WHO IS A PODIATRIST?
A Podiatrist is a lower leg and foot specialist that has studied the anatomy and functions of our feet thoroughly. They can treat physical injuries and control ailments that result from ongoing medical issues, such as obesity or diabetes.
A podiatrist is a doctor that can treat a variety of problems ranging from athletes’ feet to broken bones. While they do not attend traditional MD programs, they go through rigorous medical training which includes 4 years of podiatric school followed by 3-4 years of residency training, much like a traditional MD.
They can treat broken bones, conduct surgery, prescribe medication, fix skin conditions of the lower legs and feet, and much more.
TREATMENTS PODIATRISTS PROVIDE
Sleeping difficulty means difficulty in falling asleep, difficulty staying asleep, or waking up too early. Low quality sleep and a lack of sleep both can negatively affect a person’s health.
CAUSES OF SLEEPING DIFFICULTIES
Podiatry covers a wide variety of foot-related issues. Often problems are not simply limited to physical injuries or torn ligaments, serious infections and funguses can occur on our feet, and can last long periods of time if not attended to promptly by a medical professional.
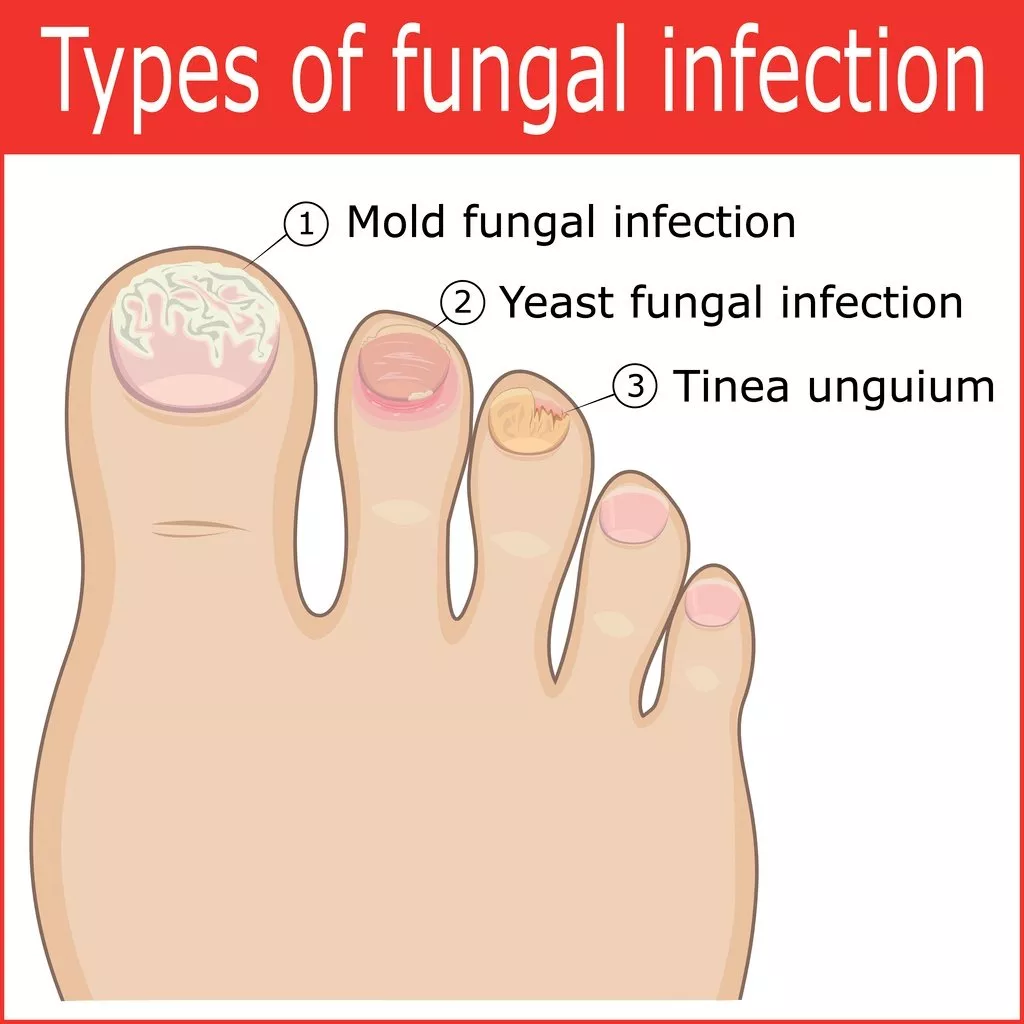
What is it? – Onychomycosis, commonly known as toenail fungus, is when fungi get underneath the surface of the nail and causes infection. This is commonly accompanied by whitening or thickening of the nail plate, discomfort, and can lead to severe pain which can impair a person’s ability to walk normally. Toenail fungus is a fungus, so it can quickly spread to other toenails, the surrounding skin, and even the fingernails.
Causes: fungi and bacteria thrive in moist environments such as pools, showers, and locker rooms. Injuries to the nail plate can leave it more vulnerable to fungi, while certain health conditions such as diabetes can also leave one more susceptible to infection.
