Meniscus Tear: Understanding the Injury and the Role of an Orthopedic Surgeon
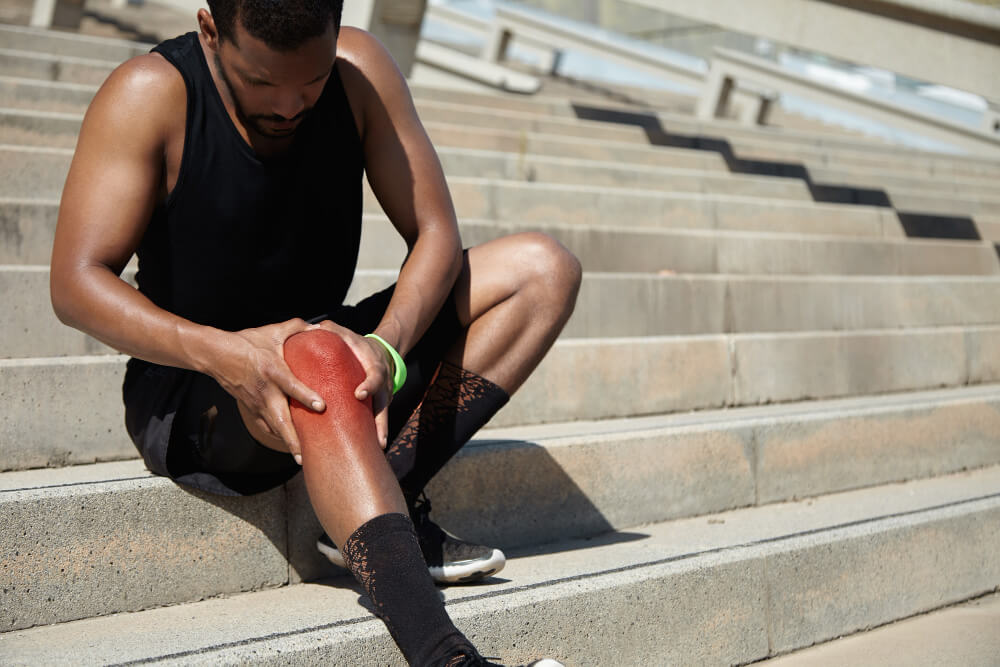
The knee joint, a marvel of biomechanics, allows us to walk, run, and jump with ease. But this intricate machinery relies on a small, crucial component called the meniscus, and when it sustains a tear, it can throw a wrench into our active lifestyles.
What is a Meniscus Tear?
The meniscus is a pair of crescent-shaped fibrocartilage pads nestled between the femur (thighbone) and tibia (shinbone) in each knee. These pads act as shock absorbers, distributing weight evenly and cushioning the joint during movement. They also provide stability and lubrication, preventing excessive bone-on-bone contact.
A meniscus tear occurs when one or both of these pads rupture. Tears can be caused by various factors, including:
- Sudden twisting or pivoting motions during sports like football, basketball, or soccer.
- Direct impact to the knee, such as a fall or collision.
- Degenerative changes from aging or overuse, leading to tears in the weakened cartilage.
Symptoms of a Meniscus Tear
The telltale signs of a meniscus tear can include:
- Pain: Sharp or stabbing pain in the knee, especially when bending, squatting, or twisting.
- Swelling: Noticeable inflammation and puffiness around the knee joint.
- Stiffness: Difficulty fully extending or flexing the knee.
- Locking: Feeling like the knee gets stuck in a bent position and won’t straighten.
- Pops or clicks: Audible popping or clicking sensations in the knee during movement.
These symptoms can vary depending on the severity and location of the tear. If you experience any of these, it’s crucial to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis.
Diagnosis and Treatment of a Meniscus Tear
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare professional, followed by imaging tests like X-rays and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). X-rays can reveal bone fractures but cannot detect meniscus tears, while an MRI provides a detailed view of the soft tissues in the knee, pinpointing the location and extent of the tear.
Treatment options for a meniscus tear depend on several factors, including the patient’s age, activity level, and the type and severity of the tear.
- Conservative Treatment: For mild tears or tears in areas with good blood supply, non-surgical treatment is often recommended. This includes:
- Rest: Avoiding strenuous activities that aggravate the pain.
- Ice: Applying ice packs to reduce swelling and inflammation.
- Compression: Wearing a knee brace to stabilize the joint.
- Elevation: Keeping the leg elevated to promote drainage and reduce swelling.
- Pain medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers can manage pain and discomfort.
- Physical therapy: Specific exercises to strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee and improve flexibility can help stabilize the joint and promote healing.
- Surgical Treatment: In cases of severe tears, tears in areas with poor blood supply, or tears that fail to respond to conservative treatment, surgical intervention might be necessary. Arthroscopic surgery, a minimally invasive procedure, is the most common approach. This involves making small incisions in the knee and inserting a camera and surgical instruments to repair or trim the torn meniscus.
The Role of an Orthopedic Surgeon
Orthopedic surgeons play a critical role in the management of meniscus tears. They are specialists in musculoskeletal disorders of the bones, joints, and muscles, equipped with the expertise to diagnose and treat meniscus tears effectively.
1 . Diagnosis:
Orthopedic surgeons perform a thorough physical examination and review the patient’s medical history to understand the cause and extent of the injury.
They interpret X-rays and MRI scans to accurately diagnose the tear and determine the optimal treatment course.
2 . Treatment:
Orthopedic surgeons can perform arthroscopic surgery to repair or trim the torn meniscus.
They can also advise on alternative treatment options, such as physical therapy or injections, based on the specific case.
They provide guidance on post-operative care and rehabilitation to ensure proper healing and recovery.
3 . Importance of an Orthopedic Surgeon:
Timely diagnosis and treatment by a qualified orthopedic surgeon can significantly improve the outcome and recovery time for patients with meniscus tears.
They can help prevent complications like arthritis and joint instability, which can occur if a meniscus tear is left untreated.
Orthopedic surgeons can also offer personalized advice and support throughout the recovery process, ensuring a smooth and successful return to activity.
Conclusion:
Meniscus tears, though common, can significantly impact your mobility and quality of life.