Understanding Bone Fractures: Types, Treatments, and Recovery
A bone fracture, also known as a broken bone, is a break or crack in the bone structure. It’s a common injury that can occur due to various factors like falls, accidents, sports injuries, or underlying medical conditions that weaken bones. While fractures can be painful and disruptive, understanding the different types, treatment options, and recovery process can help you navigate this experience with greater knowledge and confidence.
Types of Bone Fractures
Fractures can be categorized based on several factors, including the severity of the break, the location, and the presence of any additional injuries. Here’s a breakdown of some common types:
- Closed Fracture: This is the most common type, and the broken bone doesn’t pierce the skin.
- Open Fracture: Also known as a compound fracture, the broken bone breaks through the skin, increasing the risk of infection.
- Comminuted Fracture: The bone breaks into multiple fragments.
- Greenstick Fracture: This type is common in children, where the bone bends and cracks but doesn’t fully break through.
- Stress Fracture: This occurs due to repetitive stress on a bone, often seen in athletes.
- Avulsion Fracture: A small piece of bone is pulled away from the main bone due to a ligament or tendon tear.
- Stable Fracture: The broken bone fragments are aligned and don’t move significantly.
- Unstable Fracture: The broken bone fragments are misaligned or move excessively, requiring additional support.
Signs and Symptoms of a Fracture
While pain at the injury site is a common symptom, other signs of a fracture can include:
- Swelling, bruising, and redness around the affected area
- Deformity of the bone
- Difficulty moving the injured limb
- Numbness or tingling in the area
- A popping or cracking sound at the time of injury
It’s important to remember that these symptoms can sometimes overlap with other injuries. If you suspect a fracture, seeking immediate medical attention is crucial to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis of a Fracture
Diagnosis of a fracture typically involves a combination of:
- Physical examination: The doctor will examine the affected area for swelling, tenderness, and mobility.
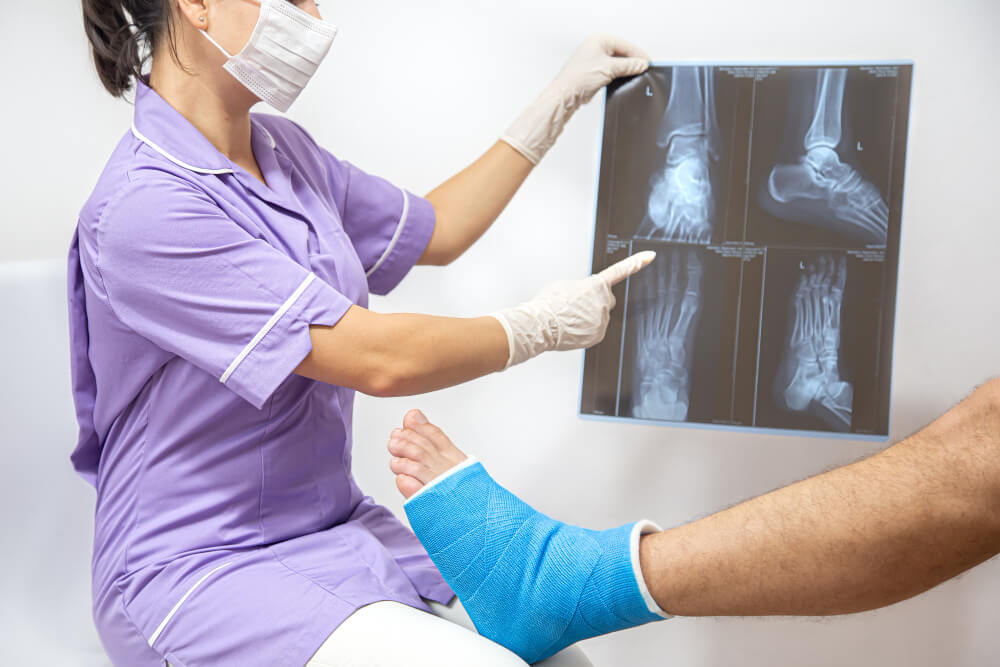
- X-rays: These provide detailed images of the bones and help confirm the presence and location of the fracture.
