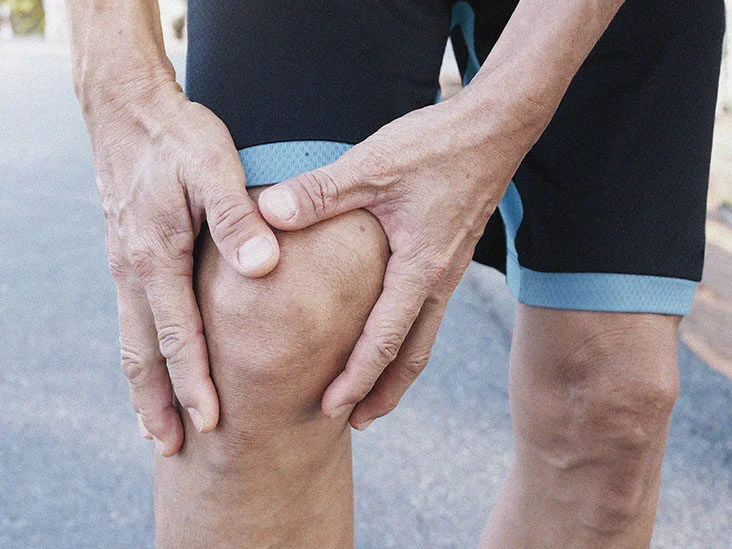
Meniscal tears are a common knee injury that can significantly impact daily life. Recognizing the signs and symptoms is crucial for early intervention and effective management. In this guide, we’ll delve into the world of meniscal tears, helping you decode the signals your knees might be sending.
The meniscus, a rubbery cartilage in the knee, acts as a cushion and stabilizer. Tears can occur due to sudden twists, pivots, or degenerative processes associated with aging. Identifying the signs early allows for timely treatment and can prevent long-term complications.
Concerned about meniscal tears and seeking expert guidance? Contact Specialty Care Clinics at (469) 545-9983. Our specialized team offers comprehensive solutions for meniscal injuries, from accurate diagnosis to personalized treatment plans.
Signs and Symptoms:
Pain and Swelling:
Persistent pain, especially along the joint line, is a key indicator. Swelling often accompanies the pain and may be noticeable within the first 24 hours after the injury.
Limited Range of Motion:
Meniscal tears can restrict the normal range of motion in the knee. If you find it challenging to fully extend or flex your knee, it could be a sign of a tear.
Joint Locking or Catching:
Some individuals with meniscal tears experience a sensation of the knee “locking” or “catching” during movement. This occurs when a torn piece of the meniscus interferes with joint function.
Popping Sounds:
A popping sound at the time of injury or during subsequent movements can be indicative of a meniscal tear. This sound is caused by the torn cartilage shifting within the joint.
Tenderness:
Tenderness around the knee joint, particularly along the joint line, is a common symptom of meniscal tears. Gently pressing on the area may elicit discomfort.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Physical Examination:
A healthcare professional will conduct a thorough physical examination, evaluating range of motion, stability, and specific maneuvers to assess for meniscal injury.
Imaging Tests:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a valuable tool for visualizing the extent and location of meniscal tears. It offers finely detailed pictures to help with precise diagnosis.
Conservative Treatments:
Minor tears may respond well to conservative treatments, including rest, ice, compression, and elevation (R.I.C.E), along with physical therapy to strengthen supporting muscles.
Medications:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation associated with meniscal tears.
Invasive Procedures:
For more severe tears, surgical interventions such as arthroscopy may be recommended to either repair the tear or trim the damaged portion of the meniscus.
Preventing Meniscal Tears:
While not all meniscal tears are preventable, certain measures can reduce the risk:
- Before engaging in physical activity, perform appropriate warm-up exercises.
- Focus on strength and flexibility training for the lower limbs.
- Use proper techniques during sports and activities to minimize the risk of sudden twists.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of meniscal tears is the first step towards effective management. If you suspect a meniscal injury, consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan. Early intervention is key to restoring knee health and preventing long-term complications. Listen to your body, be aware of the signals it sends, and take proactive steps towards maintaining the well-being of your knees.