WHAT IS CHRONIC PAIN?
Chronic pain refers to pain that lasts for months or years. It could occur anywhere in the body. The pain could be there all the time, or it might come and go.
Chronic pain could interfere with your daily activities, like working, having a social life, and taking care of yourself or others. It could lead to depression, anxiety, and trouble sleeping, which could make the pain worse. This response creates a cycle that is difficult to break.
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN CHRONIC PAIN AND OTHER PAIN?
Chronic pain differs from another type of pain known as acute pain. Acute pain occurs when something hurts you. It does not last long, and it goes away after your body heals from whatever caused the pain. In contrast, chronic pain continues long after you recover from an injury or disease. Sometimes it even occurs for no obvious reason.
CHRONIC PAIN SYMPTOMS
People with chronic pain describe it in many different ways, like:
- Aching
- Burning
- Shooting
- Squeezing
- Stiffness
- Stinging
- Throbbing
Chronic pain usually leads to other symptoms and problems, too:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Fatigue, or feeling overly tired most of the time
- Insomnia or trouble falling asleep
- Mood swings
CHRONIC PAIN CAUSES
Sometimes chronic pain has a clear cause. You might have a long-lasting disease like arthritis or cancer that could cause ongoing pain.
But injuries and diseases could also cause changes to your body that leave you more sensitive to pain. These changes could stay in place even after you have healed from the original injury or disease. So something like a sprain, a broken bone, or a brief infection could leave you with chronic pain.
Some people also have chronic pain that is not tied to an injury or physical disease. Healthcare professionals call this response psychogenic pain or psychosomatic pain. It is caused by psychological factors like stress, anxiety, and depression. Many scientists believe that this connection comes from low levels of endorphins in the blood. Endorphins are natural chemicals that start positive feelings.
It is possible to have several causes of pain overlap. You could have two different diseases, for instance. Or you can have something like migraines and psychogenic pain together.
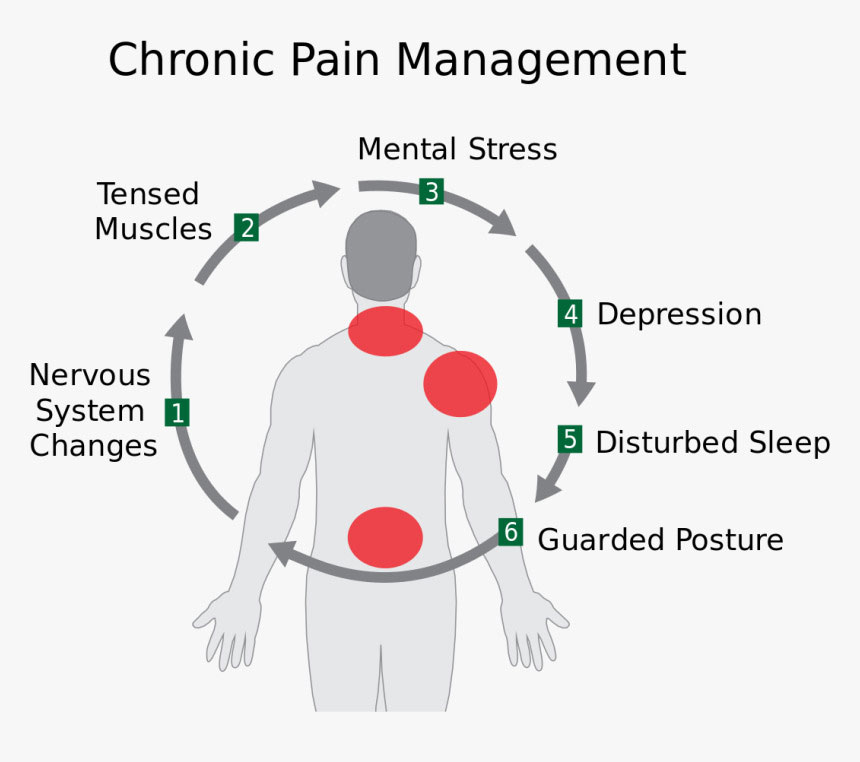
CHRONIC PAIN PREVENTION
You might be able to prevent specific conditions that lead to chronic pain. For instance, you could quit smoking to reduce your risk of lung cancer. But nothing has been proven to stop chronic pain more broadly.
