WHAT IS HYPERTHYROIDISM?
The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland in the front of our neck. It regulates the release of hormones that dictate how the body’s cells use energy. Excess production of the T3 and T4 hormones leads to excessive increase in metabolism, which can cause unhealthy levels of weight loss.
But T3 and T4 also affect nearly every organ in our body and it’s most important functions. These impacts can range from breathing and heart rate to digestion and mood.
SYMPTOMS OF HYPERTHYROIDISM
Hyperthyroidism’s effects can be felt all throughout the body, which is why self-diagnosis is difficult and requires a specialist evaluation. However, if you are concerned you or a loved one is experiencing hyperthyroidism some common symptoms are:
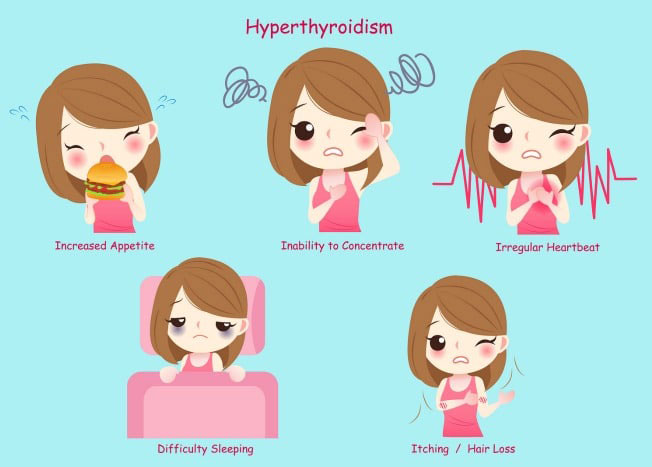
- Unintentional weight loss without disruption of usual caloric consumption
- Tremors
- Anxiety
- Arrhythmic and palpitating heartbeat
- Enlargement of thyroid gland, can be felt at the base of the neck
- Sensitivity to heat increased
- Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep
- Fine and brittle hair
- Difficulty concentrating
Please be aware immediate medical attention may be required if any of the following symptoms occur:
- Loss of consciousness
- Extremely irregular heart rate
- Dizziness
While a deviation from a healthy heartbeat is expected in hyperthyroidism patients, too much of an irregular heart beat can lead to a condition known as atrial fibrillation, which can lead to strokes and heart failure.
HYPERTHYROIDISM DIAGNOSIS
In order for a medical specialist to effectively complete a diagnosis, a medical exam will need to be conducted, along with the consideration of previous medical records. Following an initial consultation, further tests may be needed to confirm the presence of the disease. Tests may include an MRI and bloodwork.
Initial signs revealed after first evaluation include:
- Rapid pulse
- Enlarged thyroid gland
- Protruding eyes
- Loss of weight
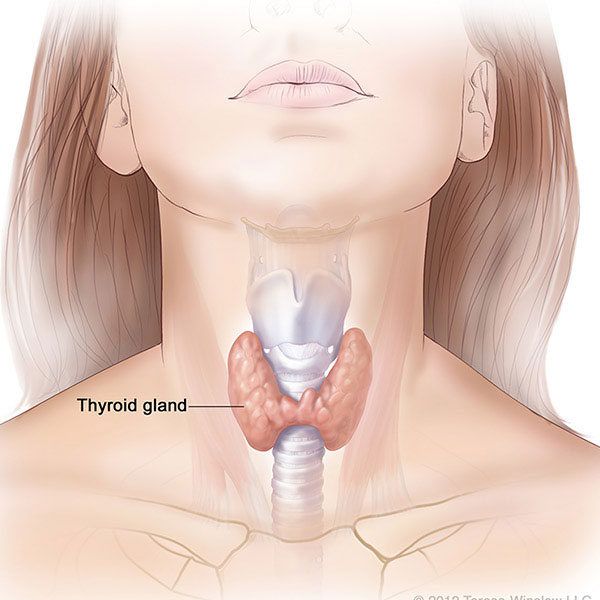
- Thyroid gland
Further tests that are highly recommended by specialists:
- Cholesterol level
- T3 and T4 (measures amount of thyroid hormone present in blood)
- Thyroid stimulating Hormone Test (TSH Test) [This hormone causes the gland to produce more of its own hormones, low TSH may
- indicate hyperthyroidism]
- Triglyceride level test
- Ultrasound (to reveal precise size of thyroid hormone)
TREATMENTS FOR HYPERTHYROIDISM
While Hyperthyroidism is a serious yet common condition, it can be resolved within months with effective medical care. A variety of treatments are available through your medical provider, but a clinical diagnosis is essential to recovery. The most effective forms of treatment are:
Medication
Prescription medications, such as Tapazole, can be very effective in curing hyperthyroidism. They target the thyroid gland and halt production of the hormone secretion.
Radioactive Iodine
While this treatment is more invasive, it is given to 70% of hyperthyroid patients in the US. It destroys the cells responsible for producing the excess hormones which lead to this condition. Further precautions are necessary following treatment
Surgery (thyroidectomy)
– If you prefer not to take radioactive iodine or can not take certain medications due to pregnancy or other conditions, surgery is also an option used by physicians for a few cases.
– In the procedure a doctor removes most of the thyroid gland, however this poses a risk to our vocal cords and parathyroid gland (4 glands located behind the thyroid which control calcium levels in the blood)
– Following surgery there will be lifelong medication therapy with levothyroxine, to supply the thyroid hormone to your body.
WHAT CAUSES HYPERTHYROIDISM?
Too much thyroxine (T4) in most cases.
- Graves’ disease – Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder in which antibodies produced by your immune system stimulate your thyroid too much
- Hyperfunctioning thyroid nodules – This form of hyperthyroidism happens if an adenomas of your thyroid produces too much T4. An adenoma is part of the gland that has walled itself off from the rest of the gland lumps that may cause an enlargement of the gland.
- Thyroiditis – Sometimes your thyroid gland can become inflamed after pregnancy. The inflammation causes excess thyroid hormone in the gland to leak into the bloodstream. Some types of thyroiditis may cause pain, some are painless.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from traumatic brain injury or brain problems, our expert providers at Specialty Care Clinics will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call us on 469-545-9983 to book an appointment with Dr. Sumana Gangi.
