Fractures, or broken bones, can occur due to various causes such as trauma, accidents, or underlying medical conditions. While fractures are typically treatable and heal with proper medical care, there are instances where complications may arise. Understanding these potential complications is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike to ensure timely intervention and optimal recovery. In this article, we will explore some common complications that can arise from fractures.

INFECTION
One of the most significant complications associated with fractures is infection. When a bone breaks, there is a risk of bacteria entering the site through an open wound or during surgical procedures. Infection can lead to delayed healing, prolonged recovery time, and in severe cases, osteomyelitis (infection of the bone). Symptoms of infection include increased pain, swelling, redness, warmth, and discharge from the fracture site. Prompt medical attention is necessary to diagnose and treat infections to prevent further complications.
NONUNION AND DELAYED UNION
Fractures typically heal through a natural process called the union, where the broken bone segments fuse back together. However, in some cases, the bones may fail to heal properly, leading to nonunion or delayed union. Nonunion occurs when the bone fails to heal at all, while delayed union refers to a significantly prolonged healing process. Factors that contribute to nonunion or delayed union include inadequate blood supply, poor immobilization, infection, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes or osteoporosis. Treatment options for nonunion may consist of surgery, bone grafting, or electrical bone stimulation to promote healing.
MALUNION
Malunion refers to a condition where a fractured bone heals in an incorrect alignment or position. This can occur if the fracture is not adequately reduced (realigned) or if proper immobilization is not maintained during the healing process. Malunion can result in functional limitations, joint stiffness, altered limb length, and aesthetic deformities. Depending on the severity and impact on functionality, treatment options for malunion may include orthopaedic surgery, corrective osteotomy, or physical therapy.
JOINT STIFFNESS AND CONTRACTURES
Fractures that involve joints can lead to joint stiffness and contractures. Immobilization of the joint during the healing process can cause a decrease in range of motion, muscle weakness, and joint stiffness. If not addressed promptly, these complications can significantly impact daily activities and reduce the quality of life. Physical therapy, exercises, and gentle joint mobilization techniques are often employed to improve joint mobility and prevent contractures.
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT)
Fractures, particularly those that require prolonged immobilization, can increase the risk of developing deep vein thrombosis (DVT). DVT occurs when a blood clot forms in the deep veins, typically in the lower extremities. Symptoms of DVT include leg pain, swelling, warmth, and discolouration. If left untreated, the blood clot can potentially dislodge and travel to the lungs, causing a life-threatening condition called pulmonary embolism. To prevent DVT, healthcare providers may recommend measures such as early mobilization, compression stockings, and anticoagulant medication.
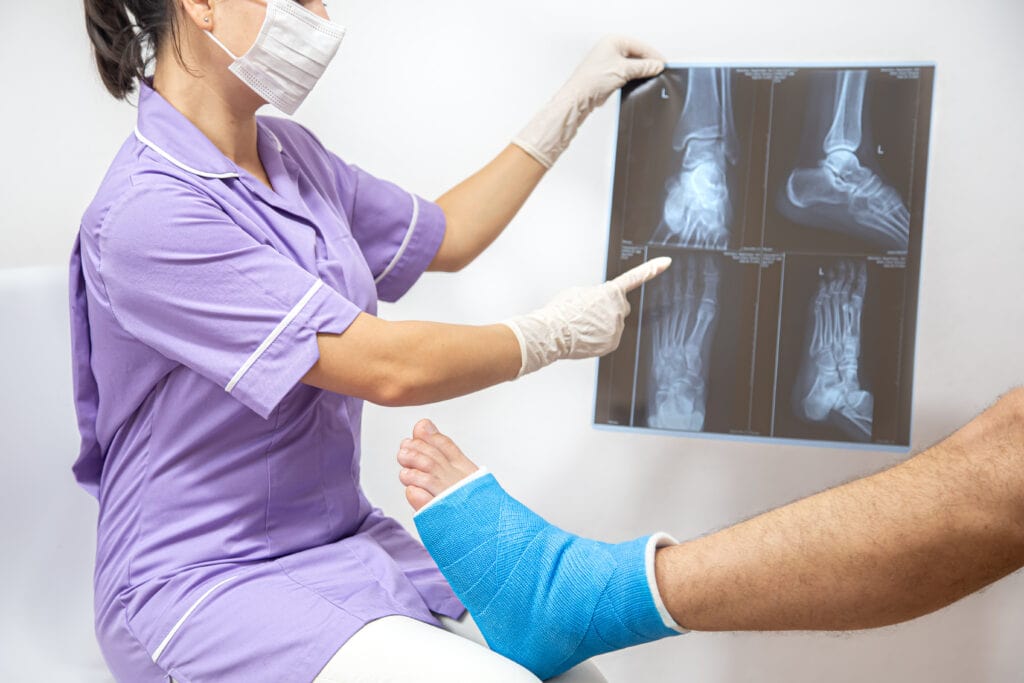
While fractures are common injuries that often heal with appropriate medical care, it is important to be aware of potential complications. Infections, nonunion, malunion, joint stiffness, and DVT are among the common complications that can arise from fractures. Early recognition and intervention are key to preventing and managing these complications effectively. If you experience prolonged pain, swelling, or any concerning symptoms during your fracture recovery, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
For specialized care and expert guidance in fracture management, contact Specialty Care Clinics. Let our dedicated team of professionals help you recover and regain your mobility.