WHERE DO PEOPLE HAVE CHRONIC PAIN?
Chronic pain could come in many different forms and appear across the body:
- Arthritis, or joint pain
- Back pain
- Cancer pain near a tumor
- Headaches, including migraines
- Lasting pain in scar tissue
- Muscle pain all over (like with fibromyalgia)
- Neurogenic pain, from damage to the nerves or other portions of the nervous system
CHRONIC PAIN DIAGNOSIS
Pain is subjective only the person experiencing it could identify and describe it. If you have long-lasting pain, look for medical attention. A healthcare professional will want to know about this:
- Where the pain is
- How intense it is, on a scale between 0 and 10
- How often it happens
- How much it is affecting your life and work
- What makes it worse or better?
- Whether you are experiencing significant stress or anxiety in your life.
- Whether you have had any diseases or surgeries
Your healthcare provider might check your body and order tests to look for the cause of the pain:
- Blood tests
- Electromyography to test muscle activity
- Imaging tests, like X-rays and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Nerve conduction studies to see if your nerves are responding properly
- Reflex and balance tests
- Spinal fluid tests
- Urine tests

CHRONIC PAIN TREATMENT AND CHRONIC PAIN MANAGEMENT
How is chronic pain treated?
To ease chronic pain, healthcare professionals first try to identify and treat the cause. But sometimes they cannot find the source. If this is the case, they turn to treating, or managing, the pain.
Healthcare professionals treat chronic pain in many different ways. The approach depends upon the type of pain, its cause if known and other factors that vary from person to person. The best treatment plans use a variety of strategies medications, lifestyle modification, and therapies.
WHAT MEDICATIONS COULD TREAT CHRONIC PAIN?
Your healthcare professional might recommend specific medications to ease chronic pain:
- Anticonvulsants (medications that stop seizures) for nerve pain
- Antidepressants like tricyclic antidepressants
- Corticosteroids
- Muscle relaxers
- Opioids (narcotics), which could be addictive and should be used carefully.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or acetaminophen
- Topical products applied to the skin that contains pain relievers or ingredients that create soothing heat or cold.
- Sedatives to help with anxiety or insomnia
COULD THERAPY HELP WITH CHRONIC PAIN?
Specific therapies also might help you manage chronic pain:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) – This counseling approach helps you think differently about pain and teaches you ways to cope.
- Counseling – Talk therapy could help you manage chronic pain, particularly psychogenic pain.
- Occupational therapy – Activities teach you how to do everyday tasks differently to lower pain or circumvent injury.
- Physical therapy – Exercises or workouts stretch and strengthen your body.

WHAT ALTERNATIVE TREATMENT OPTIONS ARE AVAILABLE FOR CHRONIC PAIN?
Specific lifestyle alterations and types of alternative medicine have also been shown to ease chronic pain over time:
- Acupuncture, which uses small needles placed in the body.
Aromatherapy, which uses crushed plants. - Biofeedback, which teaches you how to change the way your body works, influencing things like heart rate, breathing, and muscle tension.
- Exercises for example walking, swimming, yoga, and tai chi.
- Hypnotherapy, or hypnosis.
- Mindfulness training, which teaches you how to calm yourself down.
- Music, art, or pet therapy.
- Reiki or Healing Touch, with a therapist using touch to change energy fields in your body.
- Relaxation techniques, like massage, meditation, and guided imagery.
- Stress reduction
WHAT OTHER MEDICAL TREATMENT OPTIONS ARE AVAILABLE?
Your healthcare provider might also try:
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) delivers small shocks throughout patches on the skin. The electrical impulses could ease the pain.
- Nerve blocks inject anesthetic near the site of pain to reduce feeling in the region.
IS THERE A CURE FOR CHRONIC PAIN?
There is no cure for chronic pain, other than to determine and treat its cause. For instance, treating arthritis could sometimes stop joint pain.
But many people with chronic pain do not know its cause and cannot find a cure. They use a combination of medications, therapies, and lifestyle changes to lower pain.
CONCLUSION
Chronic pain generally does not go away, but you could manage it with a combination of strategies that work for you. Researchers are continuing their research into pain disorders. Advances in neuroscience and improved understanding of the human body are expected to lead to more effective treatments.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from chronic pain, our expert providers at Specialty Care Clinics will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call (469) 545-9983 to book a telehealth appointment for an at-home check-up.
