WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS?
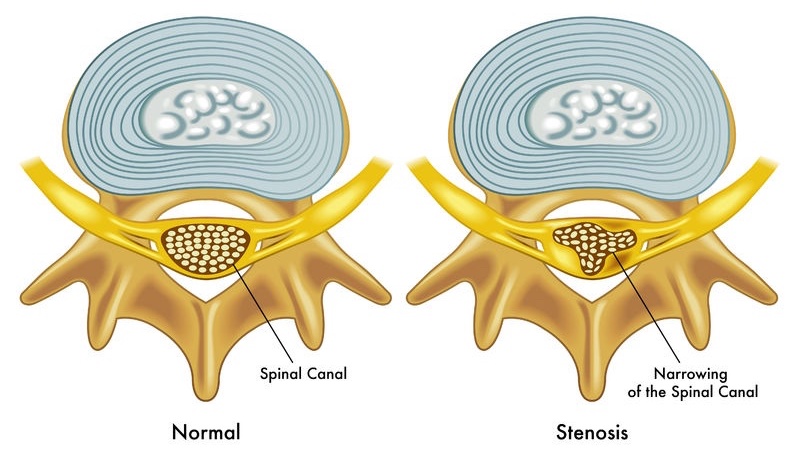
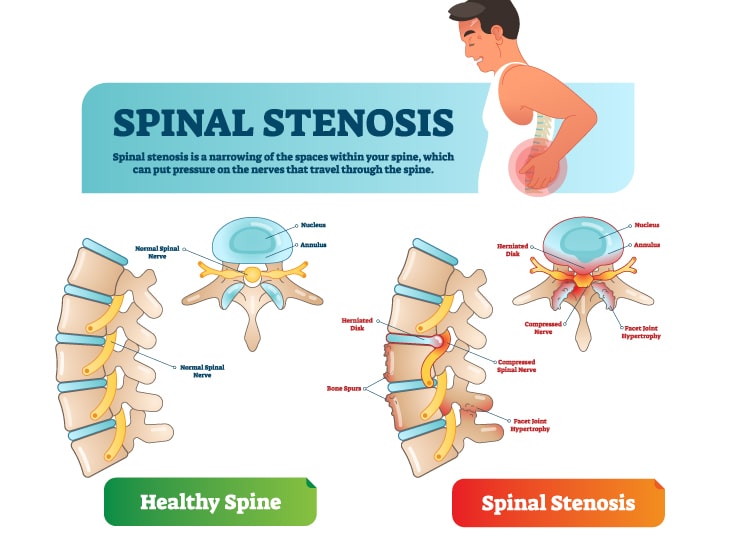
Narrowing of the spaces within the spinal canal is spinal stenosis. The narrowing puts pressure on the nerves travelling through the spine. Spinal stenosis occurs in the lower back or lumbar spine; but, it might occur in the neck or cervical spine also.
Older people are more prone to spinal stenosis due to spinal degeneration. Spinal degeneration causes deterioration of vertebral discs over a long period of time.
WHAT CAUSES SPINAL STENOSIS?
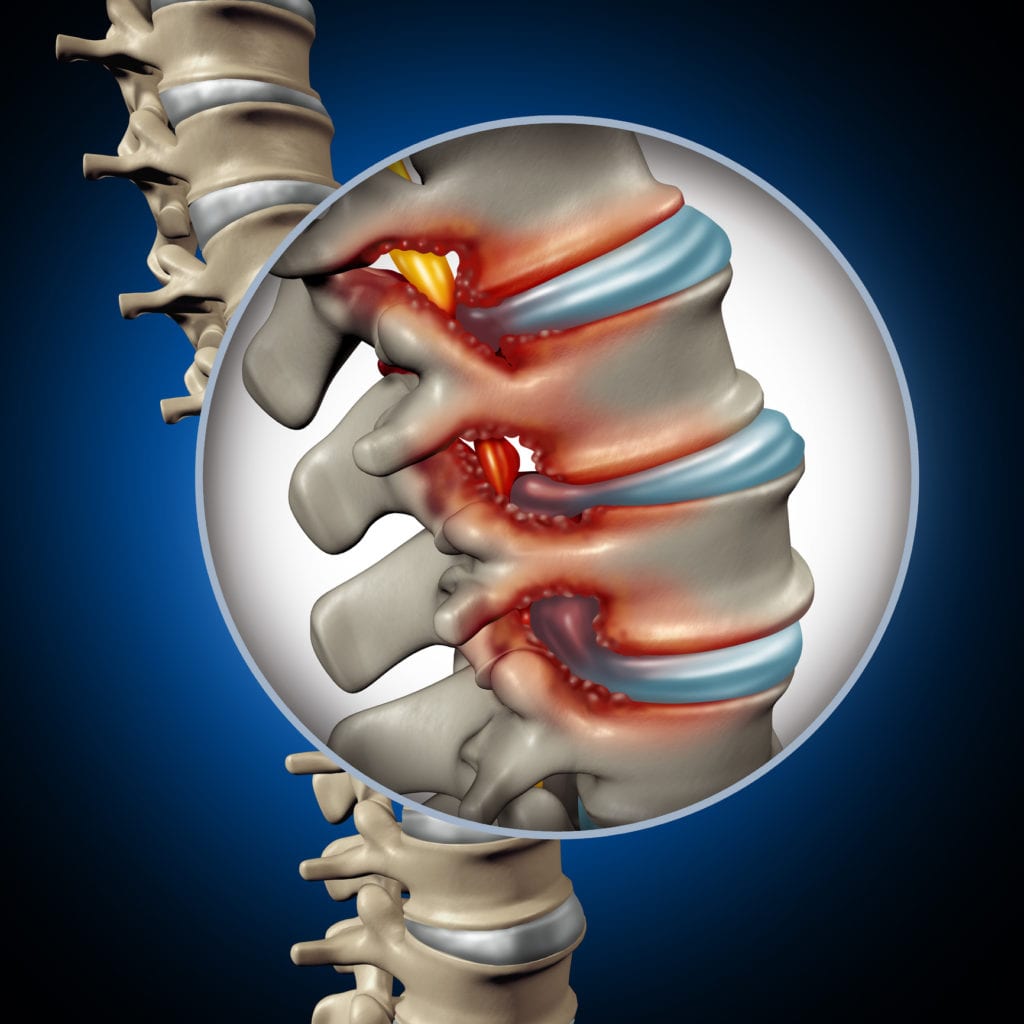
Spinal stenosis happens over-night. This is caused due to wear-and-tear within the spine that worsen. This occurs in patients suffering from osteoarthritis due to degeneration throughout their spine.
Narrowing of the spine reduces the space available for the spinal cord and nerves of the spinal cord. This tightened space irritates the spinal cord or nerves. This leads to compressed or pinched nerves causing back pain and sciatica.
THERE ARE 2 GENERAL TYPE OF SPINAL STENOSIS:
- Foraminal Stenosis or Lateral Stenosis – The intervertebral foramen is a bony opening. Here a spinal nerve exits the spinal canal between two adjacent vertebrae. Narrowing of the foramina causes pinched, painful, and dysfunctional spinal nerves.
- Central canal stenosis – The vertebral foramen is a bony opening in the center of the vertebra. This protects the spinal cord and runs down the spinal canal. Narrowing of one or more vertebral foramina known as central canal stenosis. The spinal cord has less space due to narrowing. These compressed nerves cause pain and dysfunction below the level of compression.
CAUSE OF SPINAL STENOSIS ARE:
- Overgrowth of bone – Wear and tear damages the spinal bones. This causes formation of bone spurs growing into the spinal canal.
- Herniated Disk – The soft cushions help absorb shock between your vertebrae. This would dry out with age leading to cracks in the exterior region of the disk. This allows the inner soft material to discharge and put pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
- Thickened Ligaments – The tough spinal cords holding the bones of your spine together might become stiff and thickened over time causing bulge into the spinal canal.
