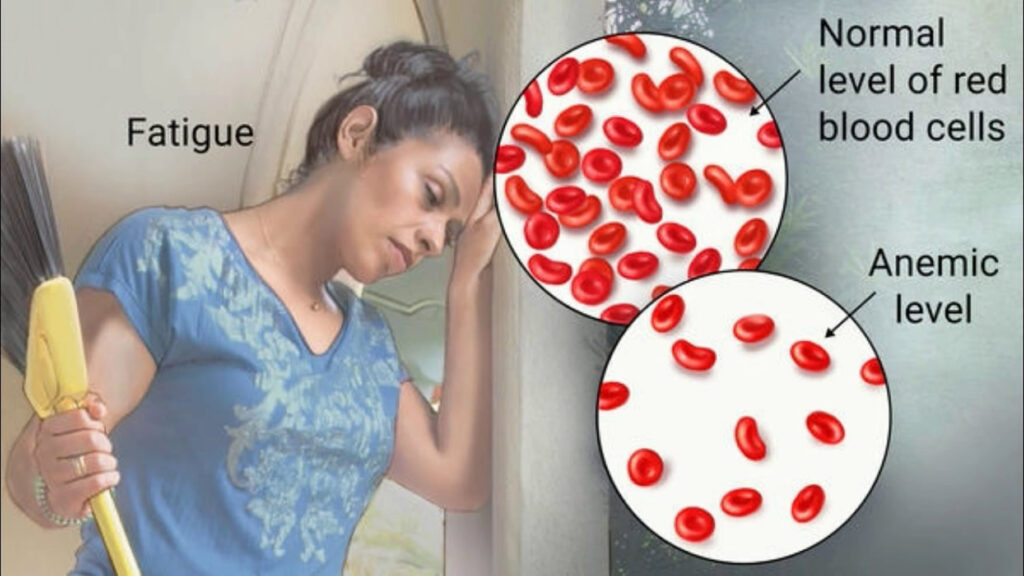
Every part of your body needs a sufficient supply of oxygen to function effectively. Anemia is a most common blood disorder that leads to pain in various parts of the body. Anemia occurs when the body lacks an adequate amount of red blood cells circulating in the body. The production of healthy red blood cells decreases in the body or the breakdown of the red blood cells increases in the body.
The blood cells contain iron and hemoglobin, which is a protein that helps carry oxygen through the blood to your organs all through the body. A person with anemia is known as “anemic”. Anemic people feel more tired or cold than usual, or the skin seems too pale as organs do not receive the oxygen they need to do their jobs.
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT KINDS OF ANEMIA?
There are many types of anemia, each with its own goal. Anemia can be an impermanent or long haul and can go from gentle to serious. As a rule, anemia has more than one reason. Each of the several types of anemia is caused by a number of red blood cells’ circulation levels in the body. Red blood cells level is low due to multiple reasons like:
- Body cannot make enough hemoglobin
- Body makes hemoglobin but it does not work properly
- Body cannot make enough red blood cells
- Red blood cells break too quickly
Some type of anemia that occurs due to decreased or impaired RBCs includes:
- Sickle Cell Anemia – The shape of RBCs is shaped like crescents. The breakdown is quicker than healthy RBCs or becomes lodged in small blood vessels. The blockage reduces the oxygen levels which causes pain further down in the bloodstream.
- Iron Deficiency Anemia – This is caused due to lack of red blood cells produced which causes a lack of iron in the body. This may result due to a diet low in iron, menstruation, frequent blood donation, certain digestive conditions (such as Crohn’s disease), and medications that irritate the gut lining (such as ibuprofen)
- Vitamin Deficiency Anemia – The 2 essential vitamins for the production of RBCs are Vitamin B-12 and folate. A lack of these vitamins may result in a low count of the RBC in the body.
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF ANEMIA?
Anemia can be because of a condition present upon entering the world (inherent) or a condition you create (acquired). Red blood cells are delivered in your bone marrow and have a typical life expectancy of 100 to 120 days. By and large, your bone marrow produces 2 million red blood cells each second while roughly a similar number are eliminated from the flow. Around 1% of your red blood cells are taken out from flow and supplanted every day.
Any interaction that adversely affects this harmony between red blood cell creation and annihilation can cause anemia. Reasons for anemia are by and large separated into those that decline red blood cell creation and those that increment red blood cell obliteration or misfortune.
Anemia happens when your blood needs more red blood cells.
- Decreased production of red blood cells – This causes fewer oxygen-carrying cells in the body
- Loss of blood – Hemorrhage- Shortage of iron in the blood leads to this condition, and low iron levels frequently occur as a result of blood loss. This can be acute or chronic.
- Break down of Red Blood Cells – Haemolysis – This causes the immune system to weaken,
- Impaired Red blood cells – The center of the bone contains soft and spongy tissue termed Bone marrow, and it plays an essential role in creating RBCs. Stem cells are produced in the marrow, which develops into RBCs, white blood cells, and platelets.
