WHAT IS CRYOGLOBULINEMIA?
Cryoglobulins are unusual proteins in the blood. These proteins might clump together at temperatures below 98.6 F (37 C) if you have cryoglobulinemia. These gelatinous protein clumps could impede your blood circulation, which could damage your skin, joints, nerves, and organs especially your kidneys and liver.
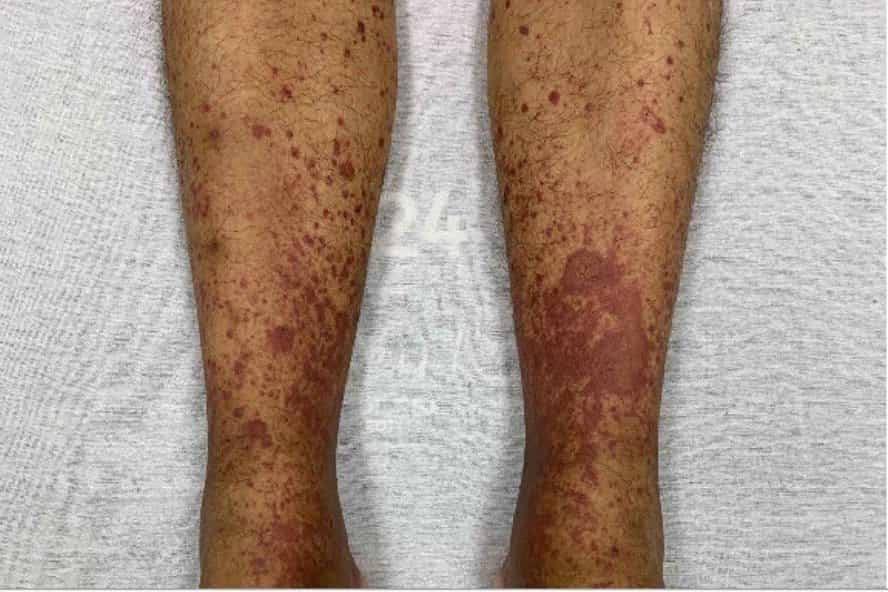
CRYOGLOBULINEMIA SYMPTOMS
Symptoms generally come and go, and might include:
- Skin lesions – Most people who have cryoglobulinemia develop purplish skin lesions on their legs. In some people, leg ulcers also happen.
- Joint pain – Symptoms resembling rheumatoid arthritis are frequent in cryoglobulinemia.
- Peripheral neuropathy – Cryoglobulinemia could damage the nerves at the tips of your fingers and toes, causing numbness and other problems.
CRYOGLOBULINEMIA CAUSES
Cryoglobulinemia has been related with:
- Infections – Hepatitis C is the most common infection related to cryoglobulinemia. Others include hepatitis B, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), Epstein-Barr, toxoplasmosis, and malaria.
- Certain cancers – Some cancers of the blood, like multiple myeloma, Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia, and chronic lymphocytic leukemia, could sometimes cause cryoglobulinemia.
- Autoimmune disorders – Diseases like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Sjogren’s syndrome increase the risk of developing cryoglobulinemia.
CRYOGLOBULINEMIA RISK FACTORS
Risk factors of cryoglobulinemia might include:
- Your sex – Cryoglobulinemia happens more frequently in women than in men.
- Age – Symptoms of cryoglobulinemia generally start in middle age.
- Other diseases – Cryoglobulinemia is related to diseases like hepatitis C, HIV, multiple myeloma, Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia, lupus, and Sjogren’s syndrome.
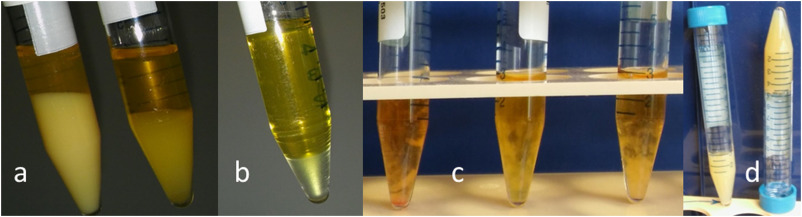
CRYOGLOBULINEMIA DIAGNOSIS
Diagnosis of cryoglobulinemia involves a blood test in which the sample should be kept at normal body temperature, 98.6 F (37 C), for a period of time before being cooled. Inaccurate test results could happen if the blood sample is not handled properly.
CRYOGLOBULINEMIA TREATMENT
Depending on the hidden cause of cryoglobulinemia, treatment might include medications that suppress the immune system or fight viral infections. For serious symptoms, your doctor or primary care physician might also recommend a procedure that exchanges your blood plasma, which contains much of the cryoglobulins, for donor plasma or replacement fluid.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from cryoglobulinemia, our expert providers at Specialty Care Clinics will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call 469-545-9983 to book a telehealth appointment for an at-home check-up.
