WHAT IS STREP THROAT?
Strep throat is a bacterial infection that could make your throat feel sore and scratchy. Strep throat accounts for only a small part of sore throats.
If untreated, strep throat could cause complications, such as kidney inflammation or rheumatic fever. Rheumatic fever could lead to painful and inflamed joints, a specific type of rash, or heart valve damage.
Strep throat is most frequent in children, but it affects people of all ages. If you or your child has signs or symptoms of strep throat, see your doctor for immediate testing and treatment
SYMPTOMS
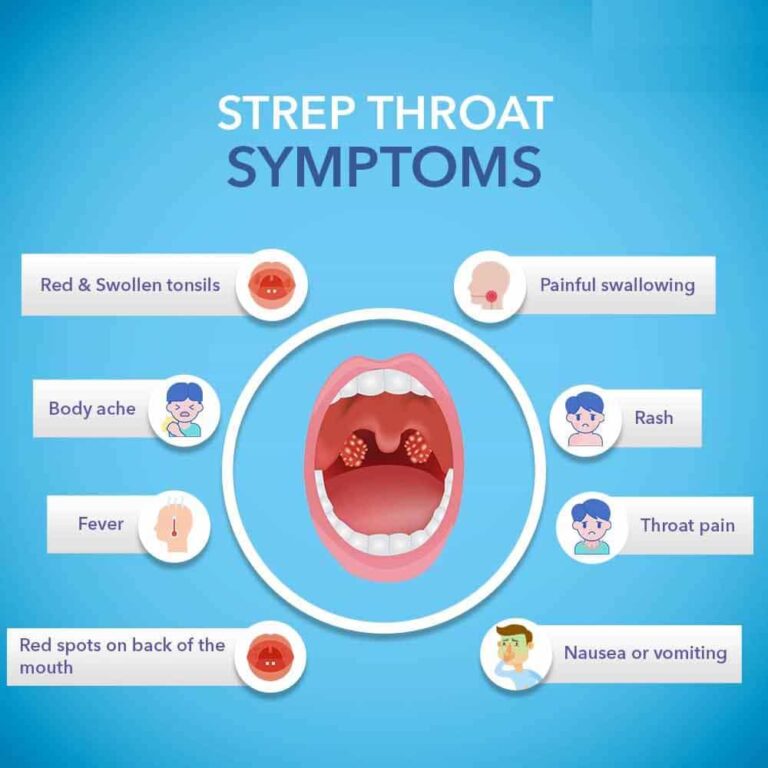
Signs and symptoms of strep throat could include :
- Throat pain that generally comes on quickly
- Painful swallowing
- Red and swollen tonsils, at times with white patches or streaks of pus
- Small red spots on the area at the back of the roof of the mouth (soft or hard palate)
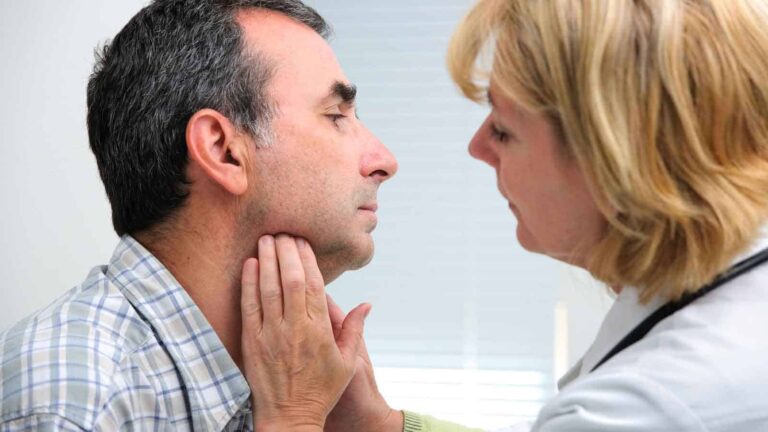
- Swollen, tender lymph nodes in your neck
- Fever
- Headache
- Rash
- Nausea or vomiting, particularly in younger children
- Body aches
It is possible for you or your child to have many of these signs and symptoms but not have strep throat. The cause of these signs and symptoms can be a viral infection or some other illness. That is why your doctor usually tests specifically for strep throat.
It is also possible for you to be exposed to a person who carries strep but shows no symptoms.
