Understanding Tendinitis: Relief Strategies with the Help of Orthopedics
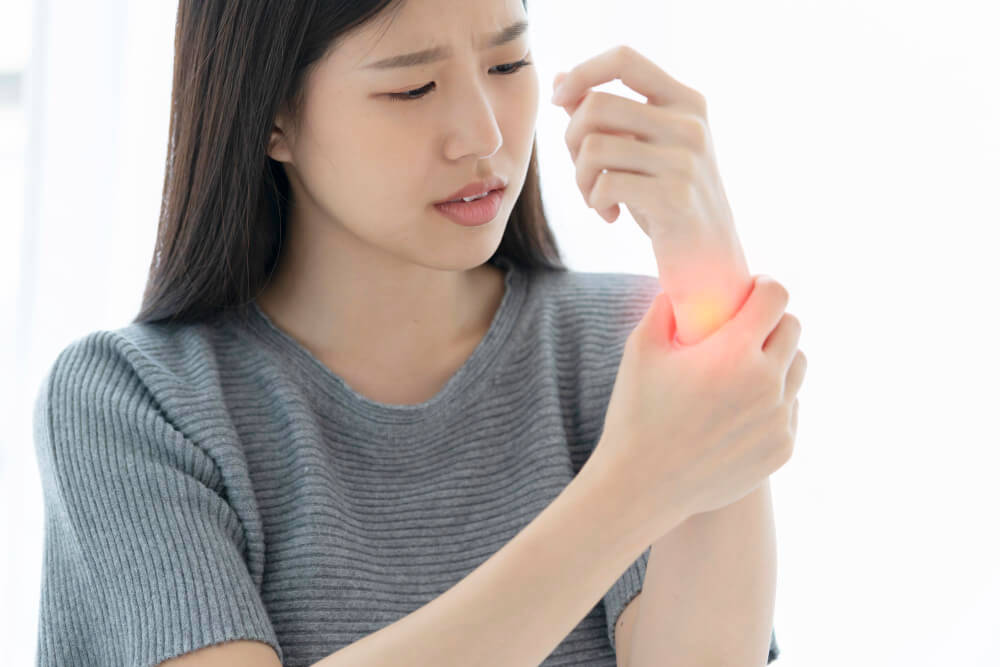
Tendinitis, a common musculoskeletal condition, affects millions of people worldwide. It refers to the inflammation of a tendon, the fibrous tissue that connects muscle to bone. This inflammation causes pain, tenderness, and stiffness around the affected joint. While tendinitis can occur anywhere in the body, it most frequently affects the shoulders, elbows, wrists, knees, and ankles.
This article delves into the world of tendinitis, exploring its causes, symptoms, and various treatment options offered by orthopedic specialists. We’ll also discuss how an orthopedic approach can help you manage tendinitis effectively and get back to your daily activities.
Delving into the Causes of Tendinitis
Tendinitis often arises from repetitive motions that overuse a particular tendon. This overuse can cause micro-tears in the tendon, leading to inflammation and pain. Some common activities that can trigger tendinitis include:
- Sports: Activities like throwing, running, or racquet sports can put excessive stress on specific tendons.
- Repetitive Jobs: Jobs involving repetitive movements, such as typing, construction work, or assembly lines, can also contribute to tendinitis.
- Improper Technique: Performing exercises or activities with incorrect form can increase the risk of overuse and tendinitis.
- Age: As we age, tendons naturally lose elasticity and become more susceptible to injury.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Tendinitis
The telltale signs of tendinitis can vary depending on the location of the affected tendon. However, some general symptoms include:
- Pain: This is the most common symptom, typically characterized as a dull ache or sharp pain around the affected joint. The pain may worsen with activity and improve with rest.
- Tenderness: The area around the inflamed tendon will often be tender to the touch.
- Stiffness: You might experience stiffness in the joint, especially in the mornings or after periods of inactivity.
- Reduced Range of Motion: The inflammation can limit your ability to move the affected joint through its full range of motion.
- Swelling: In some cases, the affected area may become swollen.
Seeking Relief: Treatment Options for Tendinitis
Fortunately, most cases of tendinitis respond well to non-surgical treatments. Here’s an overview of the different approaches an orthopedic specialist might recommend:
The RICE Method – A Foundation for Healing
The RICE method serves as a cornerstone for managing tendinitis symptoms. It stands for:
- Rest: Avoid activities that aggravate the pain. Allow the inflamed tendon time to heal.
- Ice: Apply ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day. Wrap the ice pack in a towel to prevent skin irritation.
- Compression: Use a compression bandage or wrap to reduce swelling and inflammation.
- Elevation: Elevate the affected joint above the level of your heart whenever possible to minimize swelling.
Medication for Pain Relief
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or naproxen sodium, can help manage pain and inflammation associated with tendinitis. Your orthopedic specialist may also consider stronger medications or injections in severe cases.
Physical Therapy – Strengthening and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in regaining strength and flexibility in the affected area. A physical therapist will design a customized exercise program to:
- Reduce inflammation: Gentle stretches and massage techniques can promote better blood flow and reduce inflammation.
- Strengthen muscles: Strengthening the muscles surrounding the joint helps support the tendon and prevent future injury.
- Improve flexibility: Stretching exercises improve range of motion in the affected joint.
Corticosteroid Injections
In situations where other treatments haven’t provided adequate relief, your doctor may consider corticosteroid injections. These injections deliver a powerful anti-inflammatory medication directly to the inflamed tendon, providing targeted pain relief. However, corticosteroid injections are typically used sparingly due to potential side effects with repeated use.
When Surgery Might Be Necessary
While surgery is rarely necessary for tendinitis, it might be considered in chronic cases where other treatments haven’t been successful. The specific surgical procedure will depend on the location and severity of the tendinitis.
The Orthopedic Advantage in Managing Tendinitis
Orthopedic specialists are medical professionals with extensive training in diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal disorders like tendinitis. Partnering with an orthopedic specialist offers several advantages, including:
- Accurate Diagnosis: An orthopedic doctor can accurately diagnose the type and location of your tendinitis through a physical examination, imaging tests (X-rays, ultrasounds), and other diagnostic tools.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Orthopedists tailor treatment plans based on your individual needs, considering your activity level, overall health, and severity of the condition.