Pulmonary edema is a condition caused by the buildup of fluids in the air cavities and tissues of the lung. It results in impaired or inadequate gas exchange, which causes difficulty in breathing and might culminate in respiratory failure.
COMMON CAUSES OF PULMONARY EDEMA
Pulmonary edema is a condition caused by the buildup of fluids in the air cavities and tissues of the lung. It results in impaired or inadequate gas exchange, which causes difficulty in breathing and might culminate in respiratory failure.There are two main causes of Pulmonary edema, cardiogenic (related to the heart) and noncardiogenic.
Cardiogenic
Oxygenated blood from the lungs goes to the left side of the heart by the pulmonary veins, and then to the rest of the body by the pump action of the heart. When the heart fails to pump blood, the excess fluid pressure gathers in the pulmonary veins and lungs leads to pulmonary edema. This can be also caused by underlying conditions like kidney failure and high blood pressure.
Non-cardiogenic
- Neurological conditions like seizures, strangulation, head and lung trauma.
- Pulmonary embolism.
- Upper airway tract obstructions, which increases the negative pressure in the lung. This ruptures capillaries which results in the alveoli filling with fluid.
- Recurrent blood transfusions within a short window.
- Severe infections like Pneumonia, Hantavirus infections and COVID 19.
Other than these causes listed, there are many environmental/external factors that are known to cause Pulmonary edema.
- Toxins
- Drowning
- High altitudes
- Long term drug use or overdose.
SYMPTOMS OF PULMONARY EDEMA
The most common symptoms are respiratory distress, palpitations, weakness and fatigue, loss of consciousness. The symptoms can be further classified based on the onset of the condition.
Acute Pulmonary edema
This is called rapid onset pulmonary edema. The symptoms may develop suddenly and include:
- Extreme breathlessness which worsens on lying down. It can be defined as the feeling of suffocation.
- Coughing up blood with sputum.
- Wheezing
- Crackles at the end of each breath along with an irregular heartbeat.
- Anxiety, disorientation.
- Pale and clammy skin.
- Pulmonary Edema
CHRONIC PULMONARY EDEMA
The symptoms develop over a longer period of time and include:
- Swelling that begins in the feet and progresses upwards
- Breathlessness when active or laying down flat.
- Breathlessness in the night, which eases when one sits up.
- Coughing up sputum mixed with frothy blood.
PULMONARY EDEMA DIAGNOSIS
The key factors to look out for while diagnosing pulmonary edema are:
- Increased breathing and heart rate.
- Crackling sound while breathing
- Fluid buildup in the extremities like legs and lower abdomen area.
- Pallor of the skin.
If all these symptoms are present the doctor will suggest further tests that include:
- Chest X-Rays which would show the presence of fluid in the lungs.
- Chest CT scan.
- Echocardiography to check if it is related to any underlying heart conditions.
- Blood tests: Electrolytes, arterial blood gas ratio, B-type natriuretic test, Urea and Creatinine.
TREATMENT OF PULMONARY EDEMA
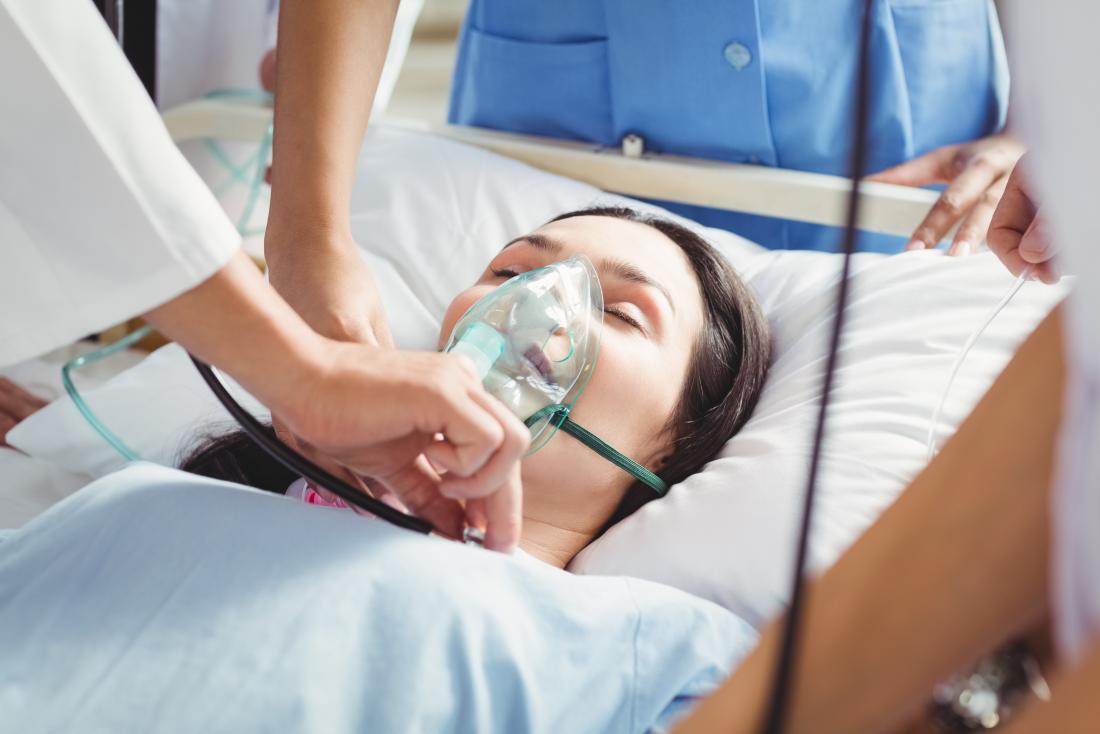
Irrespective of the cause or type of Pulmonary edema, the first step of treatment is the quick stabilization of the vitals. The first line of treatment in most cases is oxygen. If the patient is losing consciousness then he has to be moved onto mechanical ventilation where the oxygen is delivered through an endotracheal tube.
The next step of treatment involves diagnosing the type of pulmonary edema and treating it. Some routine treatments include:
- Diuretics – decreases the pressure on lungs and heart by excreting the fluid as urine. Example, Lasix or Furosemide.
- Inotropes – to increase the contractile power of the heart to correct the pump failure. Example, Noradrenaline, Adrenaline, Dopamine
- Vasodilators – to dilate blood vessels and reduce the pressure against which the heart has to pump out blood.
- Antibiotics – to treat underlying infections.
PREVENTION OF PULMONARY EDEMA
Pulmonary edema is caused by a combination of factors and the best way to prevent or control pulmonary edema onset include:
- Go for regular checkups.
- If suffering from heart condition,
- Control blood pressure and cholesterol.
- Continue prescribed medications like diuretics or blood pressure medicines.
- Exercise regularly and maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoiding smoking and recreational drug use.
- Regular flu, pneumonia vaccinations
Pulmonary edema is a condition caused by an amalgamation of factors all leading to the accumulation of fluids in the lungs. It can be prevented by controlling these collective factors. If a person presents with the symptoms, go to the doctor. A quick diagnosis results in better treatment and recovery.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from pulmonary edema, call our expert pulmonologists at 469-545-9983 to book an appointment.
