WHAT IS THROMBOCYTOPENIA?
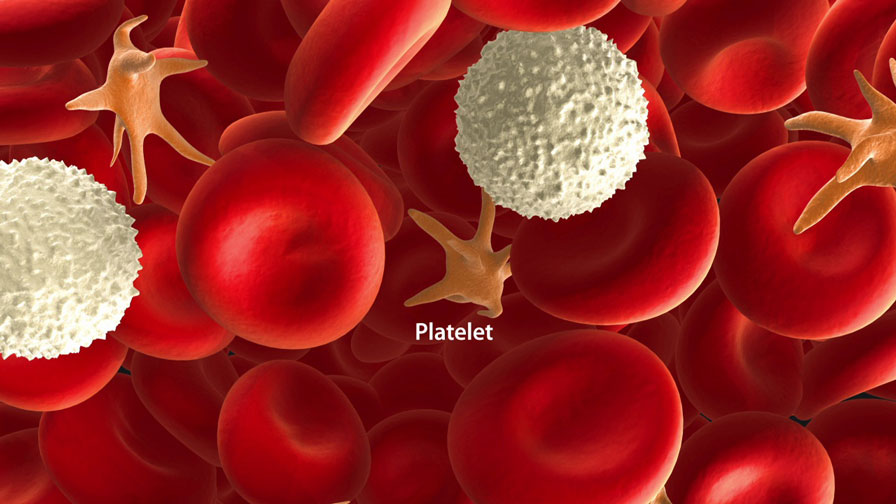
Thrombocytopenia is a condition where you have a low blood platelet count. Platelets (thrombocytes) are colorless blood cells that help your blood clot. Platelets prevent bleeding by clumping and forming plugs into blood vessel injuries.
Thrombocytopenia may happen as a result of a bone marrow disorder like leukemia or an immune system problem. Or it could be a side effect of taking certain medications. This affects not only children but also adults.
Thrombocytopenia could be mild and cause few signs or symptoms. In rare cases, the number of platelets could be so low that dangerous internal bleeding happens. Treatment options are provided.
SYMPTOMS
Thrombocytopenia signs and symptoms might include:
- Easy or excessive bruising (purpura)
- Superficial bleeding into the skin that appears as a rash of pinpoint-sized reddish-purple spots (petechiae), generally on the lower legs
- Prolonged bleeding from cuts
- Bleeding from your gums or nose
- Blood in urine or stools
- Unusually heavy menstrual flows
- Fatigue
- Enlarged spleen
WHEN SHOULD YOU SEE A DOCTOR?
Schedule an appointment with your doctor if you have signs of thrombocytopenia that worry you.
Bleeding that would not stop is a medical emergency. Seek immediate help for bleeding that cannot be controlled by the usual first-aid techniques, like applying pressure to the area
CAUSES
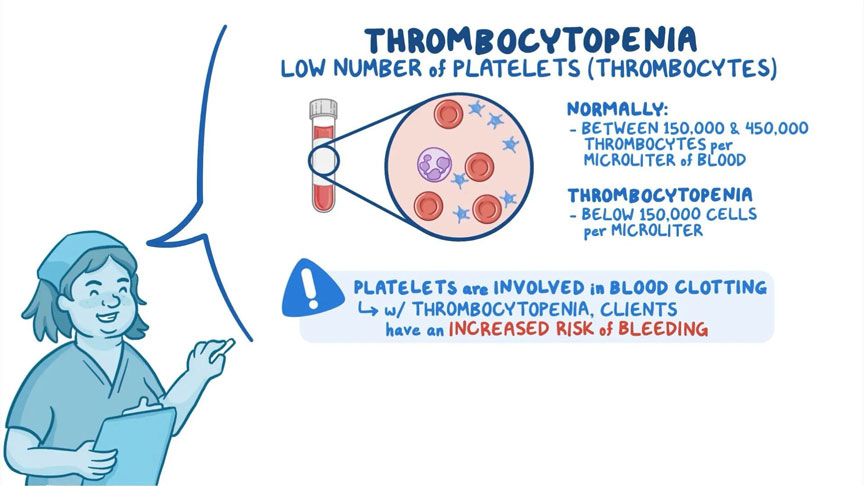
Thrombocytopenia means that you have fewer than 150,000 platelets per microliter of circulating blood. Because each platelet lives only about ten days, your body normally renews your platelet supply continually by producing new platelets in your bone marrow.
