DIABETES
Diabetes is an umbrella of diseases referring to problems involving insulin hormones. Diabetes mellitus or diabetes, is a metabolic disorder that results in high blood sugar. The hormone insulin transports sugar from the blood into the cells for storage or used for energy sources.
With diabetes, the body either does not make adequate insulin for glucose utilization or is unable to effectively use the insulin produced by the body. Diabetes if not treated on time would damage the nerves, eyes, kidneys, and other organs.
Diabetes affects around 1 in 4 people above the age of 65. About 90-95 % of cases diagnosed in adults are of type 2 diabetes.
There are different types of diabetes are:
- Type 1 Diabetes – This is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks as well as destroys cells in the pancreas that produce insulin hormone. About 10% of people are affected with this type of diabetes which is diagnosed mainly in children and young adults, though it might appear at any age.
- Type 2 Diabetes – This is the most common type of diabetes affecting middle-aged and older people due to lifestyle mismanagement. It would occur when the body becomes resistant to insulin due to which sugar builds up in the blood.
- Gestational Diabetes – This develops in some women during the pregnancy. Mostly this type of diabetes goes away after the birth of a baby. Insulin-blocking hormones are produced by the placenta which cause this type of diabetes. However, if gestational diabetes is caused the chances of developing type 2 diabetes is great in later life.
- Pre-diabetes – This is caused when the blood sugar is higher than normal range, however it does not come in the range for a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes.
There is a rare condition known as diabetes insipidus that is not related to diabetes mellitus. However, this is a different condition in which the kidneys remove abnormally large amounts of fluid from the body that are dilute and odorless.
Less common types of diabetes include monogenic diabetes that is an inherited type of diabetes, and cystic fibrosis-related diabetes.
SYMPTOMS OF DIABETES
Rise in sugar level in blood cause symptoms like increased hunger or thirst, sudden weight loss, frequent urination, blurry vision, extreme fatigue, tiredness, sores or cuts that don’t heal easily, decreased sex drive or erectile dysfunction (ED) in men, poor muscle strength, urinary tract infections or yeast infections in women, and dry or itchy skin.
Mostly in gestational diabetes the symptoms do not occur and diabetes is detected during a routine blood sugar test or oral glucose tolerance test, which is usually done between the 24th to 28th weeks of gestation.
The higher the blood sugar as well as the longer you live with diabetes, the greater becomes your risk for complications that would include:
- Heart disease such as heart attack, and stroke
- Neuropathy
- Nephropathy
- Retinopathy and vision loss
- Hearing loss
- Damage to foot like infections and sores that don’t heal easily
- Skin conditions like bacterial and fungal infections
- Depression
- Dementia
Gestational diabetes can lead to problems such as premature birth, higher-than-normal weight at birth, increased risk for type 2 diabetes later in life, low blood sugar, jaundice and stillbirth.
Doctors would run tests like fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test to measure blood sugar after 8 hour fasting and A1C test provides aggregate of over the previous 3 months. Gestational diabetes is diagnosed during the 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy.

TREATMENT FOR DIABETES
Diabetes could not be cured however it can be managed with changes in lifestyle, medication and therapy. The treatment spectrum followed for diabetes management has rapidly advanced in recent years that would include new approvals, expanded indications, and technological innovations helping to shape new approaches to care.
Along with lifestyle changes initiation of drug therapy based on glycated hemoglobin (A1C) is recommended for more benefit.
ADVANCEMENT IN TREATMENT OF DIABETES
The researchers are working vigorously to pioneer new approaches to diabetes treatment. Some of the diabetes advancement with promising results are:
Insulin Pumps – Insulin is administered to everyone with type 1 and some people with type 2 diabetes. An insulin pump is a small computerized device, which mimics the characteristic of human pancreas and delivers insulin through a thin tube directly under the skin. The basal insulin levels are set in the device which are released at steady rate as well as extra dose (known as bolus) after mealtime. The device is attached to the body with the help of infusion set that includes thin plastic tubing and a needle or a small tapered tube known as cannula under the skin at the infusion site such as belly, buttocks or thighs or attached to a belt or bra, in a pocket, or on the armband.