- CT scan or MRI: In some cases, additional imaging tests like CT scans or MRIs may be needed to assess the extent of the damage, especially around joints or complex fractures.
Treatment Options for Fractures
The treatment plan for a fracture depends on various factors, including the type, severity, and location of the fracture, as well as your overall health and age. Here’s an overview of the common treatment options:
- Immobilization: This involves restricting movement of the broken bone to promote healing. This can be achieved through:
- Casts: These are made of plaster or fiberglass and provide a rigid form of immobilization.
- Splints: These are less rigid than casts and are often used for temporary immobilization or in areas where casting is difficult.
- Braces: These offer support and limited movement to the injured area.
- Reduction: This involves realigning the broken bone fragments. In some cases, this can be done manually by a doctor, while other fractures may require surgery for proper alignment.
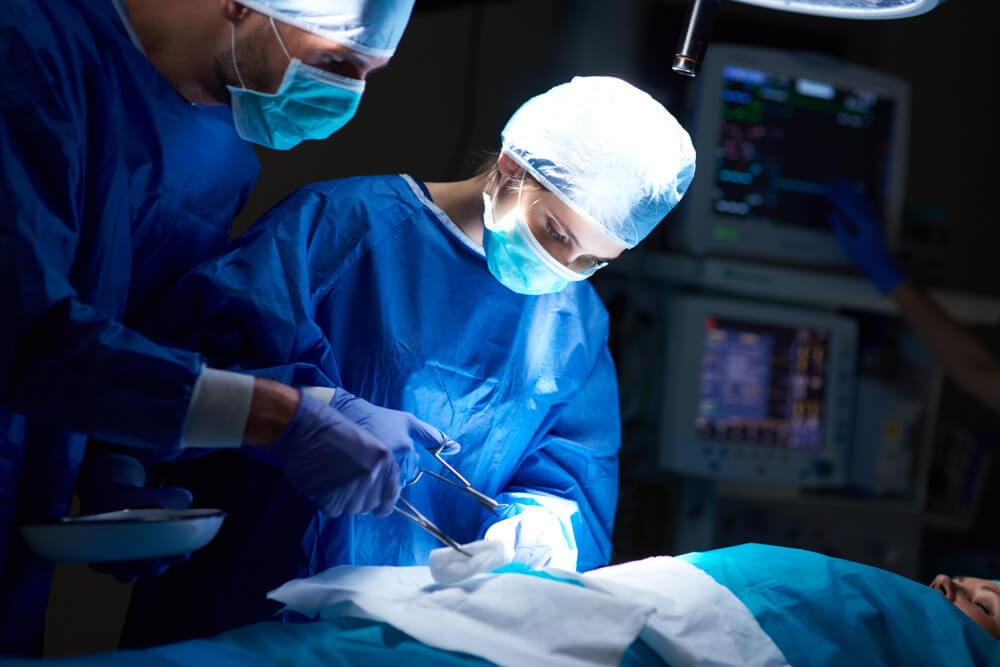
- Surgery: Surgery may be necessary for certain types of fractures, especially those that are unstable, displaced, or located near joints. Different surgical techniques exist, such as using plates, screws, pins, or rods to hold the bones together while they heal.
- Medication: Pain medication may be prescribed to manage pain and discomfort during the healing process.
- Physical Therapy: After the initial healing period, physical therapy can help regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the affected area.
Recovery from a Fracture
The recovery time for a fracture varies significantly depending on the type and severity of the injury, as well as individual factors. In general, simpler fractures take several weeks to heal, while complex fractures can take months or even longer.
Here are some tips for promoting a smooth recovery:
- Follow your doctor’s instructions: This includes wearing the cast or brace as instructed, taking medications as prescribed, and attending physical therapy sessions.
- Rest: Allow your body adequate rest to facilitate healing.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eat a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D for optimal bone health.
- Apply ice: Apply ice packs to the affected area to reduce swelling and pain in the initial stages of healing.
- Elevate the injured limb: This helps reduce swelling and pain, especially for fractures in the lower extremities.