FATTY LIVER DISEASE
Fatty liver or hepatic steatosis is caused due to fat build up in the liver. Liver is the second largest organ in the human body. Small amount of fat in the liver is normal but a large amount of fat leads to health problems.
Liver processes the nutrients from food & drinks and filters the harmful substances from the blood. It plays an important role in digestion of food, storage of energy, and removal of poisons.
Large amounts of fat in the liver would cause liver inflammation, damaging the liver and creating scarring to the liver cells. In severe cases, the scarring might even lead to liver failure.
Liver supports multiple life-supporting functions like:
- Producing bile that helps with digestion.
- Producing proteins
- Storing iron
- Converting nutrients into energy.
- Creating substance helps in blood clot (healing wounds).
- Making immune factors to fight infections
- Removing bacteria and toxins (substance harming body) from blood.
CAUSES OF FATTY LIVER
Build-up of excess fat in the liver or the fat that doesn’t metabolize efficiently is stored in liver cells, where the fat accumulates and causes fatty liver disease. A tiny amount of fat in liver cells is normal and the liver is considered fatty if fat in liver cells is more than 5%.
Fatty liver is mainly caused due to alcohol abuse known as alcohol-related liver disease but they might also be caused due to non-alcoholic liver condition. Non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) is majorly the initial and reversible stage of liver disease.
The other reasons that play important role in fatty liver condition are:
- Obesity
- High blood sugar
- Resistance to insulin
- High fat levels, mainly triglycerides, in the blood
- Pregnancy
- Rapid weight loss
- Some infections, like hepatitis C
- Side effects of certain medications, like methotrexate (Trexall), tamoxifen (Nolvadex), amiodarone (Pacerone), and valproic acid (Depakote)
- Exposure to some toxins
ALCOHOLIC FATTY ACID DISEASE
The over consumption of alcohol or alcohol abuse causes damage to the liver, leading to fat buildup, inflammation, and scarring. The liver helps in breaking down the alcohol, so it could be removed from the body. This process of breaking down of alcohol could generate harmful substances damaging liver cells, promoting inflammation, and weakening the body’s natural defense system.
Alcoholic fatty liver disease is considered the earliest stage of alcohol-related liver disease which might progress to next stages like alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis.
The first stage is reversible and the liver could return to its normal state after 2weeks of stopping alcohol consumption. Alcoholic hepatitis is caused due to alcohol misuse for a long time or binge drinking (large amounts of alcohol in a short duration of time). Mild damage from alcoholic hepatitis is reversible however it might be life threatening in case of serious infection.
Cirrhosis is the final stage and it is irreversible. However, stopping drinking alcohol immediately could prevent further damage to the liver and increase life expectancy. The risk of developing alcoholic fatty liver disease is higher in women who are heavy drinkers and have obesity, or certain genetic mutations.
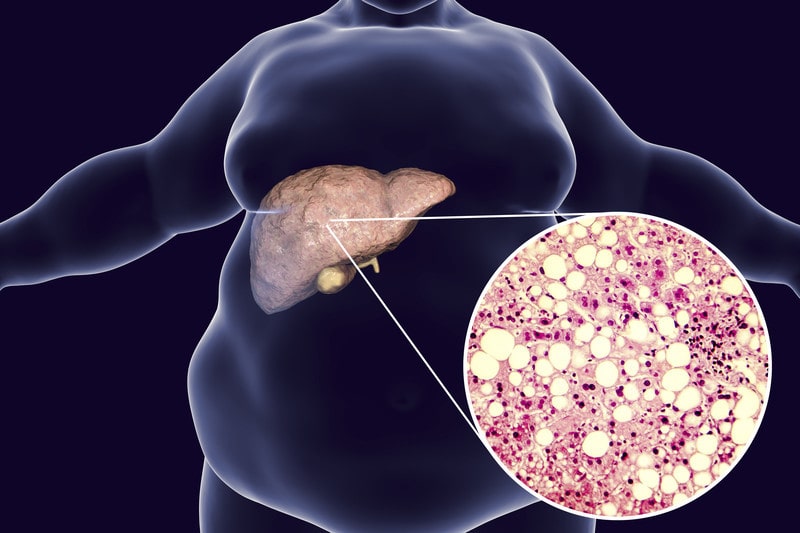
NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE (NAFLD)
NAFLD is an umbrella term combining a range of liver conditions affecting people who consume little to no alcohol. It is the most common liver disease. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is divided into isolated fatty liver that involves accumulation of fat, and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) that involves fat accumulation along with inflammation, and damage to liver cells.