Diagnosis and Treatment: Treatment depends on the intensity of the infection. A licensed Podiatrist can perform lab tests to catch the infection early on, determine the cause from a patient’s daily habits, and provide a treatment plan.
This plan may consist of topical ointments, reducing the physical movement of the feet, and/or prescribing oral antifungal medication. In severe cases of fungal infection, surgery may be the desired option. Surgery may become necessary in order to stop the spread of rapidly growing fungi to the other nails and skin.
Temporary removal of the infected nail through surgery can allow a direct antifungal ointment to be applied to the area, or permanent removal of a damaged nail can help promote the growth of a new, healthy nail.
2. CORNS AND CALLUSES
What is it? Corns and calluses are areas of skin on the top and bottom of the feet which have thickened in response to constant irritation from some rubbing or excessive pressure on a particular area. Widely spread out thickening is a callus while isolated areas with more thickness are corns.
Corns present in almost blister-type balls, often on the sides of our toes. While they do not spread rapidly like fungi, they can cause pain and discomfort, and in people with disorders such as diabetes, they lead to more severe foot problems.
Causes: Corns are often caused by excessive rubbing on areas of shoes and calluses may result from continued pressure on the heels and balls of feet, such as frequent use of high-heel shoes or walking barefoot on hard surfaces. Ill-fitting shoes or lack of sucks can cause further irritation which leads to these ailments in response.
Diagnosis & Treatment: Often corns and calluses can be self-diagnosed, but usually only require a visual examination from a doctor. Patients with diabetes must know that it is critical to consult a professional before attempting home treatment due to the decreased flow of blood in their feet.
A professional may inquire about your habits and lifestyle choices to determine whether it’s a simple blister or a corn/callus. Treatments can include the removal of the irritator, such as a different style of shoe or decreasing the activity which caused it. If they persist, a doctor can remove the excess skin surrounding the abnormality through a non-invasive procedure.
Topical treatments are also available, which contain salicylic acid which can aid in shedding skin and reducing inflammation. In rare instances, these ailments may be a result of a bone that is bulging through the skin of the foot leading to excess irritation, here a doctor may opt to suggest surgery to fix the alignment of the bone.
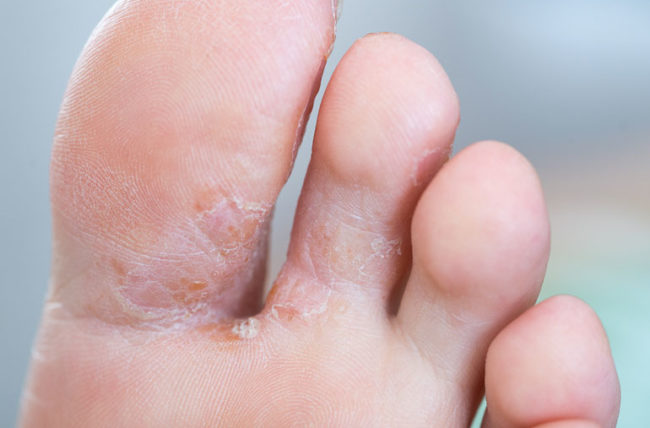
3. ATHLETES FOOT
What is it? Athletes’ foot, or tinea pedis, is a fungal infection starting in the crevices between our toes, eventually spreading throughout the rest of our foot. Usually, it is due to excess moisture from sweating in confined socks and shoes. Athletes’ foot is often accompanied by red, inflamed patches of skin, itching or burning, shedding of skin, and mosaic patterns of dry and scaly skin.
The issue with athletes’ feet is that it’s contagious. It can easily spread from the feet to the hands or groin, through direct contact. It can also linger on bathroom floors and towels.
Causes: Athletes’ feet result from moist socks or shoes, and are part of the same fungal family as jock itch and ringworm. Fungi thrive from moisture and dark spaces, which is why it is essential to catch it before it spreads.
Risk factors can include –
- Wearing damp socks and shoes for long periods of time
- Sharing towels, mats, towels, clothes, and shoes with someone infected
- Walking barefoot in areas at high risk for infection, such as swimming pools, locker rooms, and shared accommodation bathrooms
Diagnosis & Treatment:
Usually, your doctor will be able to tell from a visual examination, but to confirm sometimes may take a skin sample to send to the lab for testing. To further confirm the existence of tinea plus the doctor may inquire about your daily habits and lifestyle to determine the factors associated with the infection.
The doctor may suggest topical cream, ointment, or spray in mild cases. More severe cases will require prescription ointments or oral fungal medications.
Lifestyle changes:
While creams and medication will alleviate the infection, your doctor will most probably advise you on lifestyle adjustments to ensure the athlete’s foot does not reappear. These include:
- Keep your feet dry, allow them to air out excess moisture often.
- Periodically change socks to prevent the build-up of bacteria and moisture.
- Wear sandals or shoes in high-risk areas i.e communal bathrooms and locker rooms.
- Avoid scratching or touching the rash if it appears, it is contagious so it could very well spread from there.
If you’re experiencing any severe foot pain, don’t wait for it to pass on its own. Our team here at Specialty Care Clinics strives to improve our patients’ lives and prevent their suffering. Your health matters.
Call us today at 469-545-9983 to book an appointment with our expert podiatrists.