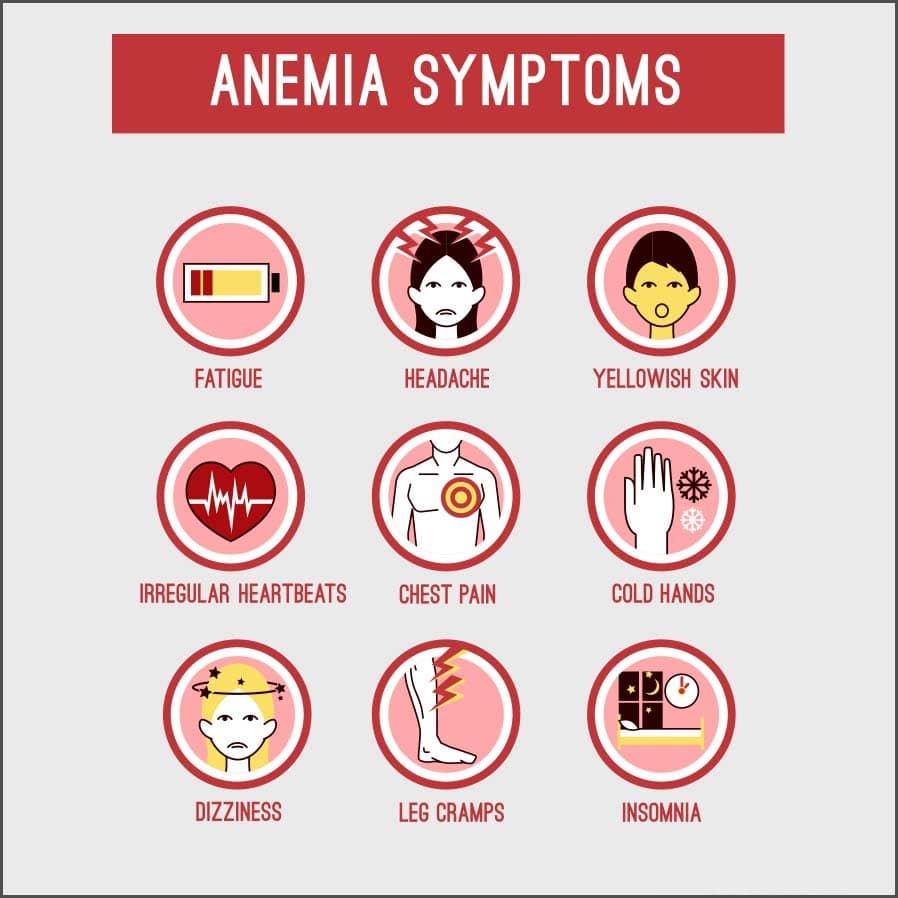
WHAT ARE THE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF ANEMIA?
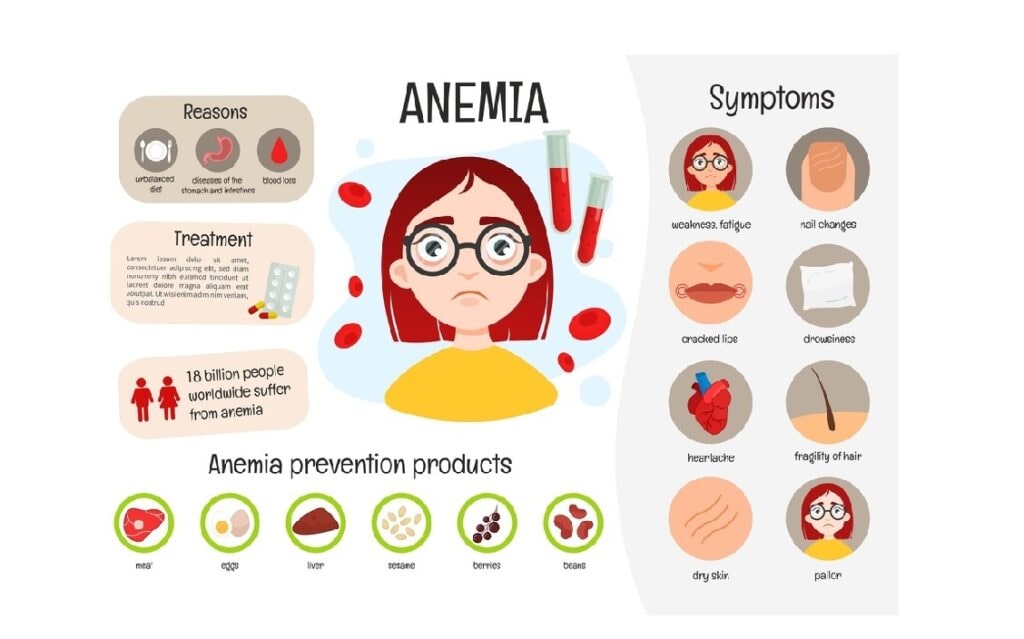
The symptoms include headache, dizziness, sore tongue, pale skin, dry skin, bruised skin, restless leg syndrome, and increased heartbeat.