NASH progresses to fibrosis or scarring of the liver and ultimately leading to cirrhosis. NAFLD is majorly caused by obesity and diabetes in people who do not consume alcohol as it is considered a manifestation to metabolic syndrome. Although it can occurs in individuals who are neither obese nor diabetic also.
People suffering from type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure or blood sugar, infections like hepatitis C, low level of HDL cholesterol, metabolic syndrome or surgeries like gallbladder removal are at higher risk of developing NAFLD. It could also be caused due to certain medications like glucocorticoids, methotrexate (Rheumatrex, Trexall), synthetic estrogen, tamoxifen (Nolvadex, Soltamox), however it is rare in this condition.
SYMPTOMS OF FATTY LIVER
NAFLD and alcoholic fatty liver disease are majorly silent diseases with few or sometimes no symptoms. The symptoms of alcoholic fatty liver or NAFLD disease would include:
- Abdominal or belly pain or a feeling full in the upper right side of the abdomen
- Feeling sick or nausea
- Edema or swollen abdomen or legs
- Sudden weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Redness in palms
- Breasts are larger than normal in men
- Confusion or drowsiness
- Vomiting blood or passing blood in your stools
DIAGNOSIS OF FATTY LIVER
Sometimes there might be no symptoms which make it difficult to diagnose fatty liver disease. Doctors might suspect fatty liver due to abnormal liver test results that were advised due to other underlying medical conditions.
They would check for your medical history, physical examination and various tests, including blood (liver function tests and blood count tests) and imaging tests (ultrasound and CT scan), and a biopsy to confirm fatty liver disease and its current stage. FibroScan is a specialized ultrasound that could be used instead of a liver biopsy to diagnose the amount of fat and scar tissue in the liver.
Imaging tests would determine the fat in the liver and the stiffness that indicates fibrosis or scarring of liver. Biopsy would help determine the extent of liver damage.

TREATMENT OF FATTY LIVER
There’s no particular medication for fatty liver disease. Health care professionals would focus on controlling the factors that contribute to the condition. Lifestyle changes like limiting or avoiding alcohol, losing weight as well as making changes to your diet would help reverse the fatty liver disease in starting stages.
The treatment regime would include lifestyle changes, medications and surgery.
Lifestyle changes –
This is the first line of treatment involving:
- Losing weight
- Reducing or cutting alcohol intake
- Eating a nutrient-rich diet which is low in excess calories, saturated fat, and trans fats
- At least 30 minutes of exercise almost everyday
- Vitamin E supplements help in preventing or treating liver damage
- Limiting consumption of refined carbohydrates or saturated fats and trans fat
- Eating diet rich in plant based foods like fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains
- Vaccination for infectious diseases like hepatitis A and B, flu and pneumococcal disease
Medications – Corticosteroids or pentoxifylline are used for reducing inflammation in the liver with acute alcoholic hepatitis. Other medications and treatment options that provide speedy recovery are probiotics and antibiotics (to fight bacterial infection), stem cell therapy and medicines that target the inflammation pathway. Supplements like milk thistle, or silymarin, vitamin E, berberine or omega-3 fatty acids help in reducing the inflammation and symptoms related to liver damage.
Insulin sensitizers are used to treat diabetes that might cause liver damage.
Surgery – Liver transplant is the last resort in case of liver failure, liver complications or cirrhosis. Weight loss is important for reducing liver damage. Bariatric surgery is helpful in getting rid of unwanted fat through the gastrointestinal tract.
OUTLOOK
Fatty liver could be controlled and reversed in early stages. The main complication for alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty liver conditions is cirrhosis, or scarring of your liver which might be life-threatening.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from severe pain in your abdomen, our expert providers at Specialty Care Clinics will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call us on (469) 545-9983 to book an appointment with our specialists.