Thrombocytopenia rarely is inherited, or it could be caused by a number of medications or conditions. Whatever the cause, circulating platelets are lowered by one or more of the following processes: trapping of platelets in the spleen, decreased platelet production, or increased destruction of platelets.
TRAPPED PLATELETS
The spleen is a small organ about the size of your fist located just below your rib cage on the left side of your abdomen. Generally, your spleen works to fight infection and filter unwanted material from your blood. An enlarged spleen — which could be caused by a number of disorders — could harbor too many platelets, which decreases the number of platelets in circulation.
DECREASED PRODUCTION OF PLATELETS
Platelets are produced within your bone marrow. Factors that could decrease platelet production include:
- Leukemia and other cancers
- Some types of anemia
- Viral infections, like hepatitis C or HIV
- Chemotherapy drugs and radiation therapy
- Heavy alcohol consumption
INCREASED BREAKDOWN OF PLATELETS
Some conditions could cause your body to use up or destroy platelets faster than they are produced, leading to a shortage of platelets in your bloodstream. Examples of such conditions are:
- Pregnancy – Thrombocytopenia caused by pregnancy is generally mild and improves soon after childbirth.
- Immune thrombocytopenia – Autoimmune diseases, like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, cause this type. The body’s immune system by mistake attacks and destroys platelets. If the exact cause of this condition is not known, it is known as idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. This type more frequently affects children.
- Bacteria in the blood – Severe bacterial infections involving the blood (bacteremia) could destroy platelets.
- Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura – This is a rare condition that happens when small blood clots suddenly form throughout your body, using up large numbers of platelets.
- Hemolytic uremic syndrome – This rare disorder causes a sharp drop in platelets, destruction of red blood cells, and damage to kidney function.
- Medications – Certain medications could reduce the number of platelets in your blood. At times a drug confuses the immune system and causes it to destroy platelets. Examples involve heparin, quinine, sulfa-containing antibiotics, and anticonvulsants.
COMPLICATIONS
Dangerous internal bleeding could occur when your platelet count falls below 10,000 platelets per microliter. Though rare, severe thrombocytopenia could cause bleeding into the brain, which can be fatal.
DIAGNOSIS
The following could be used to determine whether you have thrombocytopenia:
- Blood test – A complete blood count determines the number of blood cells, including platelets, in a specimen of your blood.
- Physical examination, including a complete medical history – Your doctor will look for signs of bleeding underneath your skin and feel your abdomen to see if your spleen is enlarged. He or she will also ask you about illnesses you have had and the types of medications and supplements you have recently taken.
Your doctor may suggest other tests and procedures to determine the cause of your condition, depending on your signs and symptoms.
TREATMENT
Thrombocytopenia could last for days or years. People with mild thrombocytopenia may not need treatment. For people who do require treatment for thrombocytopenia, treatment depends on its cause and how severe it is.
If your thrombocytopenia is caused by an underlying condition or a medication, addressing that cause may cure it. For example, if you have heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, your doctor could prescribe a different blood-thinning drug.
Other treatments may involve:
- Blood or platelet transfusions – If your platelet level becomes too low, your doctor could replace lost blood with transfusions of packed red blood cells or platelets.
- Medications – If your condition is associated with an immune system problem, your doctor might prescribe drugs to boost your platelet count. The first-choice drug may be a corticosteroid. If that does not work, stronger medications could be used to suppress your immune system.
- Surgery – If other treatments do not help, your doctor might recommend surgery to remove your spleen (splenectomy).
- Plasma exchange – Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura could result in a medical emergency requiring plasma exchange.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from thrombocytopenia, our expert providers at Specialty Care Clinics will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call 469-545-9983 to book an appointment for an at-home check-up