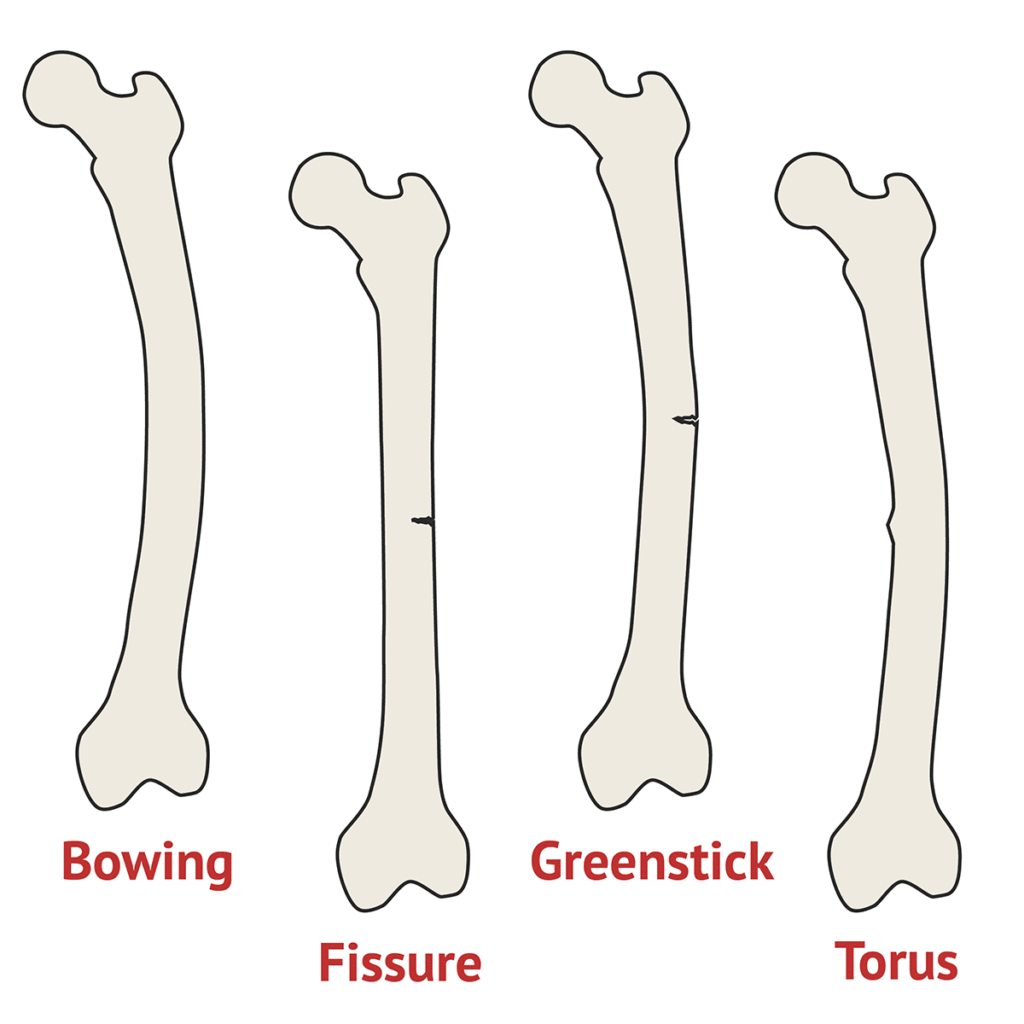
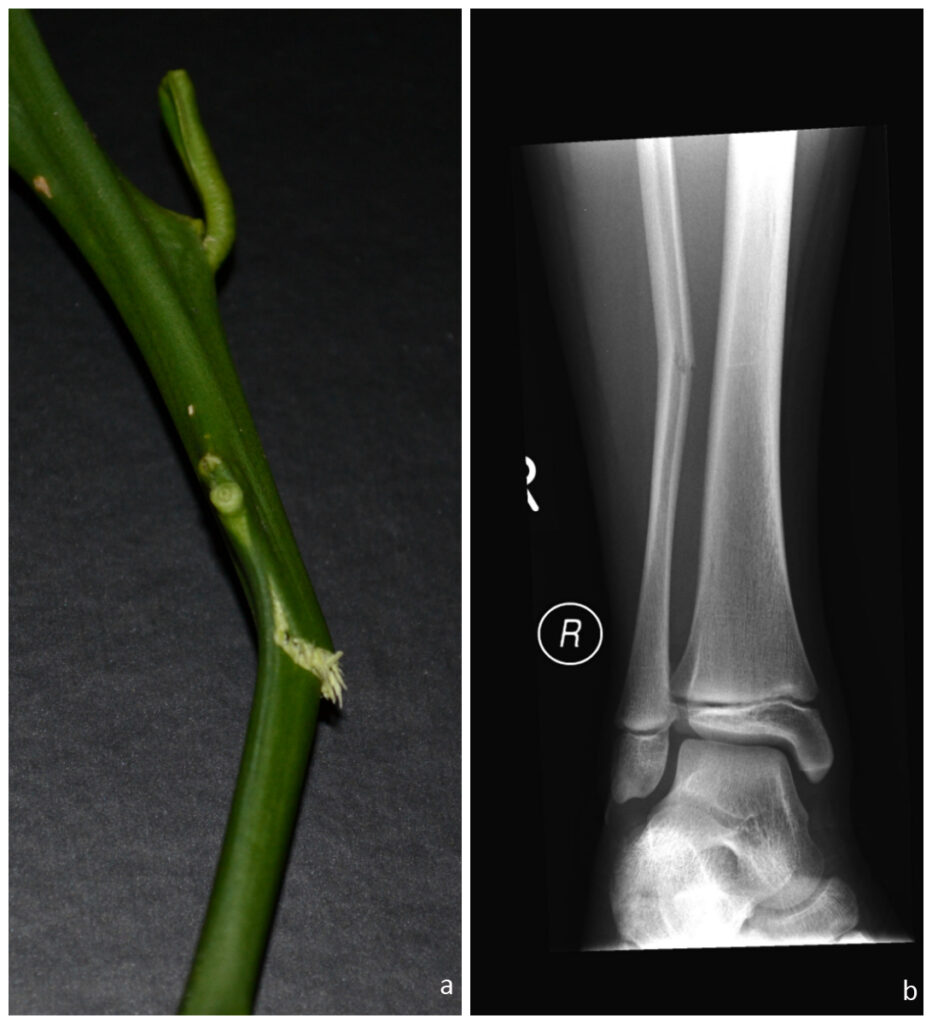
A greenstick fracture is a type of fracture that occurs in a young, soft bone when a bone bends and breaks. In this type, the bone doesn’t break into two separate pieces.