The pumps helps in:
- Improving the A1c levels of sugar
- Manage early morning high blood sugar known as dawn phenomenon
- More accurate than shots leading to better management of blood sugar levels
- Fewer needle sticks
- Substitute the need for long acting insulin
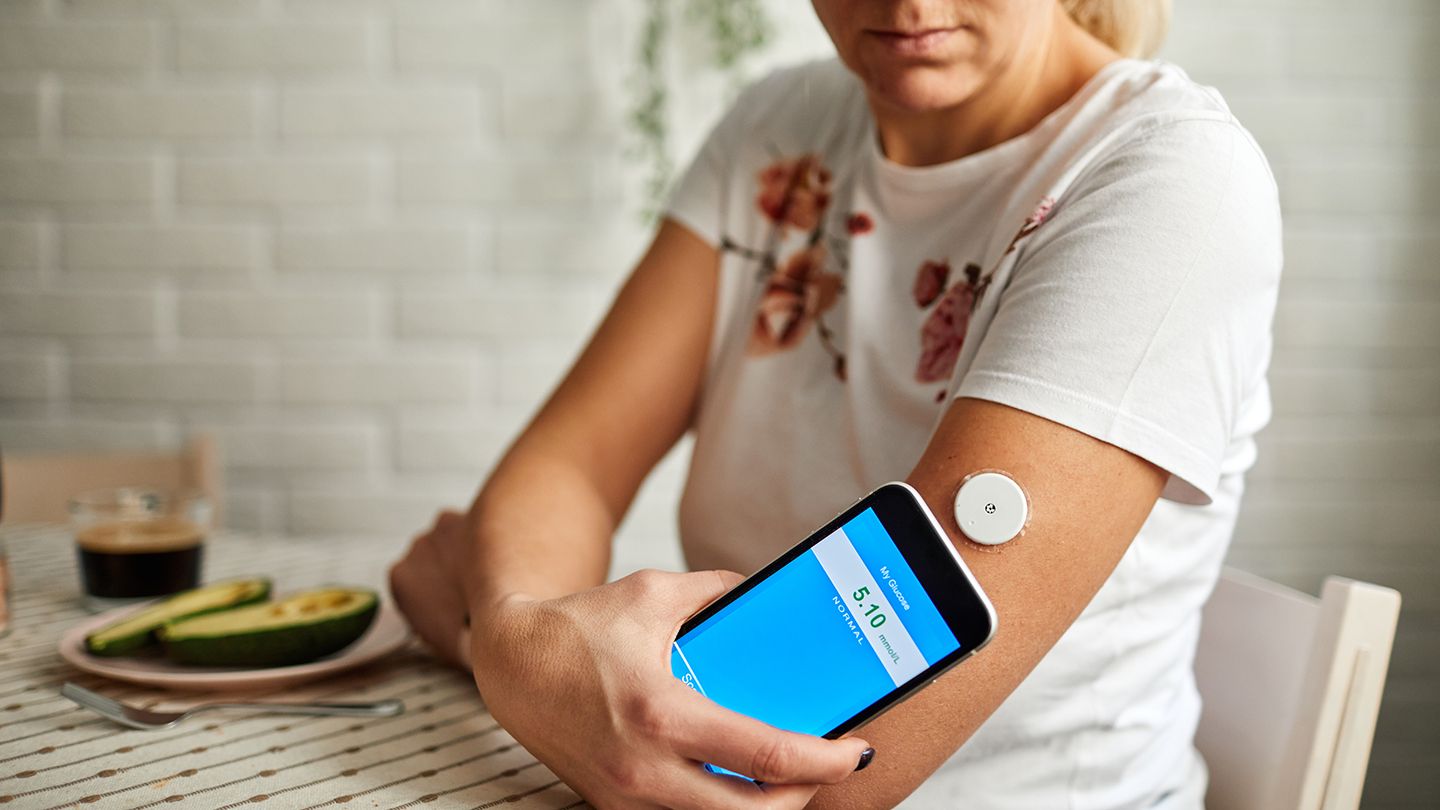
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) – This device contains a tiny sensor placed below the surface of the skin that measures the amount of glucose every few minutes in the fluid between cells and transmits the data to a device or the smartphone wirelessly. Unlike the traditional glucose monitoring system, CGM monitors the levels of blood glucose at set times throughout the day which could help you and your doctor to identify patterns and trends helpful in fine-tuning the treatment regime for type 2 diabetes. These devices might also alert in case your glucose level is too low or too high. The core benefit of using a CGM is that it can be worn for 5 or more days which would mean one poke to insert the monitor replaces checking blood sugars by poking the finger 3 or more times per day.
Connected CGM-insulin pumps – This is a combination CGM-insulin pump that enables the pump to use the data obtained from the CGM to make required changes in medication dosage or make necessary adjustments for release of insulin on its own. The integration of an insulin pump with CGM would help improve type 2 diabetes management by quickly reducing blood sugar as well as minimizing the amount of time of unsafe and unhealthy blood sugar levels causing damage to other organs.
Revitalizing beta cells –Diabetes (both type 1 and type 2) caused damage to the beta cells in the pancreas. The therapy helps in reviving the cells by decreasing the damage to the beta cells and improve outcomes such as
- Regeneration of existing beta cells
- Regeneration of beta cells with the help of stem cells
- Reprogramming beta cells with differentiated cell types
- Replacing damaged beta cells with healthy cells from nonhuman or deceased donors
- Diabetes Testing Tools
Developing an Artificial Pancreas – It is a system of devices that closely mimic the glucose regulating function of a healthy pancreas especially for people suffering with Type 1 diabetes. It helps in managing diabetes along with:
- Decreasing the rate of hypoglycemia
- Helps patients maintain a healthy blood sugar range for longer duration
OUTLOOK
Diabetes is no longer a devastating disease. Nowadays, diabetes apps help in tracking your blood sugar levels and monitor your diet, suggest recipes, keep log of exercise; and provide support from other people with diabetes.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from diabetes, our expert providers at Specialty Care Clinics will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call us on (469) 545-9983 or book an appointment with Dr. Sumana Gangi.