Common Signs and symptoms might include:
- Pain and cramps in legs
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Pale or yellowish skin
- Irregular heartbeats
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Chest pain
- Cold hands and feet
- Headaches
- Ringing in the ears
- Brittle or spoon-shaped nails
- Heart and lung complications
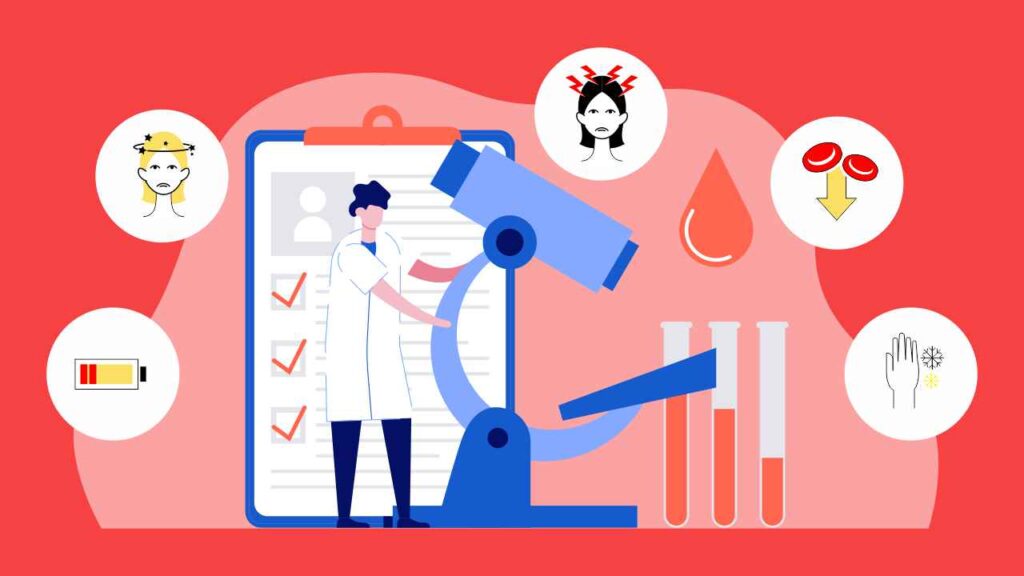
HOW DO DOCTORS DIAGNOSE ANEMIA?
Your primary care physician supplier can perform blood tests to let know if you have anemia. The fundamental test is a finished blood count test, additionally called the CBC. The CBC can let you know the number of red blood cells you have, how huge they and what shape they are. Blood tests can likewise let you know if you are low in nutrients B12 and B9 and how much iron your body has put away.
The doctor would run various tests such as:
Blood and urine tests to indicate hemolytic anemia.
A colonoscopy or fecal occult blood tests of your stool may be suggested to find gastrointestinal bleeding.
Bone marrow biopsy (removal of bone marrow tissue).
HOW TO TREAT ANEMIA?
Doctors prescribe different treatments for different types of anemia. Some are listed below.
- Iron-deficiency anemia: Incorporating Iron supplements and dietary changes help in treating this type of anemia. The doctor will identify and address the cause of excessive bleeding.
- Vitamin deficiency anemia: Doctors prescribe treatments that include dietary supplements and vitamin B-12 shots.
- Thalassemia: Folic acid supplements, and iron chelation help people in treating this type of anemia. Blood transfusions and bone marrow transplants are also used in severe cases.
- Aplastic anemia: blood transfusions or bone marrow transplants are prescribed by the doctors as part of the treatment regime.
- Sickle cell anemia: Treatment includes oxygen therapy, pain relief medication, and intravenous fluids. Doctors may also prescribe antibiotics, folic acid supplements, blood transfusions, and a cancer drug called hydroxyurea.
- Hemolytic anemia: The treatment regime includes immunosuppressant drugs, treatments for infections, and plasmapheresis, which filters the blood and helps patients to recover faster.
- It is more important to prevent anemia than to cure it. Hence it is important to fortify the diet with iron-rich food or iron supplements. The diet can contain iron-fortified cereals and bread, leafy green vegetables, such as kale, spinach, and watercress, pulses and beans, brown rice, white or red meats, nuts and seeds, fish, tofu, eggs, dried fruits, including apricots, raisins, and prunes, etc.
- In case of any symptoms please visit the doctor for quick treatment.
- Pregnant ladies are at high risk of anemia hence their diet should contain a high amount of iron in form of iron supplements as well as foods rich in iron.
OUTLOOK
Anemia happens when a low number of RBCs are coursing in the body. This diminishes the individual’s oxygen levels and can prompt side effects, for example, weariness, fair skin, chest torment, and windedness. The most widely recognized type is iron-inadequacy anemia. It is at times created because of an eating routine ailing in supplements, Crohn’s sickness, or the utilization of specific prescriptions.
A specialist can utilize a CBC blood test to assist with recognizing anemia. Treatment fluctuates, contingent upon the kind, however, it might incorporate iron or nutrient enhancements, meds, blood transfusions, and bone marrow transplants.
People Also Read –
- Hyperlipidemia – Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors and Treatment
- Effect of Diabetes on Heart Health
If you or anyone you know is suffering from joint pain our expert providers at Specialty Care Clinics will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call 469-545-9983 to book a telehealth appointment for an at-home check-up.