- Tumors – Abnormal growth of cells inside the spinal cord puts pressure within the membranes covering the spinal cord or in the space between the spinal cord and vertebrae.
- Spinal Injuries – Trauma caused by accident or other injuries cause dislocations or fractures of the vertebrae. Spinal fracture causes displaced bone damaging the contents of the spinal canal. Swelling of nearby tissue after back surgery also puts pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
Narrowing of the spine causes pain but it rarely causes paralysis. But if the spinal nerve or spinal cord is compressed for a long time it can cause permanent numbness or paralysis.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF SPINAL STENOSIS?
Not all people will experience painful symptoms due to spinal stenosis. Symptoms might begin and magnify over time in most cases. The symptoms vary in different types of spinal stenosis.
Symptoms of spinal stenosis may include:
- Neck pain
- Lower Back pain
- Sciatica Pain beginning from buttocks and extending down the legs till foot
- Problems with walking and balance
- Numbness or tingling in arm, hand, foot or leg.
- Pain or cramping in legs when walking or standing for prolonged periods of time
- Weakness in a hand, arm, foot or leg
- Bowel or bladder dysfunction (urinary urgency and incontinence)
- Loss of function in hands
- Rarely causes paralysis
WHAT DIAGNOSTIC TESTS ARE PERFORMED TO DIAGNOSE?
Doctor recommended an X-ray for diagnosis. X-ray requires electromagnetic energy to create images of the spine. This allows your doctor to identify any bony changes or masses. It also identifies the abnormality within your vertebral column.
If your X-ray is normal, but no relief after chiropractic treatments, your doctor orders an MRI. This provides details of the organs and tissues surrounding the vertebral column.
An MRI scan uses radio waves and magnetic fields. This provides detailed pictures of your spine, the surrounding tissues, and organs. Doctors would recommend computerized tomography (CT). This combines X-ray images taken from different angles to produce detailed, cross-sectional images.
A CT scan initiated after a contrast dye is injected or ingested. The dye outlines the spinal cord and nerves. This allows radiologists to reveal herniated disks, bone spurs and tumors.
