Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) injuries can be daunting, but surgery isn’t the only path to recovery. In this guide, we’ll delve into non-surgical treatment options for ACL injuries, offering insights into effective ways to regain strength and stability without going under the knife.
Before we explore non-surgical solutions, let’s briefly understand ACL injuries. The ACL is a crucial ligament that stabilizes the knee joint. Injuries often occur during sports that involve sudden stops, changes in direction, or direct impact.
Embarking on a non-surgical journey to recover from an ACL injury? Connect with Specialty Care Clinics at (469) 545-9983. Our specialized team is dedicated to guiding you through effective non-surgical solutions for ACL injuries. Take the first step toward a resilient and stable knee, schedule your consultation with Specialty Care Clinics today and embrace a comprehensive approach to ACL injury recovery.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options:
Rest and Activity Modification:
Embracing a period of rest and modifying activities that stress the knee allows the ACL to heal naturally. Avoiding strenuous movements and opting for low-impact exercises are key components.
Physical Therapy:
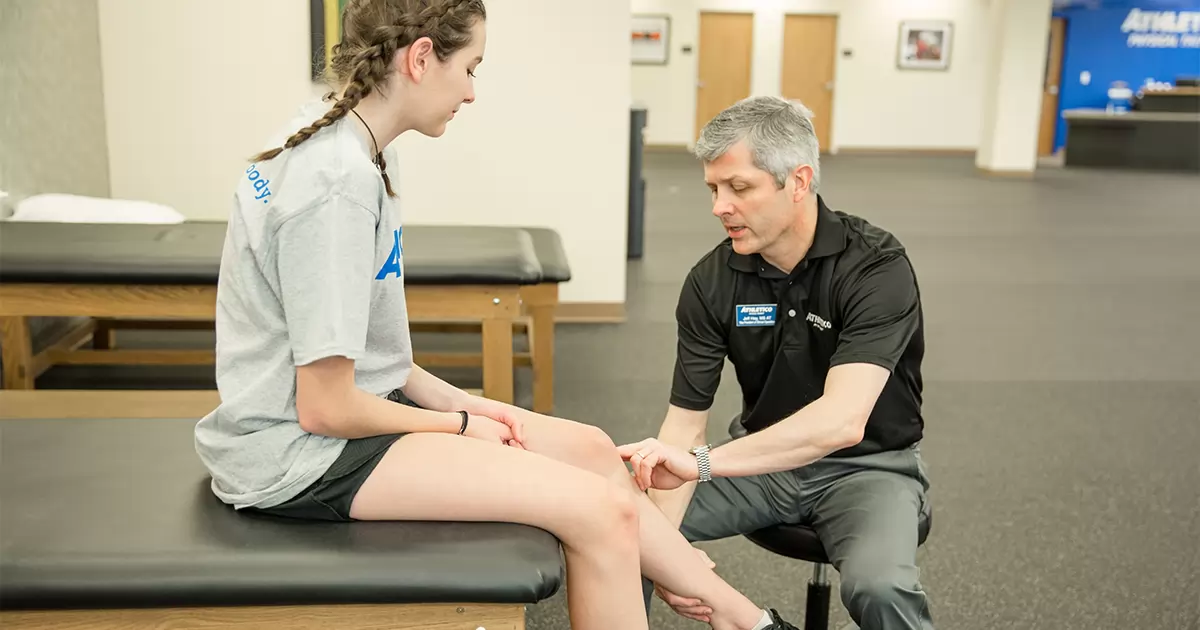
Engaging in physical therapy is a cornerstone of non-surgical ACL injury recovery. Therapists tailor exercises to strengthen surrounding muscles, improve range of motion, and enhance overall knee stability.
Bracing:
Knee braces provide external support, reducing stress on the ACL during movement. They can be particularly beneficial during rehabilitation and when returning to physical activities.
Anti-Inflammatory Medications:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage pain and reduce inflammation, contributing to a more comfortable recovery process.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
PRP therapy involves injecting a concentrated form of the patient’s blood, rich in healing factors, into the injured area. This can promote tissue repair and enhance the natural healing process.
Strengthening Exercises:
Targeted exercises focusing on the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles contribute to overall knee stability. Building strength in these muscle groups can compensate for the injured ACL.
Functional Training:
Functional exercises mimic real-life movements and activities, helping individuals regain confidence in using their knee in day-to-day scenarios.
Recovery and Prevention:
Gradual Return to Activities:
Non-surgical recovery often involves a gradual return to regular activities. Physical therapists guide individuals through a phased approach, ensuring the knee adapts to increasing levels of stress.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Incorporating lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding activities that place excessive strain on the knee, can prevent future injuries and support overall joint health.
Non-surgical treatment options for ACL injuries offer a viable and effective path to recovery. Whether you’re an athlete or someone navigating daily life, these approaches focus on strengthening the knee, improving stability, and promoting a natural healing process. It’s essential to consult with healthcare professionals to create a personalized non-surgical treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. With dedication to rehabilitation and a focus on long-term knee health, individuals can achieve significant improvements without opting for surgery.