WHEN SHOULD YOU SEE A DOCTOR?
Call your doctor if you or your child has any of these signs and symptoms :
- A sore throat accompanied by tender, swollen lymph glands
- A sore throat that lasts longer than 48 hours
- A fever
- A sore throat accompanied by a rash
- Problems breathing or swallowing
- If strep has been diagnosed, a lack of improvement after taking antibiotics for 48 hours
CAUSES :-
Strep throat is caused by infection with a bacterium known as Streptococcus pyogenes, also known as group A streptococcus.
Streptococcal bacteria are infectious. They could spread through droplets when someone with the infection coughs or sneezes, or through shared food or drinks. You could also pick up the bacteria from a doorknob or other surface and transfer them to your nose, mouth, or eyes.
RISK FACTORS :-
Several factors could increase your risk of strep throat infection :
- Young age – Strep throat happens most commonly in children.
- Time of year – Although strep throat could occur anytime, it tends to circulate in winter and early spring. Strep bacteria flourish wherever groups of persons are in close contact.
COMPLICATIONS :-
Strep throat can lead to severe complications. Antibiotic treatment lowers the risk.
Spread of infection
Strep bacteria might spread, causing infection in :
- Tonsils
- Sinuses
- Skin
- Blood
- Middle ear
Inflammatory reactions
Strep infection might lead to inflammatory illnesses, including :
- Scarlet fever is a streptococcal infection characterized by a prominent rash
- Inflammation of the kidney (post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis)
- Rheumatic fever is a severe inflammatory condition that can affect the heart, joints, nervous system, and skin
- Poststreptococcal reactive arthritis is a state that causes inflammation of the joints
A possible relationship has been suggested between strep infection and a rare condition known as a pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorder associated with group A streptococci (PANDAS). Children with this condition experience worsened symptoms of neuropsychiatric conditions, like obsessive-compulsive disorder or tic disorders, with strep. This relationship presently remains unproved and controversial.
PREVENTION :-
To prevent strep infection :
- Wash your hands – Proper hand-washing is the best way to prevent all types of infections. That is why it is important to wash your own hands regularly with soap and water for at least twenty seconds. Teach your children how to wash their hands properly with soap and water or to use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer if there is no soap and water available.
- Cover your mouth – Teach your children to cover their mouths with an elbow or a tissue when they cough or sneeze.
- Do not share personal items – Do not share drinking glasses or eating utensils. Wash dishes in hot, soapy water, or in the dishwasher.
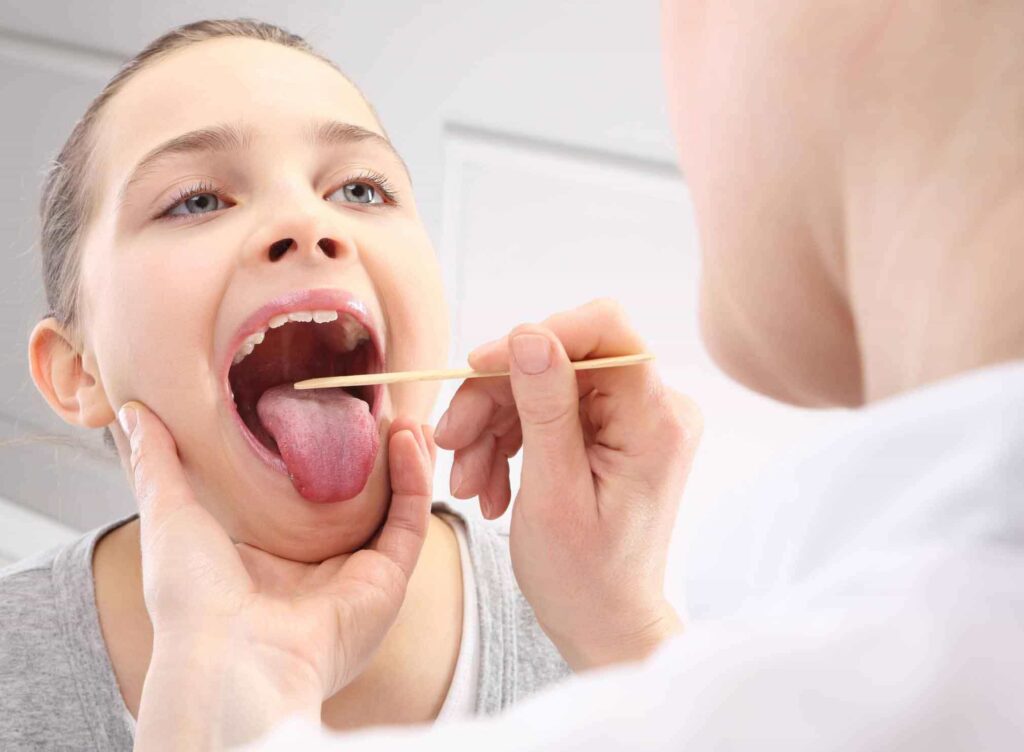
DIAGNOSIS
Your doctor will conduct a physical examination, look for signs and symptoms of strep throat, and probably order one or more of the following tests :
- Rapid antigen test – Your doctor might perform a rapid antigen test on a swab sample from your throat. This test could detect strep bacteria in minutes by looking for substances (antigens) in the throat. If the test is negative but your doctor still suspects strep, he or she may do a throat culture.