The name “Greenstick Fracture” comes from the green branch of a tree. When we try to break a branch, it breaks but sticks to the tree. This typically occurs in infants or children under 10 years. This is because their bones are softer, more flexible, and less brittle than an adult’s.
Treatment involves immobilization of the bone, it helps to hold the cracked pieces of the bone together so they can heal. It also helps prevent the bone from breaking if the child falls on it again.
For major fracture or chronic fracture surgery is another option. Greenstick fractures are common in children. In the United States, millions of children are affected by this fracture. A greenstick fracture often takes place when a child falls and tries to break the fall with his or her arms.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS:
The signs and symptoms of a greenstick fracture vary depending on the intensity of the fracture. Symptoms also depend on the location of the injury.
- Mild fractures might develop pain, sprains, bruises, or general tenderness.
- In severe cases, the fractured area is accompanied by swelling, tenderness, and chronic pain.
- In both mild and severe fractures you might not be able to move the injured part of the body for some time.
You can feel pain in the fractured area while overusing that specific bone. This can be a very gradual chronic pain or pain from a specific injury.
CAUSES:-
Greenstick fractures can be caused by many things. Fall is the most common cause of a greenstick fracture. Following are some causes of fractures:
- motor vehicle accidents
- sports injury
- jumping around
- walking or running from the slippery surface
- falling from certain heights
Most children develop greenstick fractures frequently in their arms rather than legs because they try to catch themselves as they fall.
RISK FACTORS:-
The greenstick fracture happens as bending forces are applied to the bone. In a greenstick fracture, the bone bends or cracks instead of breaking into separate pieces.
The risk of greenstick fractures is higher in young children as compared to adults because their bones are flexible and soft. Mostly it occurs in children under age 10.
The adults whose bones are more brittle are also at risk of fracture. Activities such as falling raise the risk of greenstick fracture.
HOW CAN YOU DIAGNOSE A GREENSTICK FRACTURE?
To diagnose a greenstick fracture, the doctor will perform a physical examination. During the physical examination, your doctor will inspect the affected area for tenderness, swelling, deformity, numbness, or an open wound. The doctor also inspects the injured area for signs of a fracture, such as pain and swelling.
If needed, the doctor will ask you to perform X-rays, CT (computed tomography) scan, or MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan to make sure the bone is fractured and rule out other injuries. These imaging tests help figure out major trauma.
GREENSTICK FRACTURES TREATMENT:-
Most greenstick fracture cases are treated with a cast or a removable splint. Casts can remain in place for 4-6 weeks. This helps to keep the bones in place as they heal. This also prevents further breakage of the already damaged bone.
The doctor may prescribe acetaminophen (Tylenol®) or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication (NSAID), such as ibuprofen (Advil® or Motrin®) or naproxen (Aleve®). If there is an obvious bend in the affected arm or leg, your doctor will manually straighten it. Your doctor may give you pain medication or sedatives, or occasionally general anesthesia, as the procedure can be quite painful.
More serious greenstick fractures need surgery. Surgery may be done to realign the bone. During surgery, doctors insert a slender rod or a metal plate with screws into the bone surrounding the fracture to maintain alignment of the bone. The metal plates may be permanent, or you can remove them after you heal.
WHEN SHOULD YOU CALL A DOCTOR OR SEEK MEDICAL HELP?
If you or your child is experiencing any of the following, contact a doctor:
- Pain in a limb that doesn’t go away after a day or two.
- Obvious bend in your limb.
- You are unable to put weight on your leg.
If your child has crucial pain or an obvious deformity, you need to seek an emergency or urgent care clinic. You need to go for a consultation with a pediatric orthopedic surgeon.
You can lower your child’s risk for greenstick fractures by trying to prevent falls or other injuries that lead to fractures. Take some precautions while playing sports or doing any activity which can lead to fractures.
If you or your child has significant pain because of greenstick fractures, you can contact Specialty Care Clinics. We provide high-quality, cost-effective, and emergency healthcare treatment for many diseases and conditions.
We have board-certified and licensed pain management doctors who are experts in treating all types of pain which you may experience.
We are located at multiple locations in Texas. Call us on 469-545-9983 to book an appointment with our specialists today.
