Don’t Let a Sprain Sideline You: Effective Wrist Sprain Treatment for a Speedy Recovery
The human wrist is a marvel of engineering, allowing for a wide range of motion and intricate movements. From typing and writing to gripping objects and lifting weights, our wrists play a crucial role in daily life. However, a sprained wrist can significantly disrupt this functionality, causing pain, stiffness, and making everyday tasks a challenge.
Understanding Wrist Sprains: Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the Signs of a Sprain:
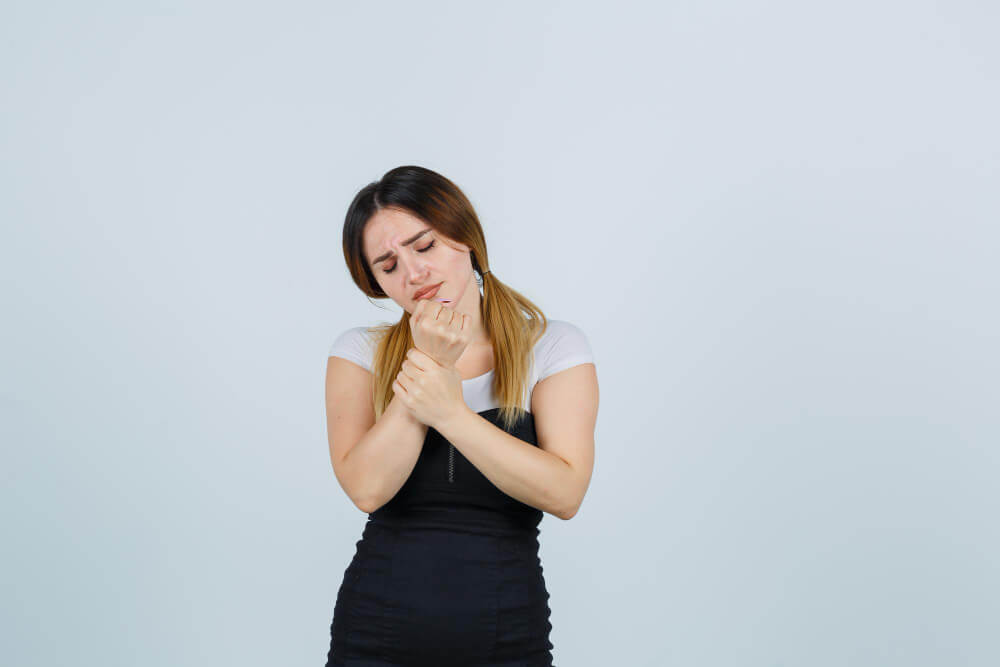
Wrist sprains occur when the ligaments connecting the wrist bones are stretched or torn beyond their normal range of motion. The telltale signs of a sprained wrist include:
- Pain: This is the most common symptom, often described as a sharp or throbbing pain in the wrist, especially when moving the joint.
- Tenderness: The area around the sprain will be tender to the touch.
- Swelling: Inflammation and swelling around the wrist joint are common after a sprain.
- Bruising: Discoloration of the skin around the wrist might occur due to underlying blood vessel damage.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Moving the wrist might be difficult or painful due to stiffness and inflammation.
Seeking Medical Evaluation:
While some mild sprains might heal on their own with proper rest and care, consulting a healthcare professional is recommended for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. During a consultation, the doctor will inquire about your symptoms, how the injury occurred, and perform a physical examination to assess the severity of the sprain. X-rays might be ordered to rule out any underlying fractures.
The Road to Recovery: Effective Treatment Options for Wrist Sprains
The RICE Method:
The RICE method is the cornerstone of treatment for most wrist sprains. It stands for:
- Rest: Avoid activities that aggravate the sprain. This might involve limiting wrist movement or using a splint for support.
- Ice: Apply ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day, to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Compression: Wrap the wrist with a compression bandage to minimize swelling.
- Elevation: Elevate the injured wrist above your heart as often as possible to promote healing.
Medication:
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and inflammation. In some cases, a doctor might prescribe stronger medication for severe pain.
Physical Therapy:
Once the initial inflammation subsides, physical therapy plays a crucial role in regaining full range of motion and strengthening the muscles and ligaments surrounding the wrist joint. A physical therapist will design a personalized exercise program to improve flexibility, strength, and stability in your wrist.
Splinting or Bracing:
In some cases, a doctor might recommend wearing a splint or brace to immobilize the wrist and promote healing. The duration of immobilization will depend on the severity of the sprain.
Preventing Future Injuries: Tips for Optimal Wrist Health
Maintaining Proper Posture:
Practice good ergonomics at work and home, ensuring your wrists are in a neutral position while using computers, typing, or writing.
Taking Breaks and Stretching:
Schedule regular breaks throughout the day to stretch your wrists and hands, preventing stiffness and reducing the risk of overuse injuries.
Strengthening Exercises:
Incorporating specific hand and wrist strengthening exercises into your routine can improve the stability and resilience of the joint.
Warming Up and Cooling Down:
Before engaging in activities that require repetitive wrist movements, perform proper warm-up exercises to prepare your muscles and tendons. Similarly, cool down with gentle stretches after strenuous activities.
Proper Lifting Techniques:
When lifting objects, use proper lifting techniques to avoid straining your wrists. Bend at your knees and lift with your legs, not your back or wrists.