- Molecular (polymerase chain reaction, or PCR) test – This test is also performed using a swab sample from your throat.
- Throat culture – A sterile swab is rubbed onto the back of the throat and tonsils to get a sample of the secretions. It is not painful, but it might cause gagging. The sample is then cultured in a laboratory for the presence of bacteria, but the results could take as long as two days.
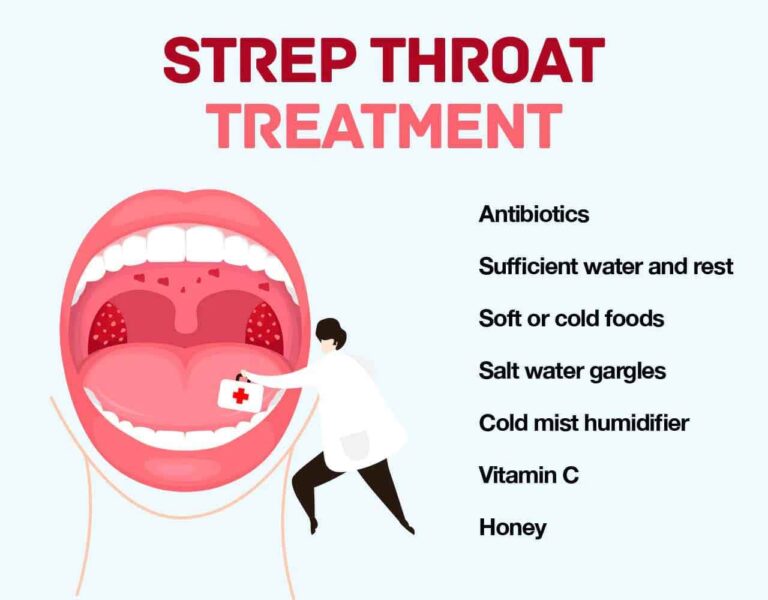
TREATMENT
Medications are available to cure strep throat, ease its symptoms, and prevent its complications and spread.
Antibiotics
If your doctor diagnoses you or your child with strep throat, your doctor will probably prescribe an oral antibiotic. If taken within 48 hours of the beginning of the illness, antibiotics reduce the duration and severity of symptoms, as well as the risk of complications and the likelihood that infection will spread to others.
With treatment, you or your child should begin feeling better in a day or two. Call your doctor if there is no improvement after taking antibiotics for 48 hours.
Children taking an antibiotic who feel well and do not have a fever often can return to school or child care when they are no longer contagious — usually 24 hours after beginning treatment. But be sure to finish all the medication. Stopping early could lead to recurrences and severe complications, such as rheumatic fever or kidney inflammation.
Symptom relievers
To ease throat pain and reduce fever, try over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others), or acetaminophen (Tylenol, others).
Be cautious about giving aspirin to children or teenagers. Even if aspirin is approved for use in children older than age three, children and teenagers recovering from chickenpox or flu-like symptoms should never take aspirin. This is because aspirin has been linked to Reye’s syndrome, a rare but possibly life-threatening condition, in such children.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from strep throat, our expert providers at Specialty Care Clinics will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call 469-545-9983 to book a telehealth appointment for an at-home check-up.