Whiplash Injury: A Comprehensive Guide for effective Treatment, & Recovery
Whiplash injury is a common result of sudden acceleration or deceleration, often occurring during car accidents, sports collisions, or falls. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of whiplash, including its symptoms, causes, and various treatment options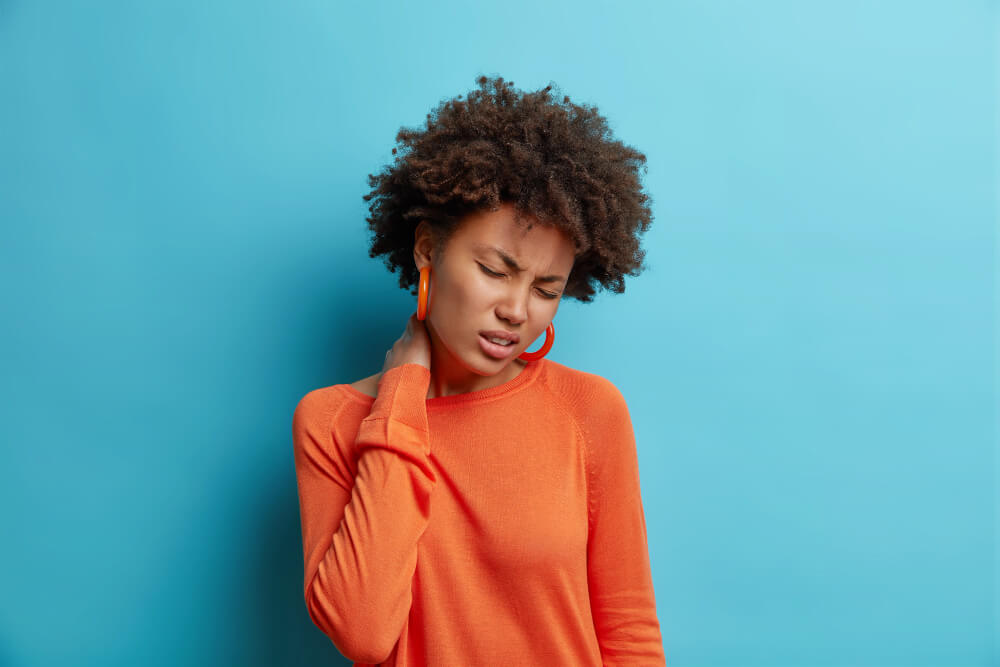
Unraveling Whiplash: What Causes It?
Whiplash occurs when the neck undergoes a rapid back-and-forth movement, resembling the cracking of a whip. This abrupt motion puts immense strain on the cervical spine, leading to injury. The primary causes of whiplash include:
- Car Accidents: Rear-end collisions are the most common cause of whiplash. The sudden impact can force the neck beyond its normal range of motion, resulting in injury.
- Sports Injuries: Athletes engaged in contact sports, such as football or hockey, are susceptible to whiplash. Impact or collisions during play can cause the neck to hyperextend or hyperflex.
- Physical Assault: Any incident involving forceful blows to the head or neck, such as physical assault, can lead to whiplash.
Recognizing Whiplash Symptoms
Whiplash symptoms can manifest immediately after the injury or take several days to appear. Understanding these signs is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment. Common whiplash symptoms include:
- Neck Pain: Persistent pain in the neck is a hallmark symptom of whiplash. The severity can vary, ranging from mild discomfort to debilitating pain.
- Stiffness: Whiplash often causes stiffness in the neck, limiting the range of motion. Patients may find it challenging to turn their heads or tilt them in different directions.
- Headaches: Intense headaches, often originating from the base of the skull, can be a result of whiplash. These headaches may be accompanied by dizziness or nausea.
- Fatigue: Whiplash can lead to chronic fatigue, affecting the overall energy levels of the individual.
Diagnosing Whiplash
Diagnosing whiplash involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history, a physical examination, and sometimes, imaging tests. Common diagnostic tools include:
- Medical History: Gathering information about the incident and understanding the patient’s symptoms is crucial for accurate diagnosis.
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination of the neck’s range of motion, tenderness, and muscle strength helps identify signs of whiplash.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans may be recommended to assess the extent of damage to the cervical spine and surrounding tissues.
Treatment Options for Whiplash
The treatment approach for whiplash aims to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and restore normal neck function. Depending on the severity of the injury, various treatment options are available:
1. Rest and Ice
In the initial stages of whiplash, rest is crucial for allowing the body to heal. Applying ice to the affected area helps reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
2. Medications
Pain relievers, muscle relaxants, and anti-inflammatory medications may be prescribed to manage whiplash symptoms. These can provide temporary relief and aid in the recovery process.
3. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in whiplash recovery. Targeted exercises help improve neck strength, flexibility, and overall function. Therapists may also employ techniques such as massage and ultrasound therapy.
4. Neck Braces and Collars
In some cases, wearing a neck brace or collar may be recommended to provide support and limit movement during the initial stages of recovery.
5. Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic adjustments can help realign the spine and reduce tension in the neck muscles, promoting healing and pain relief.
6. Injection Therapy
For severe cases of whiplash, injections such as corticosteroids may be administered to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
Long-Term Effects and Complications
While most individuals recover from whiplash with proper treatment, some may experience long-term effects or complications. Chronic pain, stiffness, and recurring headaches are potential issues that may require ongoing management.
Preventing Whiplash
Preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of whiplash. These include:
- Proper Headrest Positioning: Adjusting car headrests to the appropriate height and positioning can minimize the impact of a rear-end collision.
- Seatbelt Use: Wearing seatbelts is crucial for minimizing the risk of injury during car accidents.
- Strengthening Neck Muscles: Engaging in exercises to strengthen neck muscles can enhance their ability to absorb shock and reduce the risk of whiplash.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding whiplash, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for both healthcare professionals and the general public. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment significantly contribute to the successful recovery of individuals affected by whiplash injuries. By incorporating preventive measures and adopting a multidisciplinary approach to treatment, we can minimize the impact of whiplash on individuals’ lives and enhance overall neck health.