WHAT ARE POSSIBLE DIAGNOSES ALONGSIDE SPINAL STENOSIS?
An overgrowth of bone or bone spurs, herniated disks, and thickened ligaments occur with spinal stenosis.
Cervicalgia, radiculopathy, subluxation or segmental dysfunction, cervical spondylosis, low back pain (LBP), and lumbar spondylosis are common.
In rare cases, severe cases of spinal stenosis may progress to cause permanent numbness, weakness, balance problems, incontinence, or paralysis.
WHAT ARE THE TREATMENT OPTIONS OF SPINAL STENOSIS?
The treatment regime varies on an examination by your chiropractor. Your chiropractor will realign your spine. Chiropractor will remove the kinks in your nervous system.
These spinal adjustments allow your nervous system to flow. This also reduces pain and inflammation naturally. Some common treatment options recommended are:
- Apply Heat or cold – Heat increases the blood flow and relaxes the muscles and relieves aching joints. Whereas, application of ice reduces swelling, tenderness and inflammation.
- Medication – Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen, naproxen, aspirin or acetaminophen helps in relieving inflammation and relief from pain. Your doctor might also provide anti-seizure drug gabapentin or tricyclic antidepressants along with pain killers. For short term pain relief opioids are also effective. Muscle cramps and spasm are common symptoms of spinal stenosis. Thus, muscle relaxants are helpful.
- Physical Therapy – Physical rehabilitation with chiropractic care is the best option for most patients suffering from spinal stenosis. Physical rehabilitation involves stretching, strengthening, and stabilizing the body through exercises tailored to fit your specific needs. Physical therapy develops a healthy back helpful in gaining strength and improving your balance, flexibility and spine stability. Manual massage, cupping, and scraping therapies help to release the lactic and uric acid build up within your intrinsic back muscles that run along both sides of the spine.
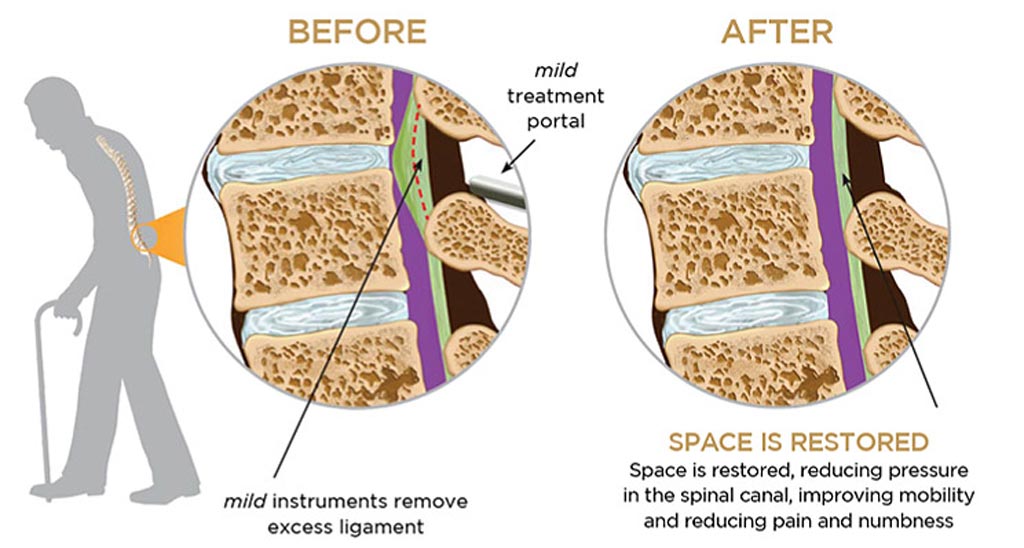
- Decompression procedure – Also known as percutaneous image-guided lumbar decompression (PILD) is a procedure helpful in treating lumbar spinal stenosis. Lumbar spinal stenosis is caused by a thickening of a ligamentum flavum in the back of the spinal column. A tiny incision is made to remove a section of the thickened ligament. This would free-up space within the spinal canal and reduce compression on nerve roots.
- Steroid injection – This is recommended if the oral medication does not provide relief. Injecting corticosteroids helps in relieving the nerve roots that are pinched or worn areas of bone rub together near the space in the spine. This also reduces inflammation, pain and irritation.
- Surgery – Surgery is the last resort because the spine is delicate in nature. But if the symptoms are intolerable, quality of life is impacted, walking & maintaining balance is difficult or you have lost bowel or bladder control and sexual problems, surgery is required. Depending on the diagnosis, the surgical procedures for spinal stenosis are laminectomy, laminotomy, and laminoplasty.
Spinal Stenosis
OUTLOOK
Using certain medications puts some patients at risk of becoming addicted, so it is extremely important to take your prescribed medication as directed and to pay attention to the way your body reacts to it. Surgery is the last resort for a patient.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from back pain, our expert providers at Specialty Care Clinics will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call us on (469) 545-9983 to book an telehealth appointment with our specialists.
