VAGINAL AGENESIS – SYMPTOMS, CAUSES, AND TREATMENT
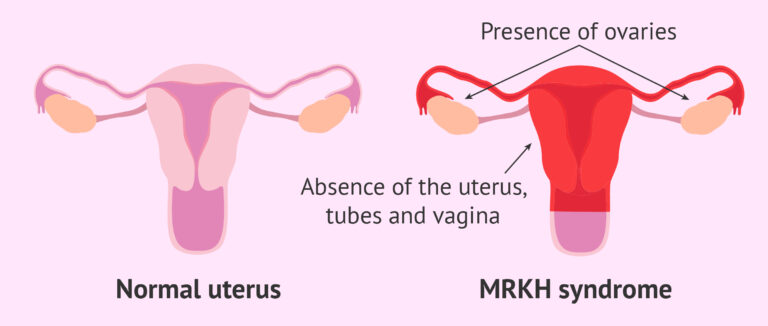
Vaginal agenesis is a rare disorder that happens when the vagina does not develop, and the womb (uterus) might only develop partially or not at all. This condition is present before birth, and might also be related to kidney, heart, or skeletal abnormalities.
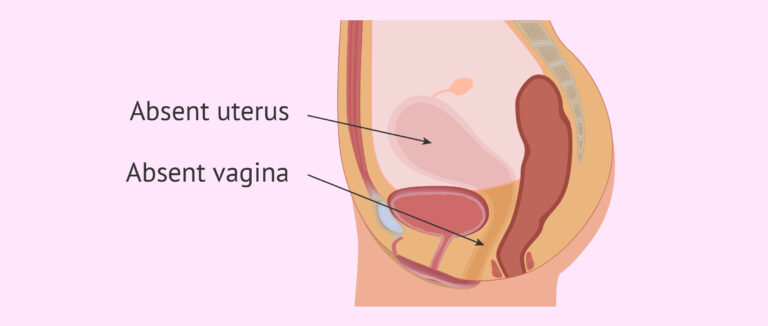
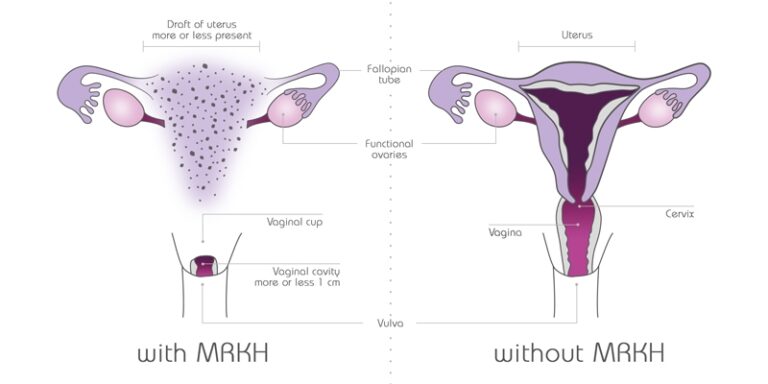
The condition is also called Mullerian aplasia or Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser (MRKH) syndrome. Surgical and nonsurgical treatments are available.
After treatment, you might be able to have a normal sex life. Women with a missing or partially missing uterus cannot get pregnant. If you have healthy ovaries, however, it might be possible to have a baby through in vitro fertilization using a gestational carrier.
SYMPTOMS
Signs and symptoms of vaginal agenesis usually go unnoticed until girls reach their teens, but do not menstruate (amenorrhea). Some women experience monthly cramping or abdominal pain.
WHEN SHOULD YOU SEE A DOCTOR?
If you have not had a menstrual period by age fifteen, see your doctor.
CAUSES
It is not clear what causes vaginal agenesis. Scientists think that at some point during the first twenty weeks of pregnancy, tubes known as the Mullerian ducts do not develop properly. Generally, one of these ducts develops into the uterus and vagina, and the other grows into fallopian tubes.
COMPLICATIONS
Prior to treatment, vaginal agenesis might impact your sexual relationships.
After the treatment, you should have a normal, satisfying sex life. However, if your uterus is also affected, you would not be able to become pregnant on your own.
DIAGNOSIS
Depending upon your age, your pediatrician or gynecologist will diagnose your condition based on your medical history and a physical examination. Vaginal agenesis diagnosis could occur at different times in your life, for example:
- As a baby, if your parents or doctor find out that you have no vaginal or anal opening
- As a young girl, during an examination for a suspected kidney issue
- During puberty, when your menstrual periods do not start even after you have developed breasts and have underarm and pubic hair
To determine your treatment options, your doctor might recommend another testing, including:
- Blood tests – Blood tests to assess your chromosomes and measure your hormone levels could confirm your diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
- Ultrasound – Ultrasound pictures show your doctor whether you have a uterus and ovaries and where your kidneys are located.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – An MRI gives your doctor a detailed image of your reproductive tract and kidneys.
TREATMENT
Treatment for vaginal agenesis usually happens in the late teens or early 20s, but you might wait until you are older. If your parents learned about your condition when you were an infant or young girl, you might begin treatment earlier.
Depending on your individual condition, your doctor might recommend one of the following courses of treatment.
Self-dilation
As a first step, your doctor will likely recommend self-dilation. Self-dilation might allow you to create a vagina without surgery. You press a small, round rod (dilator) against your skin or inside your existing vagina for thirty minutes to two hours a day.
Your skin stretches more easily after a warm bath, so that might be the best time to do it. As the weeks go by, you switch to bigger dilators. It might take a few months to get the result you want.

Vaginal dilation through intercourse
This method has not yet been well-studied, but an option for self-dilation is vaginal dilation through frequent intercourse for women who have willing partners.
Artificial lubrication is usually required. Bleeding and pain are possible side effects, particularly in the starting. If you would like to give this method a try, talk to your doctor about the best way to proceed.
Surgery
If self-dilation does not work, surgery to create a functional vagina (vaginoplasty) might be an option. Doctors generally delay surgical treatments until you have the maturity to handle follow-up dilation.
Options for vaginoplasty surgery include:
- Using a skin graft (McIndoe procedure) – In the McIndoe procedure, your surgeon uses skin from your buttocks to make a vagina. Your surgeon makes an incision in the area where you will have your vagina, inserts the skin graft to make the structure, and places a mold in the newly formed canal. The mold remains in place for 1 week.
After that, you use a vaginal dilator, identical to a firm tampon, which you remove when you use the bathroom or have sexual intercourse. After about three months, you will use the dilator only at night. Sexual intercourse with artificial lubrication and occasional dilation helps you to maintain a functional vagina. - Inserting a medical device (Vecchietti procedure) – In the Vecchietti procedure, your surgeon puts an olive-shaped device at your vaginal opening. Using a thin, lighted viewing instrument (laparoscope) as a guide, your surgeon joins the olive-shaped device to a separate traction device on your lower abdomen.
You tighten the traction device every day, slowly pulling the olive-shaped device inward to create a vagina over about a week. After your doctor removes the device, you will require further manual dilation. Sexual intercourse will likely need artificial lubrication. - Using a portion of your colon (bowel vaginoplasty) – In a bowel vaginoplasty, your surgeon diverts a portion of your colon to an opening in your genital area, making a new vagina. Your surgeon then re-joins your remaining colon. You would not have to use a vaginal dilator every day after this surgery, and you are less likely to need artificial lubrication for sexual intercourse.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from vaginal agenesis, our expert providers at Specialty Care Clinics will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call us on (469) 545-9983 to book an appointment with our specialists.
